Funding rate arbitrage exploits disparities in perpetual futures funding rates to generate profits without exposure to spot price fluctuations. Cash and carry arbitrage involves simultaneously buying the underlying asset and selling the futures contract when futures prices trade at a premium, capturing the difference as profit. Explore the nuances of these strategies to optimize trading performance and risk management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between funding rate arbitrage and cash and carry is crucial for traders to optimize profit strategies in derivative and spot markets. Funding rate arbitrage exploits interest rate differences in perpetual swaps, while cash and carry involves simultaneous buying of the underlying asset and selling a futures contract to lock in price discrepancies. Mastering these techniques reduces risk exposure and enhances portfolio returns by leveraging market inefficiencies. Accurate knowledge allows traders to select strategies aligned with market conditions and funding costs.
Comparison Table
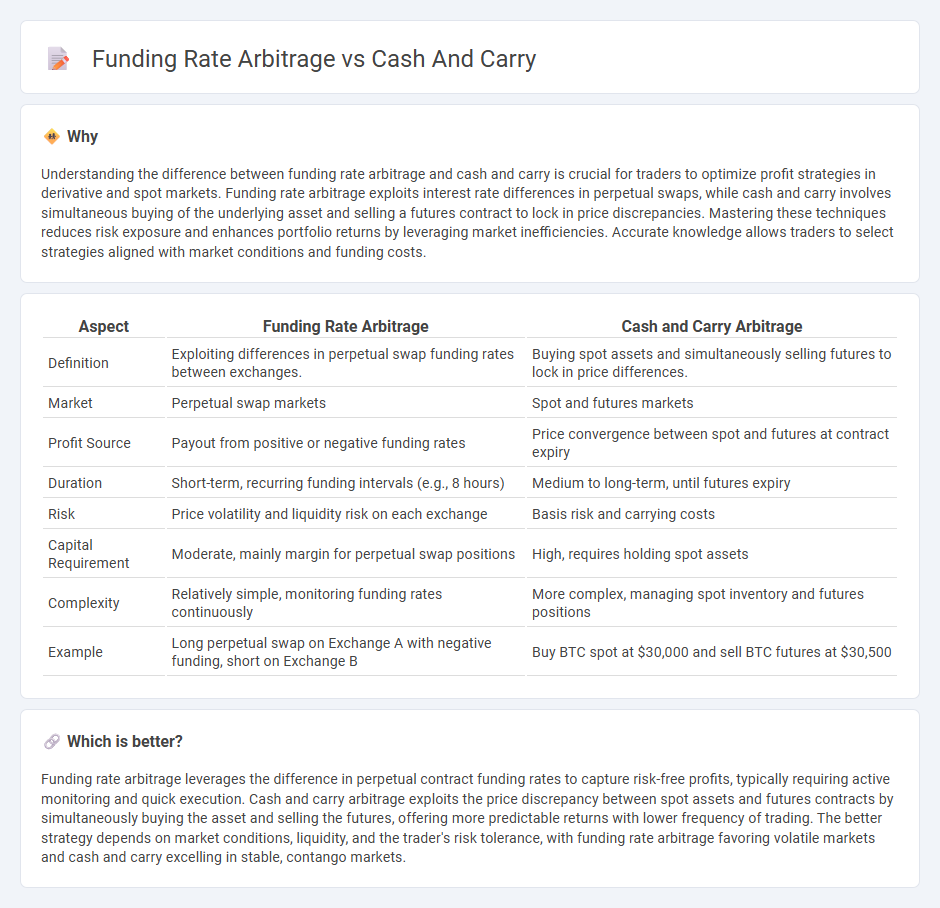
| Aspect | Funding Rate Arbitrage | Cash and Carry Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting differences in perpetual swap funding rates between exchanges. | Buying spot assets and simultaneously selling futures to lock in price differences. |
| Market | Perpetual swap markets | Spot and futures markets |
| Profit Source | Payout from positive or negative funding rates | Price convergence between spot and futures at contract expiry |
| Duration | Short-term, recurring funding intervals (e.g., 8 hours) | Medium to long-term, until futures expiry |
| Risk | Price volatility and liquidity risk on each exchange | Basis risk and carrying costs |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate, mainly margin for perpetual swap positions | High, requires holding spot assets |
| Complexity | Relatively simple, monitoring funding rates continuously | More complex, managing spot inventory and futures positions |
| Example | Long perpetual swap on Exchange A with negative funding, short on Exchange B | Buy BTC spot at $30,000 and sell BTC futures at $30,500 |
Which is better?
Funding rate arbitrage leverages the difference in perpetual contract funding rates to capture risk-free profits, typically requiring active monitoring and quick execution. Cash and carry arbitrage exploits the price discrepancy between spot assets and futures contracts by simultaneously buying the asset and selling the futures, offering more predictable returns with lower frequency of trading. The better strategy depends on market conditions, liquidity, and the trader's risk tolerance, with funding rate arbitrage favoring volatile markets and cash and carry excelling in stable, contango markets.
Connection
Funding rate arbitrage exploits the difference between perpetual futures funding rates and spot prices, enabling traders to profit from the cost of holding positions across markets. Cash and carry strategy involves buying the underlying asset while simultaneously selling futures contracts, locking in a risk-free profit when futures trade at a premium to spot. Both strategies capitalize on price discrepancies between spot and futures markets, leveraging differences in funding rates and carrying costs for arbitrage opportunities.
Key Terms
Spot-Futures Spread
Cash and carry arbitrage involves buying the underlying asset in the spot market and simultaneously selling futures contracts to lock in a risk-free profit when the spot price plus carrying costs is lower than the futures price. Funding rate arbitrage exploits differences in funding payments between perpetual futures and the spot market, profiting from funding rate divergences without holding the underlying asset. Explore detailed strategies and risk considerations to master spot-futures spread arbitrage effectively.
Cost of Carry
Cash and carry arbitrage exploits the price difference between a commodity's spot price and its futures price by simultaneously buying the commodity and selling the futures contract, profiting from the cost of carry, which includes storage, insurance, and financing costs. Funding rate arbitrage, commonly seen in cryptocurrency markets, involves exploiting disparities between funding rates on perpetual futures contracts and spot price movements, effectively profiting from interest rate differentials without physical holding or storage costs. Explore detailed strategies and quantitative models to optimize your cost of carry arbitrage approach and maximize returns.
Funding Rate
Funding rate arbitrage exploits differences in perpetual swap funding rates to gain risk-free profits, leveraging the periodic payments exchanged between longs and shorts. This strategy hinges on accurately predicting or capturing funding rate imbalances on decentralized or centralized derivatives platforms. Explore deeper insights into funding rate mechanisms and arbitrage opportunities to enhance your trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Cash and carry (World War II) - Wikipedia - "Cash and Carry" was a U.S. policy announced in 1939 allowing belligerents in WWII to purchase military and nonmilitary goods as long as they paid immediately in cash and transported the goods themselves, replacing earlier neutrality acts.
Cash and carry - Wikipedia - "Cash and carry" refers to a wholesale operation model where customers pay in cash and carry away the goods themselves, commonly used in wholesale clubs and markets.
Restaurant Depot | A Wholesale Cash & Carry Foodservice Supplier - Restaurant Depot is an example of a wholesale "cash and carry" supplier offering restaurant equipment and food products where buyers pay cash and take goods immediately.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com