Flash loans provide instant, uncollateralized borrowing within a single transaction, ideal for arbitrage and quick trades, while credit lines offer longer-term borrowing with set limits and interest, suitable for ongoing liquidity needs. Flash loans entail lower risk for lenders due to immediate repayment, contrasting with credit lines that carry credit risk over time. Explore the differences in detail to optimize your trading strategy.
Why it is important
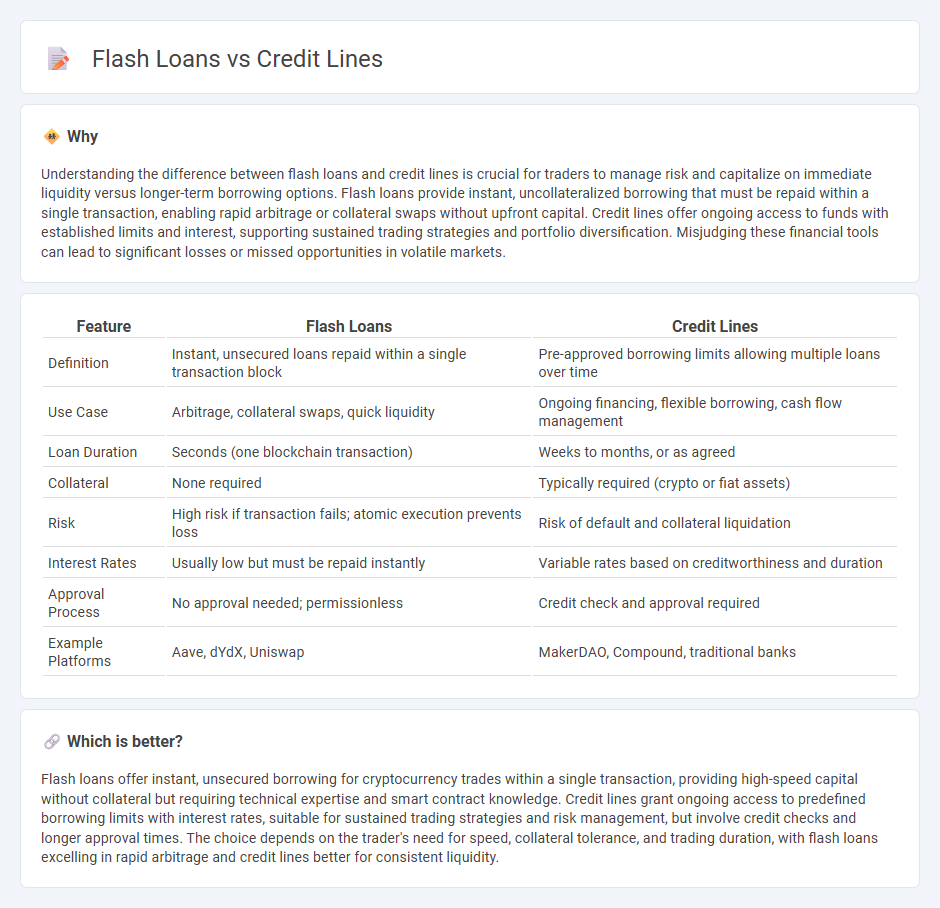
Understanding the difference between flash loans and credit lines is crucial for traders to manage risk and capitalize on immediate liquidity versus longer-term borrowing options. Flash loans provide instant, uncollateralized borrowing that must be repaid within a single transaction, enabling rapid arbitrage or collateral swaps without upfront capital. Credit lines offer ongoing access to funds with established limits and interest, supporting sustained trading strategies and portfolio diversification. Misjudging these financial tools can lead to significant losses or missed opportunities in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Flash Loans | Credit Lines |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant, unsecured loans repaid within a single transaction block | Pre-approved borrowing limits allowing multiple loans over time |
| Use Case | Arbitrage, collateral swaps, quick liquidity | Ongoing financing, flexible borrowing, cash flow management |
| Loan Duration | Seconds (one blockchain transaction) | Weeks to months, or as agreed |
| Collateral | None required | Typically required (crypto or fiat assets) |
| Risk | High risk if transaction fails; atomic execution prevents loss | Risk of default and collateral liquidation |
| Interest Rates | Usually low but must be repaid instantly | Variable rates based on creditworthiness and duration |
| Approval Process | No approval needed; permissionless | Credit check and approval required |
| Example Platforms | Aave, dYdX, Uniswap | MakerDAO, Compound, traditional banks |
Which is better?
Flash loans offer instant, unsecured borrowing for cryptocurrency trades within a single transaction, providing high-speed capital without collateral but requiring technical expertise and smart contract knowledge. Credit lines grant ongoing access to predefined borrowing limits with interest rates, suitable for sustained trading strategies and risk management, but involve credit checks and longer approval times. The choice depends on the trader's need for speed, collateral tolerance, and trading duration, with flash loans excelling in rapid arbitrage and credit lines better for consistent liquidity.
Connection
Flash loans and credit lines are interconnected through their role in providing instant liquidity within decentralized finance (DeFi). Flash loans enable users to borrow assets without collateral, provided the loan is repaid within a single transaction, while credit lines offer ongoing borrowing capacity with set limits and interest rates. Both tools enhance trading strategies by allowing traders to leverage capital efficiently, manage risk, and capitalize on arbitrage opportunities in real-time.
Key Terms
Collateral
Credit lines require borrowers to provide collateral, securing the loan with tangible assets to reduce lender risk and increase borrowing capacity. Flash loans operate without collateral, relying on smart contracts and atomic transactions to ensure loans are repaid instantly within a single blockchain transaction. Discover more about how collateral impacts these decentralized finance tools and shapes lending strategies.
Liquidity
Credit lines provide pre-approved access to a fixed amount of liquidity, enabling borrowers to draw funds as needed with flexible repayment terms. Flash loans offer instant, uncollateralized liquidity that requires repayment within a single blockchain transaction, primarily used in decentralized finance (DeFi) for arbitrage or refinancing. Explore the distinct mechanisms and use cases of credit lines and flash loans to optimize liquidity management strategies.
Counterparty risk
Credit lines involve borrowing funds with a predetermined limit and typically undergo thorough credit assessments, reducing counterparty risk through established agreements and collateral requirements. Flash loans, on the other hand, are uncollateralized, instant loans that must be repaid within a single transaction block, significantly increasing counterparty risk due to the lack of credit checks and the reliance on smart contract execution. Explore the nuances of counterparty risk in credit lines versus flash loans to understand their implications for financial security and trust.
Source and External Links
Lines of credit: What they are & how they work - Capital One - A line of credit is a revolving loan account allowing borrowers to withdraw and repay repeatedly up to a preset limit, available in personal, home equity, or business forms, and can be secured or unsecured.
What Is a Line of Credit? - Experian - Lines of credit provide flexible borrowing up to a credit limit with key types including personal, home equity (secured by your home), and business lines of credit, each with distinct features like finite draw periods.
Line of credit - Wikipedia - A line of credit is a credit facility from a bank or lender enabling a customer to draw funds up to a limit as needed, which can be secured or unsecured, with interest paid only on withdrawn amounts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com