Dark pool aggregation consolidates large institutional orders into private, non-public trading venues that minimize market impact and enhance price discovery. In contrast, retail brokerage platforms provide individual investors with direct access to public exchanges, often exposing trades to visible order books and higher market impact. Explore the differences in execution quality and cost efficiency between dark pool aggregation and retail brokerage services.
Why it is important
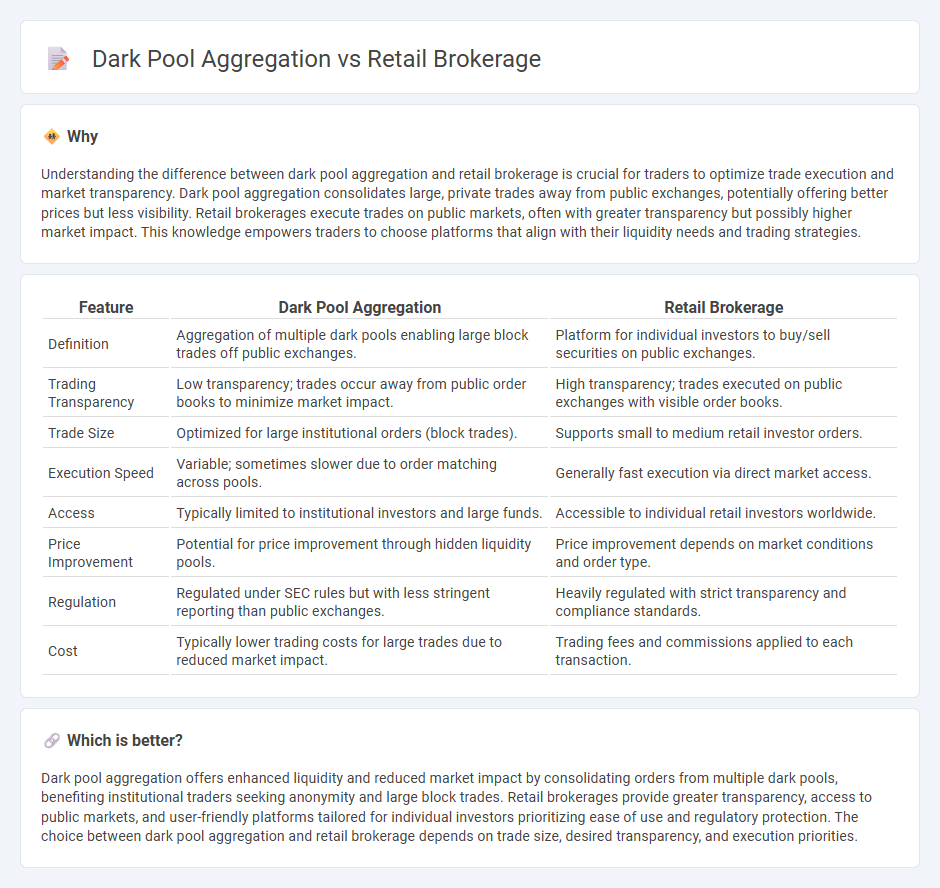
Understanding the difference between dark pool aggregation and retail brokerage is crucial for traders to optimize trade execution and market transparency. Dark pool aggregation consolidates large, private trades away from public exchanges, potentially offering better prices but less visibility. Retail brokerages execute trades on public markets, often with greater transparency but possibly higher market impact. This knowledge empowers traders to choose platforms that align with their liquidity needs and trading strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dark Pool Aggregation | Retail Brokerage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Aggregation of multiple dark pools enabling large block trades off public exchanges. | Platform for individual investors to buy/sell securities on public exchanges. |
| Trading Transparency | Low transparency; trades occur away from public order books to minimize market impact. | High transparency; trades executed on public exchanges with visible order books. |
| Trade Size | Optimized for large institutional orders (block trades). | Supports small to medium retail investor orders. |
| Execution Speed | Variable; sometimes slower due to order matching across pools. | Generally fast execution via direct market access. |
| Access | Typically limited to institutional investors and large funds. | Accessible to individual retail investors worldwide. |
| Price Improvement | Potential for price improvement through hidden liquidity pools. | Price improvement depends on market conditions and order type. |
| Regulation | Regulated under SEC rules but with less stringent reporting than public exchanges. | Heavily regulated with strict transparency and compliance standards. |
| Cost | Typically lower trading costs for large trades due to reduced market impact. | Trading fees and commissions applied to each transaction. |
Which is better?
Dark pool aggregation offers enhanced liquidity and reduced market impact by consolidating orders from multiple dark pools, benefiting institutional traders seeking anonymity and large block trades. Retail brokerages provide greater transparency, access to public markets, and user-friendly platforms tailored for individual investors prioritizing ease of use and regulatory protection. The choice between dark pool aggregation and retail brokerage depends on trade size, desired transparency, and execution priorities.
Connection
Dark pool aggregation consolidates anonymous, large-volume trades from multiple private venues, enhancing liquidity discovery for retail brokerages. Retail brokerage platforms integrate dark pool liquidity to execute client orders with minimal market impact and improved price efficiency. This connection enables retail traders to access institutional-grade trading environments while maintaining transparency and best execution standards.
Key Terms
Order Execution
Retail brokerage platforms execute orders directly on public exchanges, providing transparency and market access, often at lower fees but with varying execution speeds. Dark pool aggregation involves routing orders through multiple private venues to minimize market impact and achieve better prices, leveraging hidden liquidity for optimal trade execution. Explore the nuances of order execution strategies and their impacts on trading outcomes for deeper insights.
Liquidity Access
Retail brokerage platforms primarily offer direct access to public exchanges, ensuring transparent and regulated liquidity for individual investors. Dark pool aggregation collects liquidity from multiple private venues, providing institutional traders with access to large block trades without significant market impact. Explore the differences in liquidity access to optimize your trading strategy effectively.
Price Transparency
Retail brokerage platforms offer high price transparency, enabling investors to see real-time bid and ask prices and understand order execution processes clearly. Dark pool aggregation aggregates liquidity from multiple private venues but often lacks transparent pricing, resulting in less visibility into executed trade prices compared to retail brokers. Explore how these differences impact trade execution and investor confidence to gain deeper insights.
Source and External Links
The rise of newly empowered retail investors - Deloitte - Retail brokerage is evolving with digital platforms making investing more accessible, creating a new class of empowered individual investors, and driving shifts in brokerage firms' business models, customer experiences, and regulatory focus.
Brokerage account - Charles Schwab - A retail brokerage account is an arrangement between an individual and a licensed brokerage firm where the individual deposits funds to invest in securities like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, with options such as margin accounts and cash accounts available.
Best Brokerage Accounts for Online Stock Trading - NerdWallet - Retail brokerage accounts enable investing with money deposited in the account to buy stocks, ETFs, and mutual funds, with most online brokers requiring little to no minimum deposits and providing options for taxable or retirement-focused accounts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com