Liquidity sweeps occur when large orders rapidly absorb available liquidity, causing temporary price spikes that traders exploit for short-term gains. Price gaps represent significant shifts in asset prices between trading sessions, often driven by news or market imbalances, creating unique entry and exit opportunities. Explore the nuances and strategies behind liquidity sweeps and price gaps to enhance your trading expertise.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweeps and price gaps is crucial for traders to accurately identify market sentiment and potential entry or exit points. Liquidity sweeps indicate the clearing of stop orders or hidden liquidity, often signaling institutional activity, while price gaps reflect sudden market movements caused by news or events. Knowing this distinction helps in predicting price reversals or continuations more effectively and managing risk. Mastery of these concepts enhances trade timing and decision-making precision in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
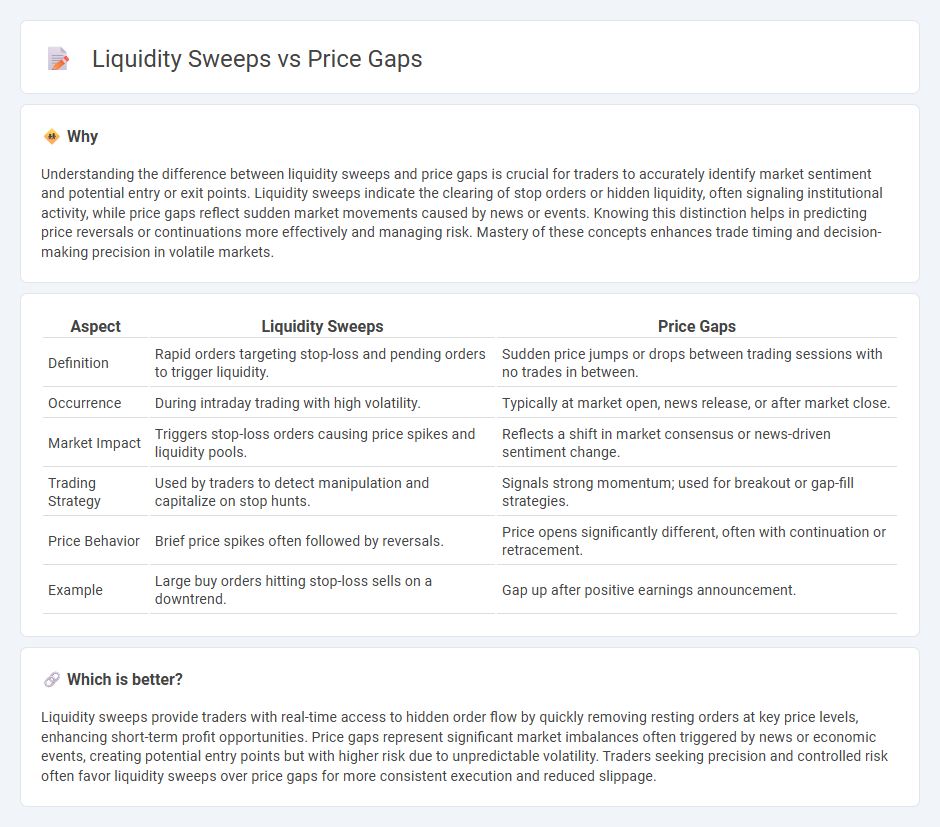
| Aspect | Liquidity Sweeps | Price Gaps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid orders targeting stop-loss and pending orders to trigger liquidity. | Sudden price jumps or drops between trading sessions with no trades in between. |
| Occurrence | During intraday trading with high volatility. | Typically at market open, news release, or after market close. |
| Market Impact | Triggers stop-loss orders causing price spikes and liquidity pools. | Reflects a shift in market consensus or news-driven sentiment change. |
| Trading Strategy | Used by traders to detect manipulation and capitalize on stop hunts. | Signals strong momentum; used for breakout or gap-fill strategies. |
| Price Behavior | Brief price spikes often followed by reversals. | Price opens significantly different, often with continuation or retracement. |
| Example | Large buy orders hitting stop-loss sells on a downtrend. | Gap up after positive earnings announcement. |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweeps provide traders with real-time access to hidden order flow by quickly removing resting orders at key price levels, enhancing short-term profit opportunities. Price gaps represent significant market imbalances often triggered by news or economic events, creating potential entry points but with higher risk due to unpredictable volatility. Traders seeking precision and controlled risk often favor liquidity sweeps over price gaps for more consistent execution and reduced slippage.
Connection
Liquidity sweeps occur when large market orders absorb available liquidity at specific price levels, often triggering stop-loss orders and causing rapid price movements. Price gaps form when sudden liquidity sweeps lead to a discontinuity on the price chart, with no trades executed between two price levels. This connection highlights how aggressive liquidity hunting by institutional traders can create gaps reflecting volatile market conditions and shifts in supply and demand.
Key Terms
Gap Up/Gap Down
Price gaps occur when a security's opening price is significantly higher or lower than its previous closing price, indicating a shift in market sentiment. Liquidity sweeps involve large orders that quickly fill available liquidity at multiple price levels, often causing rapid price movement within gap ups or gap downs. Explore detailed strategies to effectively trade gap scenarios and liquidity sweeps for enhanced market timing.
Stop-Loss Hunt
Price gaps often indicate rapid moves in stock or forex markets, exposing points where stop-loss orders cluster and may be targeted by large traders. Liquidity sweeps occur when these traders aggressively trigger stop-loss stops to capture liquidity before reversing the price direction. Explore in-depth strategies to identify and leverage stop-loss hunts effectively in volatile markets.
Order Block
Price gaps occur when there is a significant difference between the closing price of one period and the opening price of the next, often indicating strong market momentum or news events, while liquidity sweeps involve rapid order executions that trigger stop-losses or pending orders around key levels, causing temporary price spikes. Order Blocks represent institutional buying or selling zones where price consolidates before a strong move, acting as high-liquidity areas targeted during liquidity sweeps to trigger market reactions. Explore the intricate relationship between price gaps, liquidity sweeps, and order blocks to enhance your trading strategy understanding.
Source and External Links
Price gaps in Forex: types, causes, and how to trade them - Oanda - Price gaps occur when the market price skips a range of price levels between sessions, often visible as empty spaces on a chart, and can be gap ups or downs caused by factors like after-hours events or weekend news.
Understanding Price Gaps in Trending - Society of Technical Analysts - Price gaps happen due to a significant difference between the closing price of one period and the next opening price, commonly caused by market sentiment shifts or news, with different types like common gaps that tend to be filled quickly.
Gaps and Gap Analysis - ChartSchool - StockCharts.com - There are four main types of price gaps (common, breakaway, runaway, exhaustion), each driven by market events or sentiment leading to opening prices that differ sharply from prior closes, often followed by a "gap fill" where the price retraces to close the gap.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com