Flash loans enable traders to borrow significant capital instantly without collateral, allowing for rapid arbitrage or liquidation opportunities within a single transaction. Perpetual swaps provide a derivative trading platform with no expiration, offering leverage to speculate on asset price movements while maintaining continuous exposure. Explore the mechanics and strategic uses of flash loans versus perpetual swaps to enhance your trading toolkit.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loans and perpetual swaps is crucial for successful trading because flash loans enable instant, uncollateralized borrowing for arbitrage or liquidation opportunities, while perpetual swaps are derivative contracts allowing traders to speculate or hedge with leverage over extended periods. Flash loans require precise, atomic transaction execution within a single blockchain block, minimizing risk exposure, whereas perpetual swaps involve continuous funding rates and market risk management. Knowing these distinctions helps traders optimize strategies, manage risks effectively, and leverage market mechanisms appropriately. Mastery of both instruments can enhance capital efficiency and profit potential in decentralized finance and derivatives markets.
Comparison Table
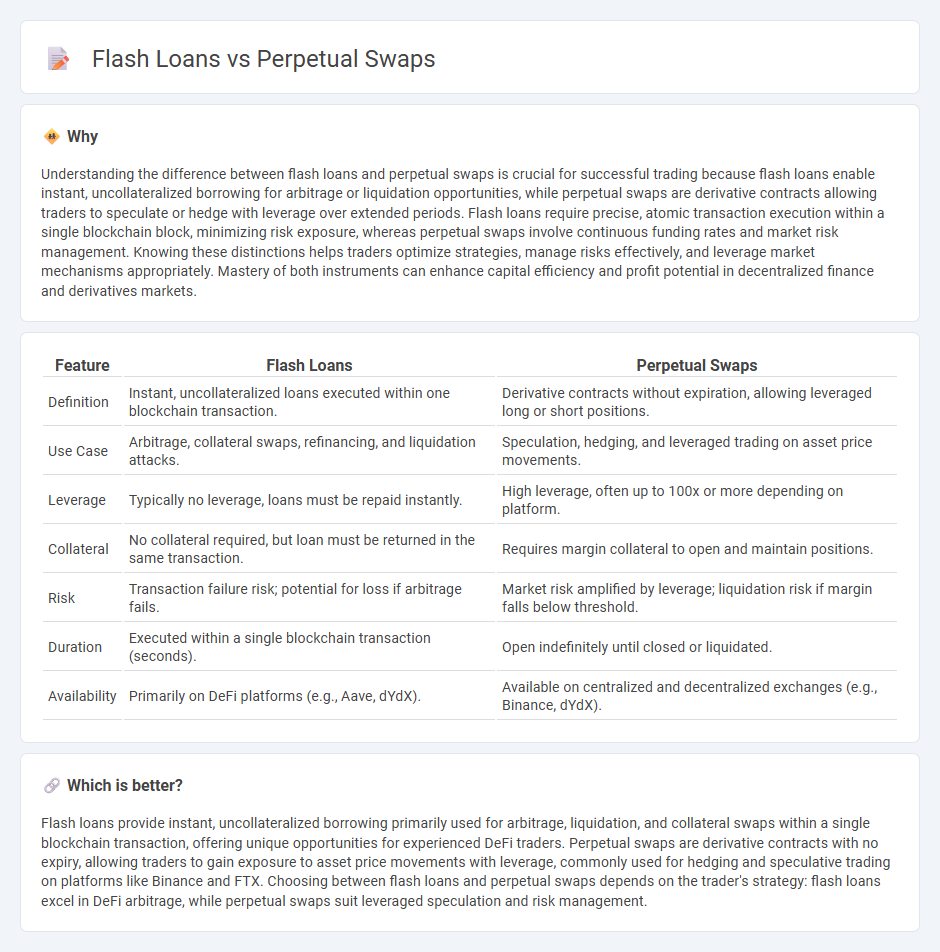
| Feature | Flash Loans | Perpetual Swaps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant, uncollateralized loans executed within one blockchain transaction. | Derivative contracts without expiration, allowing leveraged long or short positions. |
| Use Case | Arbitrage, collateral swaps, refinancing, and liquidation attacks. | Speculation, hedging, and leveraged trading on asset price movements. |
| Leverage | Typically no leverage, loans must be repaid instantly. | High leverage, often up to 100x or more depending on platform. |
| Collateral | No collateral required, but loan must be returned in the same transaction. | Requires margin collateral to open and maintain positions. |
| Risk | Transaction failure risk; potential for loss if arbitrage fails. | Market risk amplified by leverage; liquidation risk if margin falls below threshold. |
| Duration | Executed within a single blockchain transaction (seconds). | Open indefinitely until closed or liquidated. |
| Availability | Primarily on DeFi platforms (e.g., Aave, dYdX). | Available on centralized and decentralized exchanges (e.g., Binance, dYdX). |
Which is better?
