Penny jump refers to the minimum price increment by which a stock or asset's price can move, often set at one cent for penny stocks, influencing trading strategies and price volatility. Market depth represents the volume of buy and sell orders at various price levels, providing insight into liquidity and potential price movements. Explore how understanding penny jump and market depth can enhance your trading precision and decision-making.
Why it is important
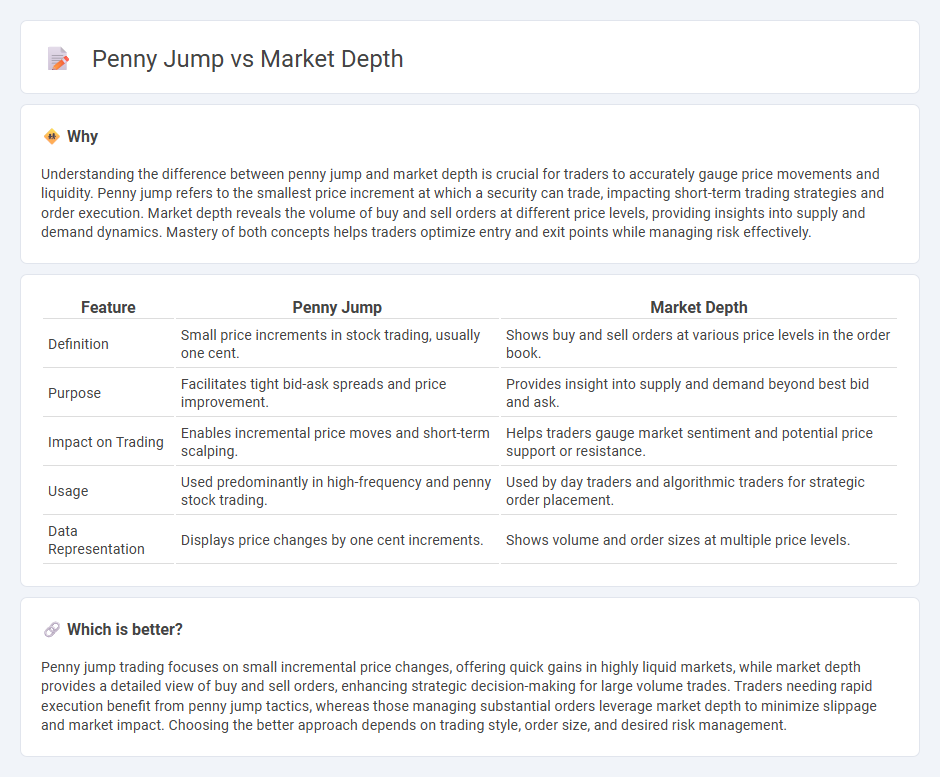
Understanding the difference between penny jump and market depth is crucial for traders to accurately gauge price movements and liquidity. Penny jump refers to the smallest price increment at which a security can trade, impacting short-term trading strategies and order execution. Market depth reveals the volume of buy and sell orders at different price levels, providing insights into supply and demand dynamics. Mastery of both concepts helps traders optimize entry and exit points while managing risk effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Penny Jump | Market Depth |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small price increments in stock trading, usually one cent. | Shows buy and sell orders at various price levels in the order book. |
| Purpose | Facilitates tight bid-ask spreads and price improvement. | Provides insight into supply and demand beyond best bid and ask. |
| Impact on Trading | Enables incremental price moves and short-term scalping. | Helps traders gauge market sentiment and potential price support or resistance. |
| Usage | Used predominantly in high-frequency and penny stock trading. | Used by day traders and algorithmic traders for strategic order placement. |
| Data Representation | Displays price changes by one cent increments. | Shows volume and order sizes at multiple price levels. |
Which is better?
Penny jump trading focuses on small incremental price changes, offering quick gains in highly liquid markets, while market depth provides a detailed view of buy and sell orders, enhancing strategic decision-making for large volume trades. Traders needing rapid execution benefit from penny jump tactics, whereas those managing substantial orders leverage market depth to minimize slippage and market impact. Choosing the better approach depends on trading style, order size, and desired risk management.
Connection
Penny jumps, small incremental price changes in stock trading, directly influence market depth by altering the bid-ask spread and visible liquidity at various price levels. Enhanced market depth with narrow penny jumps facilitates smoother order execution and reduces slippage, benefiting traders seeking precise entry and exit points. Real-time analysis of both penny jumps and market depth offers critical insights for algorithmic trading strategies and high-frequency traders aiming to capitalize on micro price movements.
Key Terms
Order Book
Market depth displays the volume of buy and sell orders at varying price levels within the order book, providing insight into potential price movements and liquidity. Penny jump refers to the smallest price increment change seen on an order book, influencing order execution and trading strategies in highly liquid markets. Explore the intricacies of order book dynamics to leverage market depth and penny jump for optimized trading decisions.
Bid-Ask Spread
Market depth reveals the volume of buy and sell orders at various price levels, providing insight into liquidity and price stability, while penny jump focuses on minimal price increments typically reflecting tight bid-ask spreads. A narrow bid-ask spread indicates high liquidity and low transaction costs, making penny jumps frequent in highly liquid markets. Explore detailed strategies on how understanding market depth and bid-ask spread dynamics can optimize trading decisions.
Price Slippage
Price slippage occurs when a trade is executed at a different price than expected, often due to limited market depth, especially in penny jump scenarios where small price increments cause rapid order book changes. Market depth reveals the volume of buy and sell orders at various price levels, directly influencing liquidity and the likelihood of slippage during high-frequency or large-volume trades. Explore how analyzing market depth data can minimize price slippage and optimize trading strategies in volatile markets.
Source and External Links
The Ultimate Guide to Market Depth in Finance - Number Analytics - Market depth measures a market's ability to sustain large orders without affecting the security's price, providing critical insights on liquidity, order flow, and price formation for effective trading and risk management.
Market Depth Definition | - B2Prime - Market depth is a real-time indicator showing market conditions through aggregated buy and sell orders, revealing potential price movements by reflecting supply and demand and trading sentiment.
Market Depth - Definition, How It's Used, Examples - Market depth refers to the market's capacity to absorb large orders without impacting the price, measured by the total volume and number of limit orders at various price levels visible in the order book.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com