Front running involves traders exploiting non-public information to execute orders ahead of large pending trades, gaining unfair profit advantages. Pump and dump schemes manipulate market prices by artificially inflating a stock's value before selling off shares at a profit, causing subsequent price crashes and investor losses. Explore these strategies in-depth to understand their impact on market integrity and regulation.
Why it is important
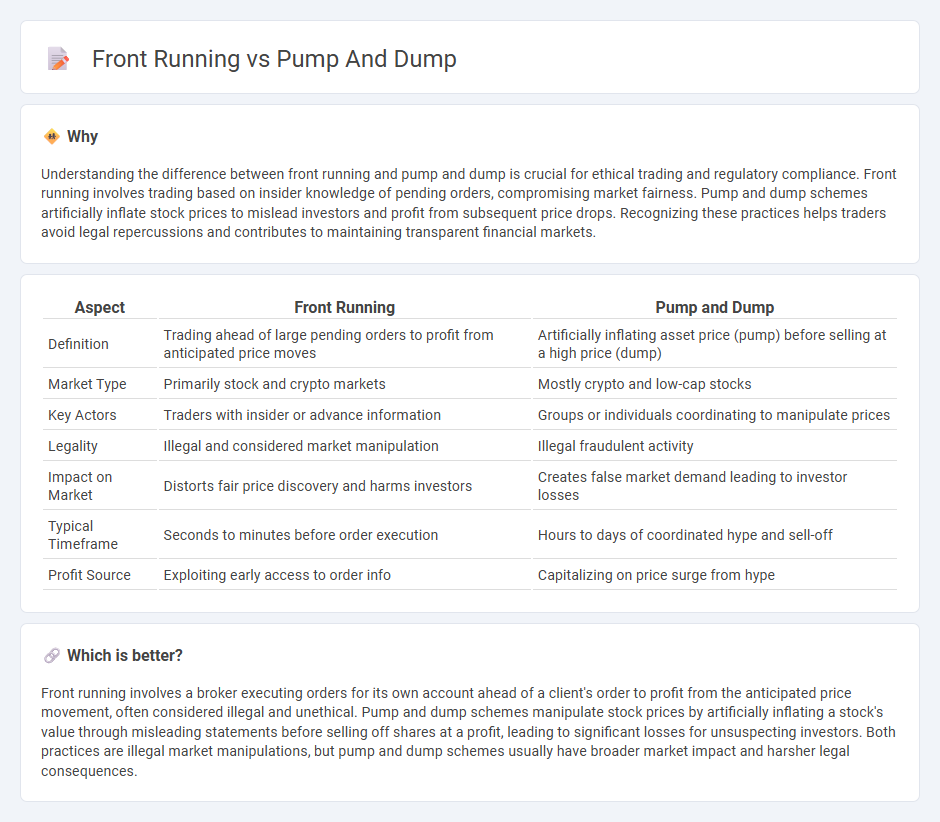
Understanding the difference between front running and pump and dump is crucial for ethical trading and regulatory compliance. Front running involves trading based on insider knowledge of pending orders, compromising market fairness. Pump and dump schemes artificially inflate stock prices to mislead investors and profit from subsequent price drops. Recognizing these practices helps traders avoid legal repercussions and contributes to maintaining transparent financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Front Running | Pump and Dump |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading ahead of large pending orders to profit from anticipated price moves | Artificially inflating asset price (pump) before selling at a high price (dump) |
| Market Type | Primarily stock and crypto markets | Mostly crypto and low-cap stocks |
| Key Actors | Traders with insider or advance information | Groups or individuals coordinating to manipulate prices |
| Legality | Illegal and considered market manipulation | Illegal fraudulent activity |
| Impact on Market | Distorts fair price discovery and harms investors | Creates false market demand leading to investor losses |
| Typical Timeframe | Seconds to minutes before order execution | Hours to days of coordinated hype and sell-off |
| Profit Source | Exploiting early access to order info | Capitalizing on price surge from hype |
Which is better?
Front running involves a broker executing orders for its own account ahead of a client's order to profit from the anticipated price movement, often considered illegal and unethical. Pump and dump schemes manipulate stock prices by artificially inflating a stock's value through misleading statements before selling off shares at a profit, leading to significant losses for unsuspecting investors. Both practices are illegal market manipulations, but pump and dump schemes usually have broader market impact and harsher legal consequences.
Connection
Front running and pump and dump schemes both manipulate market prices for profit by exploiting insider knowledge or coordinated actions. Front running involves a broker executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large trades, while pump and dump artificially inflate a stock's value before selling off at a profit. Both tactics disrupt fair market operations and are illegal under securities regulations.
Key Terms
Pump and Dump:
Pump and dump schemes involve artificially inflating the price of a stock through false or misleading statements to attract unsuspecting investors, who then buy the stock at inflated prices. This practice manipulates market perception and often leads to a sharp price decline once the perpetrators sell off their shares, causing significant losses for other investors. To understand the risks and detection methods associated with pump and dump schemes, explore our detailed analysis.
Manipulation
Pump and dump schemes manipulate stock prices by artificially inflating the value through false or misleading statements, enticing investors to buy before the perpetrators sell at a profit. Front running involves brokers or traders exploiting advanced knowledge of pending orders to trade ahead, profiting from the expected market movement caused by those transactions. Explore the distinctive mechanisms and legal implications of these manipulative tactics to understand their impact on market integrity.
Volume
Pump and dump schemes manipulate trading volume by artificially inflating asset prices through coordinated buying, followed by mass sell-offs that capitalize on the increased volume and investor interest. Front running exploits non-public information about impending large-volume trades to execute orders ahead, profiting from the anticipated price movement once the market absorbs the volume impact. Explore how monitoring volume patterns can help identify these fraudulent activities and protect investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Pump and dump - Wikipedia - Pump and dump is a securities fraud involving artificially inflating the price of a stock through false or misleading statements to sell the stock at a higher price, then dumping shares causing the price to collapse and investors to lose money; it is common with small-cap cryptocurrencies and microcap companies.
Micro-cap Stock Fraud ("Pump and Dump") - Law.Cornell.Edu - Pump and dump schemes manipulate microcap stocks by promoters spreading false information to inflate prices, then selling their shares at the peak, leaving other investors with losses once the price falls.
Avoiding Pump-and-Dump Scams - FINRA - Pump-and-dump fraud involves accumulating low-priced stocks, promoting false positive news to increase demand and price, then selling shares at the inflated price, with fraudsters often using social media and encrypted platforms for promotion.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com