Social copy trading allows investors to replicate the strategies of experienced traders, providing a hands-off approach to market participation. Scalping, in contrast, focuses on rapid, high-frequency trades aiming to exploit small price movements for quick profits. Explore the differences to determine which trading style aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between social copy trading and scalping is crucial because social copy trading involves replicating the strategies of experienced traders for long-term gains, while scalping focuses on executing rapid, short-term trades to capitalize on small market fluctuations. Misapplying one strategy in place of the other can lead to significant financial losses and ineffective risk management. Traders need to align their investment goals and risk tolerance with the appropriate method to maximize profitability. Clear knowledge of these approaches helps optimize trading decisions and portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
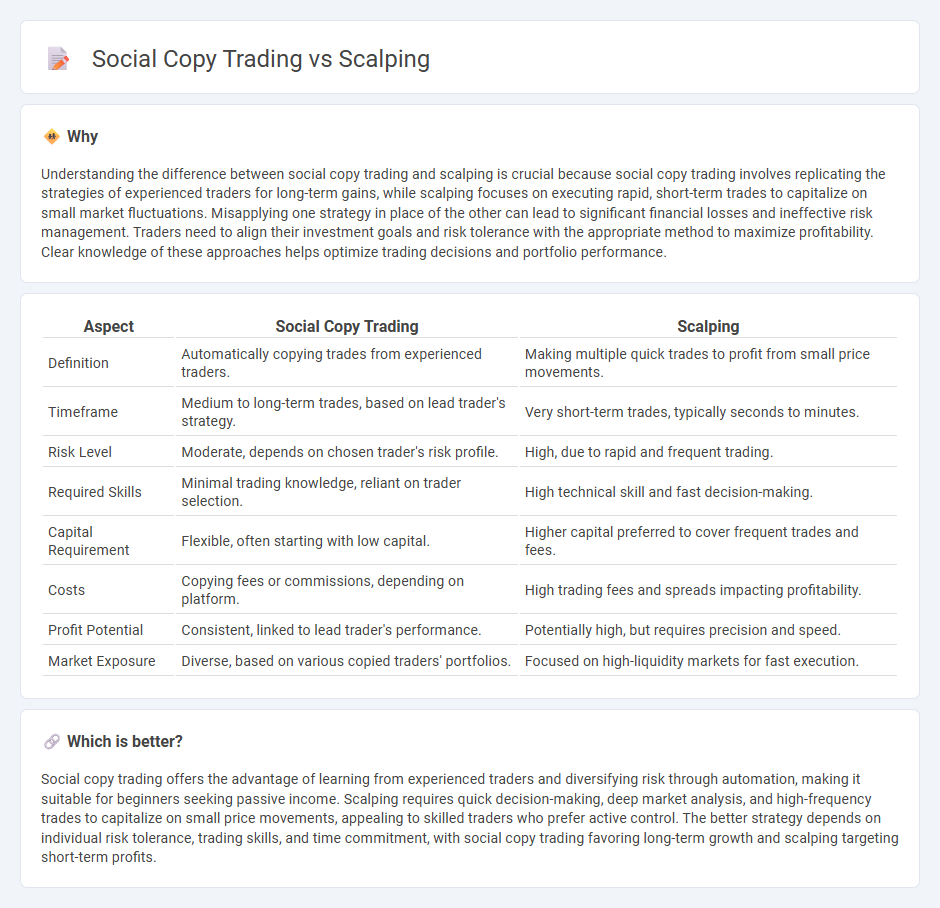
| Aspect | Social Copy Trading | Scalping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatically copying trades from experienced traders. | Making multiple quick trades to profit from small price movements. |
| Timeframe | Medium to long-term trades, based on lead trader's strategy. | Very short-term trades, typically seconds to minutes. |
| Risk Level | Moderate, depends on chosen trader's risk profile. | High, due to rapid and frequent trading. |
| Required Skills | Minimal trading knowledge, reliant on trader selection. | High technical skill and fast decision-making. |
| Capital Requirement | Flexible, often starting with low capital. | Higher capital preferred to cover frequent trades and fees. |
| Costs | Copying fees or commissions, depending on platform. | High trading fees and spreads impacting profitability. |
| Profit Potential | Consistent, linked to lead trader's performance. | Potentially high, but requires precision and speed. |
| Market Exposure | Diverse, based on various copied traders' portfolios. | Focused on high-liquidity markets for fast execution. |
Which is better?
Social copy trading offers the advantage of learning from experienced traders and diversifying risk through automation, making it suitable for beginners seeking passive income. Scalping requires quick decision-making, deep market analysis, and high-frequency trades to capitalize on small price movements, appealing to skilled traders who prefer active control. The better strategy depends on individual risk tolerance, trading skills, and time commitment, with social copy trading favoring long-term growth and scalping targeting short-term profits.
Connection
Social copy trading and scalping are interconnected through real-time strategy replication, allowing traders to mimic scalpers' high-frequency, short-term trades automatically. This integration leverages social platforms to share and execute rapid trade decisions, maximizing profits from small market movements. The synergy enhances trading efficiency by combining collective insights with scalping's precise timing and liquidity exploitation.
Key Terms
Execution speed
Scalping relies heavily on ultra-fast execution speed to capitalize on small price movements within seconds, requiring cutting-edge trading platforms and low-latency connections. Social copy trading, while less dependent on speed, depends on timely replication of trades from experienced investors, where slight delays can impact profitability but execution speed is not as critical. Discover more about how execution speed influences trading strategies and which approach suits your financial goals.
Signal providers
Scalping relies on rapid trade execution by signal providers who analyze short-term market fluctuations to generate high-frequency trade signals. In social copy trading, signal providers offer more strategic, longer-term insights that followers can automatically replicate in their portfolios. Explore the distinct roles and benefits of signal providers in both methods to enhance your trading strategy.
Trade volume
Scalping involves executing a high volume of trades within short time frames to capitalize on small price movements, often requiring rapid decision-making and technical analysis. Social copy trading aggregates the trade volume of multiple investors by replicating the strategies of experienced traders, enabling users to diversify and leverage collective market insights. Discover how understanding trade volume differences can enhance your trading strategy.
Source and External Links
Scalping (Day Trading Technique) - Corporate Finance Institute - Scalping is a day trading strategy where investors buy and sell an individual stock multiple times within the same day aiming to make small profits on many quick trades, often focusing on highly volatile stocks to take advantage of price swings.
What is a scalping strategy in the stock market and how does it work? - Scalping involves very fast buying and selling of securities using technical analysis and momentum indicators like Stochastic Oscillator, Moving Averages, and RSI to identify short-term price trends and reversal points.
Scalping (trading) - Wikipedia - Scalping refers to a trading method exploiting small price gaps created by bid-ask spreads, involving opening and closing positions quickly to make tiny profits, often used in markets like foreign exchange and stocks; it can be legitimate arbitrage or a form of market manipulation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com