Market making involves providing liquidity by placing both buy and sell orders to profit from the bid-ask spread, whereas scalping focuses on executing quick trades to capture small price movements within short time frames. Market makers earn consistent returns through spread capture, while scalpers rely on rapid execution and high trade volume to accumulate profits. Discover more about these distinct trading strategies and how they fit your investment style.
Why it is important
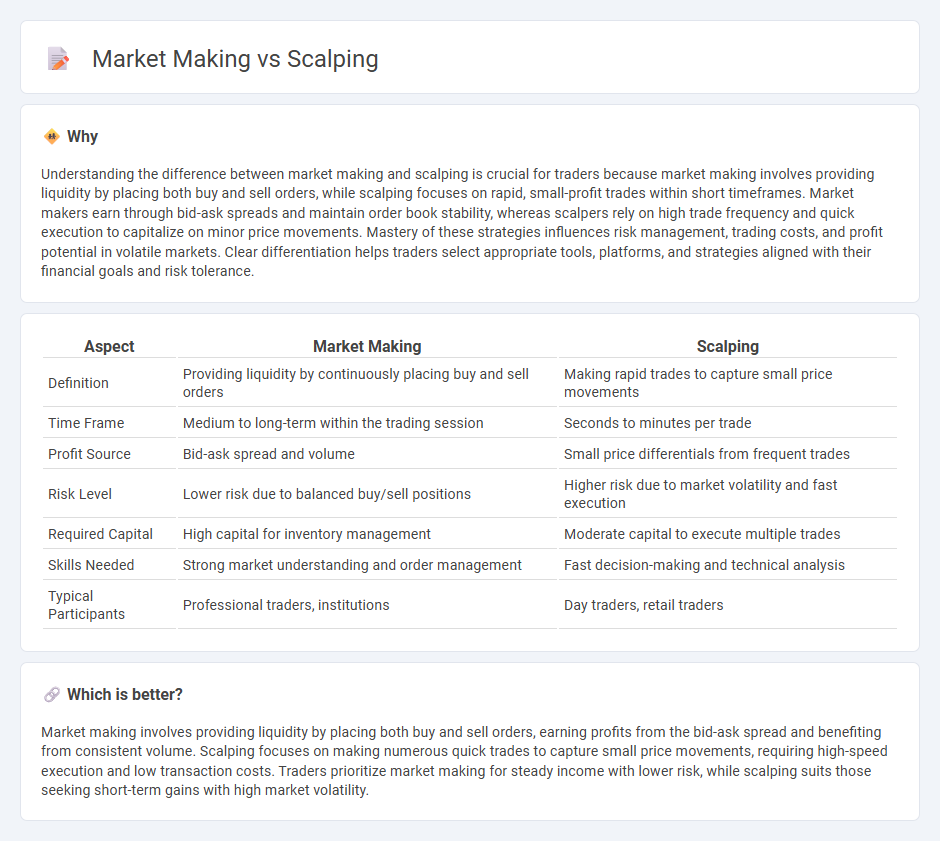
Understanding the difference between market making and scalping is crucial for traders because market making involves providing liquidity by placing both buy and sell orders, while scalping focuses on rapid, small-profit trades within short timeframes. Market makers earn through bid-ask spreads and maintain order book stability, whereas scalpers rely on high trade frequency and quick execution to capitalize on minor price movements. Mastery of these strategies influences risk management, trading costs, and profit potential in volatile markets. Clear differentiation helps traders select appropriate tools, platforms, and strategies aligned with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Market Making | Scalping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing liquidity by continuously placing buy and sell orders | Making rapid trades to capture small price movements |
| Time Frame | Medium to long-term within the trading session | Seconds to minutes per trade |
| Profit Source | Bid-ask spread and volume | Small price differentials from frequent trades |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to balanced buy/sell positions | Higher risk due to market volatility and fast execution |
| Required Capital | High capital for inventory management | Moderate capital to execute multiple trades |
| Skills Needed | Strong market understanding and order management | Fast decision-making and technical analysis |
| Typical Participants | Professional traders, institutions | Day traders, retail traders |
Which is better?
Market making involves providing liquidity by placing both buy and sell orders, earning profits from the bid-ask spread and benefiting from consistent volume. Scalping focuses on making numerous quick trades to capture small price movements, requiring high-speed execution and low transaction costs. Traders prioritize market making for steady income with lower risk, while scalping suits those seeking short-term gains with high market volatility.
Connection
Market making and scalping are connected through their shared focus on liquidity and rapid trade execution in financial markets. Market makers provide continuous bid and ask quotes, enabling scalpers to profit from small price fluctuations by executing quick, high-frequency trades. Both strategies rely on tight spreads and short holding periods to minimize risk and capitalize on minor price movements.
Key Terms
Spread
Scalping and market making both strategize around the bid-ask spread, but scalpers exploit small, quick price movements by rapidly buying and selling at tight spreads to capture minimal profits repeatedly, while market makers provide liquidity by quoting both buy and sell prices, profiting primarily from the consistent spread between these quotes. Market makers face inventory risk but benefit from steady income by narrowing spreads to attract trades, whereas scalpers rely on high trade frequency and speed to maximize gains on price fluctuations. Discover how these approaches balance risk and reward effectively in dynamic trading environments.
Liquidity
Scalping targets rapid trades to exploit small price movements, contributing to market liquidity through frequent order executions. Market making involves continuously quoting buy and sell prices to provide liquidity and narrow bid-ask spreads, stabilizing the trading environment. Explore the distinctive impacts of scalping and market making on market liquidity in greater detail.
Order flow
Scalping and market making both rely heavily on order flow analysis but differ in execution speed and order book interaction. Scalpers capitalize on small price movements by rapidly placing and canceling orders using real-time order flow data, while market makers provide liquidity by continuously posting buy and sell orders, profiting from the bid-ask spread. Explore the nuances of order flow strategies to enhance your trading approach.
Source and External Links
Scalping (Day Trading Technique) - Scalping is a day trading strategy involving buying and selling the same stock multiple times within the same day to gain small profits from each trade, often focusing on highly volatile stocks.
Scalping (trading) - In trading, scalping refers to making quick trades to gain small profits from bid-ask spreads or small price movements, either as a legitimate arbitrage method or, sometimes, as a form of market manipulation.
What is a scalping strategy in the stock market and how ... - Scalping relies on rapid buying and selling aided by technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, and MACD to identify short-term price trends and momentum shifts for quick profits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com