Microstructure modeling examines the detailed mechanisms of trade execution, order flow, and price formation at the highest frequency to understand liquidity and transaction costs. Market efficiency analysis focuses on how quickly and accurately prices reflect all available information, influencing investment strategies and risk management. Explore these approaches to deepen your understanding of trading dynamics and optimize market performance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between microstructure modeling and market efficiency analysis is crucial for traders because microstructure modeling focuses on the mechanisms of trading processes and order flows, enabling precise strategy development and liquidity assessment. Market efficiency analysis evaluates how quickly and accurately prices reflect all available information, guiding expectations for arbitrage opportunities and risk management. Mastering both concepts allows traders to optimize execution strategies while anticipating market behavior effectively. This dual insight enhances decision-making in volatile environments and improves profit potential.
Comparison Table
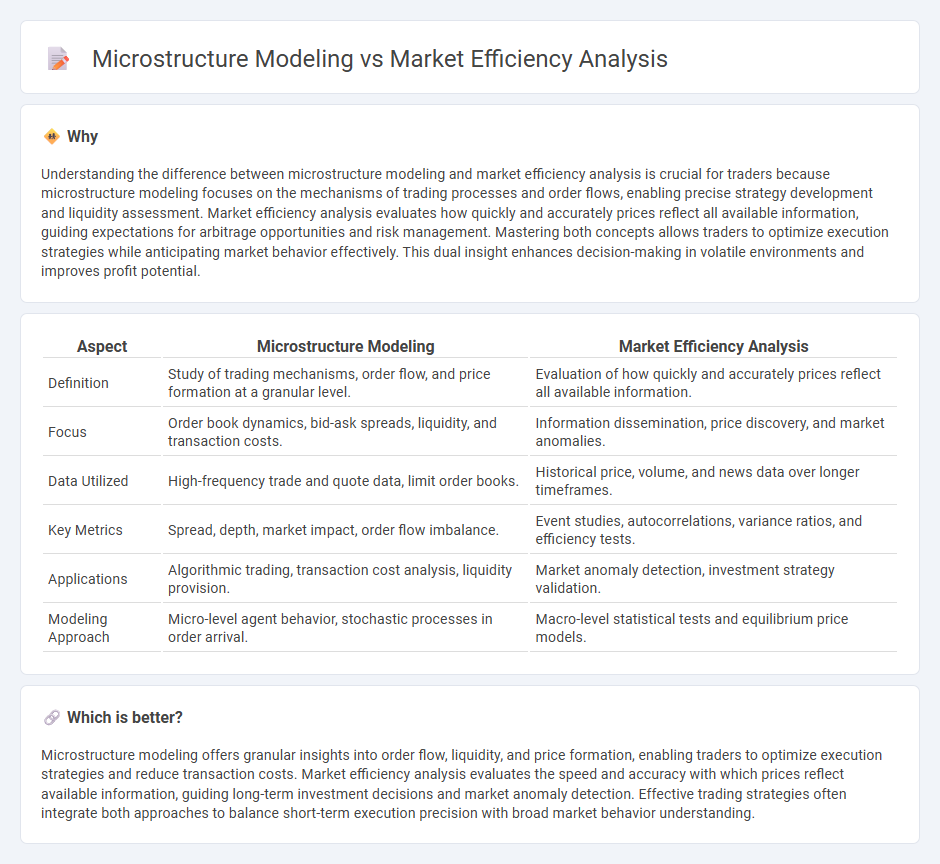
| Aspect | Microstructure Modeling | Market Efficiency Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of trading mechanisms, order flow, and price formation at a granular level. | Evaluation of how quickly and accurately prices reflect all available information. |
| Focus | Order book dynamics, bid-ask spreads, liquidity, and transaction costs. | Information dissemination, price discovery, and market anomalies. |
| Data Utilized | High-frequency trade and quote data, limit order books. | Historical price, volume, and news data over longer timeframes. |
| Key Metrics | Spread, depth, market impact, order flow imbalance. | Event studies, autocorrelations, variance ratios, and efficiency tests. |
| Applications | Algorithmic trading, transaction cost analysis, liquidity provision. | Market anomaly detection, investment strategy validation. |
| Modeling Approach | Micro-level agent behavior, stochastic processes in order arrival. | Macro-level statistical tests and equilibrium price models. |
Which is better?
Microstructure modeling offers granular insights into order flow, liquidity, and price formation, enabling traders to optimize execution strategies and reduce transaction costs. Market efficiency analysis evaluates the speed and accuracy with which prices reflect available information, guiding long-term investment decisions and market anomaly detection. Effective trading strategies often integrate both approaches to balance short-term execution precision with broad market behavior understanding.
Connection
Microstructure modeling examines the detailed mechanisms of how trades are executed and prices are formed in financial markets, providing insights into market liquidity, bid-ask spreads, and order flow dynamics. Market efficiency analysis evaluates whether asset prices fully reflect all available information, which can be influenced by microstructure factors such as transaction costs and information asymmetry. Understanding microstructure allows for a more precise assessment of market efficiency, revealing imperfections that impact price discovery and trading strategies.
Key Terms
**Market Efficiency Analysis:**
Market Efficiency Analysis assesses the extent to which asset prices fully reflect all available information, emphasizing the evaluation of price accuracy, information dissemination, and trading strategies' effectiveness. It serves to identify anomalies or inefficiencies within financial markets, offering insights into liquidity, volatility, and arbitrage opportunities. Explore detailed methodologies and applications of market efficiency analysis to enhance your understanding of dynamic financial environments.
Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)
Market efficiency analysis evaluates how well prices reflect all available information based on the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH), which posits that asset prices fully incorporate public and private data, making it impossible to consistently achieve abnormal returns. Microstructure modeling studies the processes and mechanisms of trading, including price formation, order flow, and liquidity, to understand deviations from EMH at a granular level. Explore deeper insights into market behavior and trading dynamics by examining the relationship between EMH and market microstructure models.
Random Walk
Market efficiency analysis evaluates price movements based on the hypothesis that asset prices fully reflect all available information, implying that returns follow a Random Walk pattern. Microstructure modeling delves into the mechanisms of order flow, transaction processes, and information asymmetry that might cause deviations from a pure Random Walk. Explore the nuances of Random Walk behavior within these frameworks to better understand market dynamics and trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Market Efficiency Process Scope and Input Assumptions - Market efficiency analysis assesses economic benefits of transmission projects in regional planning by simulating market conditions and comparing outcomes with and without proposed transmission upgrades.
Market Efficiency - Overview, Efficient Markets, Implications - Market efficiency measures how well and quickly information is transmitted and reflected in asset prices, with efficient markets ensuring prices reflect all information instantly and costlessly, making consistent excess profits impossible.
Efficient Market Hypothesis - The Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) explains market efficiency in three forms--weak, semi-strong, and strong--based on information sets reflected in prices, concluding that no form of analysis can consistently generate abnormal returns in an efficient market.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com