Quantitative backtesting leverages historical market data to simulate trading strategies, allowing evaluation of performance and risk metrics without financial exposure. Real-time trading involves executing trades in live markets, requiring rapid decision-making and adaptation to real-time fluctuations and liquidity conditions. Discover how combining both approaches can optimize trading outcomes and enhance strategic robustness.
Why it is important
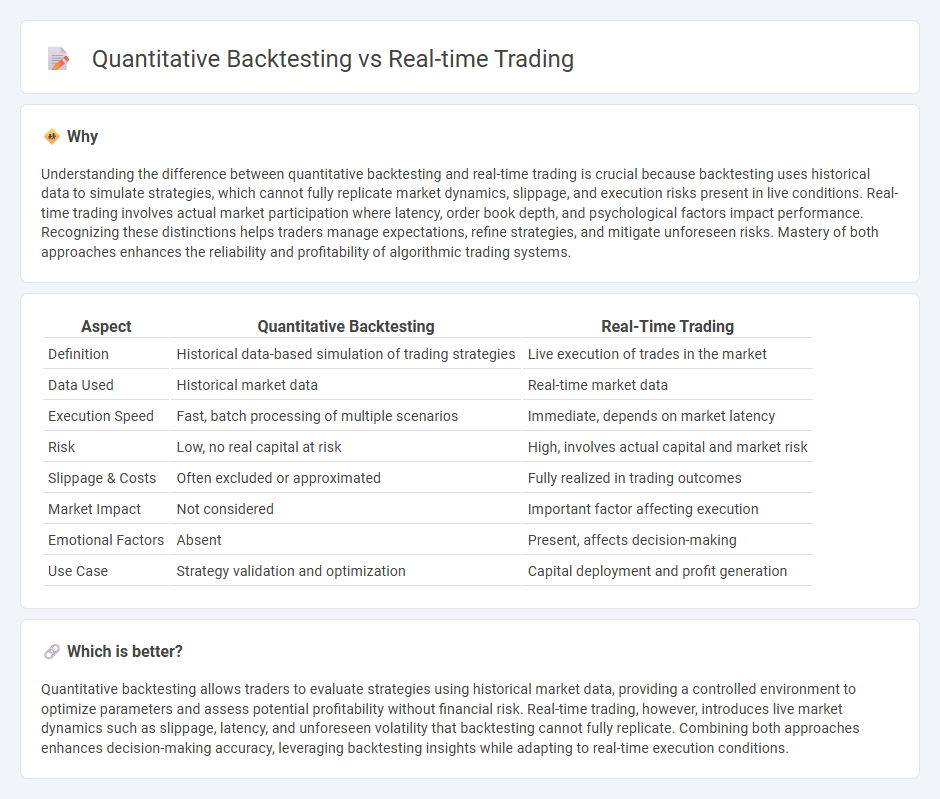
Understanding the difference between quantitative backtesting and real-time trading is crucial because backtesting uses historical data to simulate strategies, which cannot fully replicate market dynamics, slippage, and execution risks present in live conditions. Real-time trading involves actual market participation where latency, order book depth, and psychological factors impact performance. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders manage expectations, refine strategies, and mitigate unforeseen risks. Mastery of both approaches enhances the reliability and profitability of algorithmic trading systems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Backtesting | Real-Time Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Historical data-based simulation of trading strategies | Live execution of trades in the market |
| Data Used | Historical market data | Real-time market data |
| Execution Speed | Fast, batch processing of multiple scenarios | Immediate, depends on market latency |
| Risk | Low, no real capital at risk | High, involves actual capital and market risk |
| Slippage & Costs | Often excluded or approximated | Fully realized in trading outcomes |
| Market Impact | Not considered | Important factor affecting execution |
| Emotional Factors | Absent | Present, affects decision-making |
| Use Case | Strategy validation and optimization | Capital deployment and profit generation |
Which is better?
Quantitative backtesting allows traders to evaluate strategies using historical market data, providing a controlled environment to optimize parameters and assess potential profitability without financial risk. Real-time trading, however, introduces live market dynamics such as slippage, latency, and unforeseen volatility that backtesting cannot fully replicate. Combining both approaches enhances decision-making accuracy, leveraging backtesting insights while adapting to real-time execution conditions.
Connection
Quantitative backtesting employs historical market data to validate trading strategies by simulating their performance, enabling traders to identify profitability and risk metrics before deployment. Real-time trading applies these pre-tested algorithms in live markets, executing trades based on real-time data streams and market conditions to capitalize on identified opportunities. The continuous feedback loop between backtesting results and live performance allows for iterative refinement of models, improving accuracy and adaptive capabilities in dynamic trading environments.
Key Terms
Latency
Latency plays a critical role in real-time trading by directly impacting the speed at which market data is processed and trades are executed, often measured in microseconds to gain competitive advantage. Quantitative backtesting, while essential for strategy validation, operates on historical data without the latency constraints faced in live markets, allowing exhaustive simulation but lacking real-time urgency. Discover how optimizing latency bridges the gap between effective backtesting models and live trading performance.
Historical Data
Real-time trading relies on live market data to make immediate buy or sell decisions, while quantitative backtesting uses historical data to evaluate trading strategies' performance over time. Historical data, including price movements, volume, and volatility metrics, is crucial for backtesting to simulate realistic market conditions and assess risk factors before deployment. Explore further to understand how accurate historical datasets enhance strategy development and risk management.
Execution Simulation
Real-time trading involves executing orders based on live market data, emphasizing speed, accuracy, and the ability to adapt to rapidly changing conditions. Quantitative backtesting simulates trade execution using historical data to evaluate strategies, focusing on detecting potential slippage, latency, and order fill assumptions. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how execution simulation impacts strategy performance in both domains.
Source and External Links
ProRealTime Trading - A leading online trading platform offering real-time trading from charts and orderbooks with several world-renowned brokers, supporting multiple order types and automatic trading systems.
NinjaTrader: Futures Trading - Award-winning futures trading platform with real-time multi-device trading, low margins and commissions, simulated trading, and extensive customization for automated strategies and technical analysis.
Live Stocks Chart - Investing.com - Provides comprehensive, real-time stock charts with customizable indicators, time scales, and integration with news and economic events to support active trading decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com