Flash loans provide instant, uncollateralized borrowing primarily used for arbitrage, liquidation, and collateral swaps within a single blockchain transaction, offering unique opportunities for experienced DeFi traders. Perpetual swaps are derivative contracts with no expiry, allowing traders to gain exposure to asset price movements with leverage, commonly used for hedging and speculative trading on platforms like Binance and FTX. Choosing between flash loans and perpetual swaps depends on the trader's strategy: flash loans excel in DeFi arbitrage, while perpetual swaps suit leveraged speculation and risk management.
Connection
Flash loans enable traders to borrow significant capital instantly without collateral, which can be strategically utilized in executing perpetual swaps. Perpetual swaps are derivative contracts allowing traders to speculate on asset prices with leverage and no expiry, often requiring precise timing and capital flexibility. Using flash loans, traders can amplify exposure or arbitrage opportunities in perpetual swaps by quickly accessing liquidity to open or close large positions within a single transaction.
Key Terms
Funding Rate
Perpetual swaps use a funding rate mechanism to maintain parity between the perpetual contract price and the underlying asset price by periodically transferring payments between long and short position holders. Flash loans, on the other hand, are uncollateralized loans executed within a single blockchain transaction and do not involve any funding rate as they are repaid instantly. Explore the dynamics of funding rates in perpetual swaps and their impact on trading strategies for deeper insights.
Liquidation
Perpetual swaps are derivatives that allow traders to hold leveraged positions without expiry, with liquidation triggered when margin falls below maintenance requirements, often resulting in forced position closure and loss of collateral. Flash loans offer instant, uncollateralized borrowing within a single transaction, where liquidation risk is minimized since the loan must be repaid immediately or the entire transaction reverts. Explore the intricacies of liquidation mechanisms in decentralized finance to better understand risk management strategies for both perpetual swaps and flash loans.
Borrowing Mechanism
Perpetual swaps enable traders to maintain leveraged positions with continuous funding payments, eliminating settlement dates and allowing persistent borrowing directly through the contract. Flash loans provide instant, uncollateralized borrowing within a single transaction, requiring repayment before the transaction ends to avoid default. Explore the distinct borrowing mechanisms further to optimize your DeFi strategies.
Source and External Links
Understanding Perpetual Swaps Funding Rates - BlockFills - Perpetual swaps are derivative contracts with no expiration, allowing leverage and short positions without borrowing, using a funding rate mechanism to keep the contract's price aligned to the underlying asset, primarily used in cryptocurrency markets.
What are perpetual futures contracts? - Kraken - Perpetual futures or swaps have no expiration date and use a funding rate paid between traders to ensure the contract price closely follows the spot price of the underlying asset, facilitating market efficiency and arbitrage.
How to Use Perpetual Futures in Crypto Trading - Bitstamp - Perpetual futures (perps) allow traders to hold long or short positions indefinitely with leverage and a funding rate settlement system, differing from traditional futures by having no expiration and enabling flexible long-term trading strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com