Quantitative momentum trading focuses on identifying assets with strong price trends and buying those expected to continue their upward movement, utilizing statistical measures like moving averages and rate of change. Quantitative volatility trading, on the other hand, emphasizes exploiting patterns in price fluctuations by targeting assets with significant variance, using indicators such as historical volatility and the VIX index. Explore in-depth strategies and data analysis techniques behind these quantitative trading approaches.
Why it is important
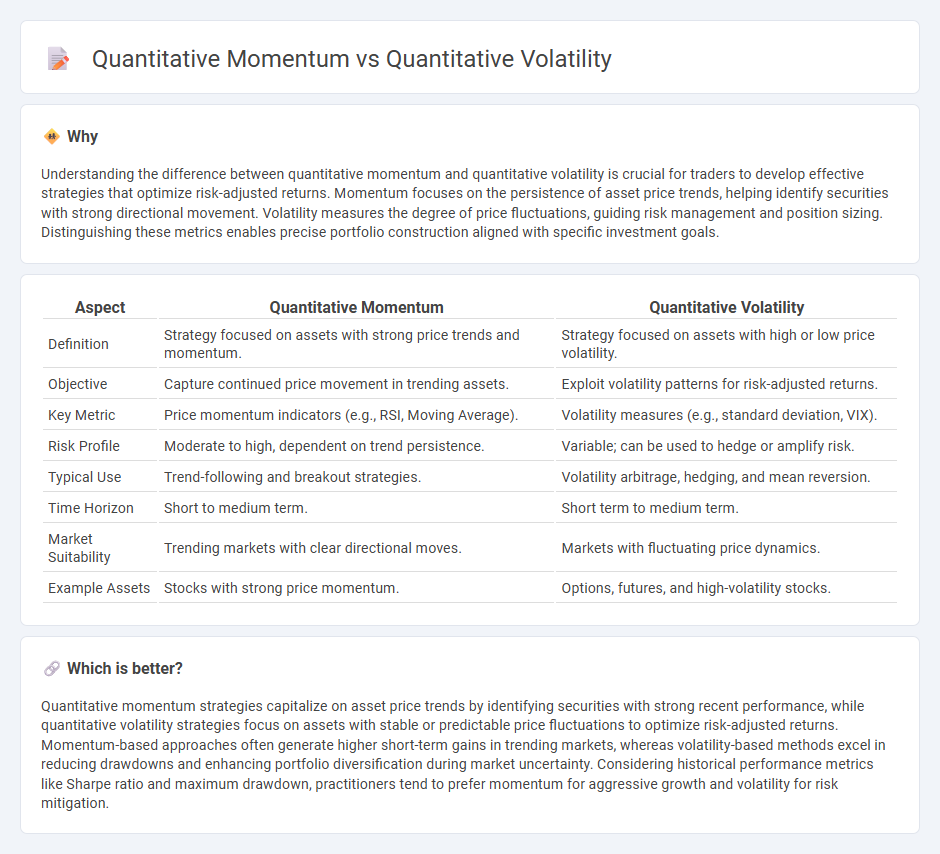
Understanding the difference between quantitative momentum and quantitative volatility is crucial for traders to develop effective strategies that optimize risk-adjusted returns. Momentum focuses on the persistence of asset price trends, helping identify securities with strong directional movement. Volatility measures the degree of price fluctuations, guiding risk management and position sizing. Distinguishing these metrics enables precise portfolio construction aligned with specific investment goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Momentum | Quantitative Volatility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy focused on assets with strong price trends and momentum. | Strategy focused on assets with high or low price volatility. |
| Objective | Capture continued price movement in trending assets. | Exploit volatility patterns for risk-adjusted returns. |
| Key Metric | Price momentum indicators (e.g., RSI, Moving Average). | Volatility measures (e.g., standard deviation, VIX). |
| Risk Profile | Moderate to high, dependent on trend persistence. | Variable; can be used to hedge or amplify risk. |
| Typical Use | Trend-following and breakout strategies. | Volatility arbitrage, hedging, and mean reversion. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term. | Short term to medium term. |
| Market Suitability | Trending markets with clear directional moves. | Markets with fluctuating price dynamics. |
| Example Assets | Stocks with strong price momentum. | Options, futures, and high-volatility stocks. |
Which is better?
Quantitative momentum strategies capitalize on asset price trends by identifying securities with strong recent performance, while quantitative volatility strategies focus on assets with stable or predictable price fluctuations to optimize risk-adjusted returns. Momentum-based approaches often generate higher short-term gains in trending markets, whereas volatility-based methods excel in reducing drawdowns and enhancing portfolio diversification during market uncertainty. Considering historical performance metrics like Sharpe ratio and maximum drawdown, practitioners tend to prefer momentum for aggressive growth and volatility for risk mitigation.
Connection
Quantitative momentum measures the rate of price change to identify trend strength, while quantitative volatility assesses price fluctuations over time to gauge risk. Their connection lies in the fact that high momentum often correlates with increased volatility, influencing risk-adjusted returns in trading strategies. Integrating both metrics allows traders to optimize entry and exit points by balancing trend strength and market uncertainty.
Key Terms
Standard Deviation (Volatility)
Quantitative volatility strategies focus on the standard deviation of asset returns to measure risk and identify price fluctuations, targeting investments that exhibit lower variability for more stable performance. Quantitative momentum strategies, while also considering return data, prioritize assets showing consistent upward or downward trends irrespective of their volatility levels. Explore more about how standard deviation influences quantitative models to optimize portfolio decisions.
Rate of Return (Momentum)
Quantitative volatility measures the degree of variation in asset prices, while quantitative momentum focuses on the rate of return, tracking the speed and magnitude of price changes over a specific period. Momentum strategies capitalize on assets with strong positive returns, hypothesizing that they will continue to outperform due to market inertia. Explore more to understand how momentum-based models leverage rate of return data for predictive investment strategies.
Signal Generation
Quantitative volatility strategies prioritize signal generation by analyzing market fluctuations and price variability to identify periods of high risk and potential reversals, often using statistical measures like standard deviation or Average True Range (ATR). Quantitative momentum approaches generate signals based on price trends, focusing on the strength and persistence of asset price movements through indicators such as Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). Explore in-depth methodologies and performance comparisons to better understand how signal generation differentiates these quantitative trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Volatility | Robeco USA - Volatility in finance quantitatively measures the dispersion of returns of a security or portfolio, typically calculated as the variance or standard deviation over a set period, serving as a proxy for risk.
A Practical Guide to Quantitative Volatility Trading - SSRN - Quantitative volatility trading involves modeling market multifractality, managing risk, and systematically trading volatility through arbitrage-free models of the implied volatility surface.
Machine learning-based analysis of volatility quantitative investment - Quantitative volatility strategies use forecasted and historical volatility data combined with machine learning to inform buy/sell decisions, achieving positive returns in simulated trading across stocks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com