Retail flow chasing involves individual traders reacting to market sentiment and price movements driven by retail investor activity, often resulting in short-term, momentum-based trades. Quantitative trading employs advanced algorithms and statistical models to execute trades based on vast datasets and historical patterns, aiming for systematic profitability and risk management. Explore deeper insights to understand how these contrasting strategies impact market dynamics and trading outcomes.
Why it is important
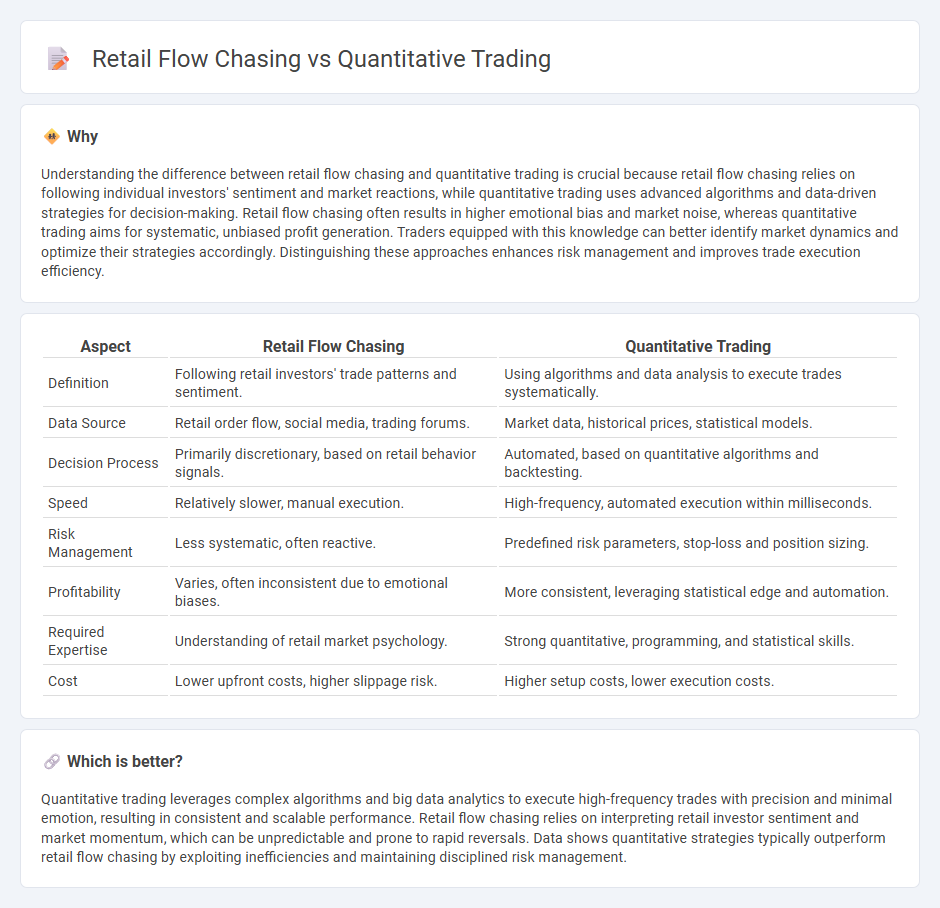
Understanding the difference between retail flow chasing and quantitative trading is crucial because retail flow chasing relies on following individual investors' sentiment and market reactions, while quantitative trading uses advanced algorithms and data-driven strategies for decision-making. Retail flow chasing often results in higher emotional bias and market noise, whereas quantitative trading aims for systematic, unbiased profit generation. Traders equipped with this knowledge can better identify market dynamics and optimize their strategies accordingly. Distinguishing these approaches enhances risk management and improves trade execution efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Retail Flow Chasing | Quantitative Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Following retail investors' trade patterns and sentiment. | Using algorithms and data analysis to execute trades systematically. |
| Data Source | Retail order flow, social media, trading forums. | Market data, historical prices, statistical models. |
| Decision Process | Primarily discretionary, based on retail behavior signals. | Automated, based on quantitative algorithms and backtesting. |
| Speed | Relatively slower, manual execution. | High-frequency, automated execution within milliseconds. |
| Risk Management | Less systematic, often reactive. | Predefined risk parameters, stop-loss and position sizing. |
| Profitability | Varies, often inconsistent due to emotional biases. | More consistent, leveraging statistical edge and automation. |
| Required Expertise | Understanding of retail market psychology. | Strong quantitative, programming, and statistical skills. |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs, higher slippage risk. | Higher setup costs, lower execution costs. |
Which is better?
Quantitative trading leverages complex algorithms and big data analytics to execute high-frequency trades with precision and minimal emotion, resulting in consistent and scalable performance. Retail flow chasing relies on interpreting retail investor sentiment and market momentum, which can be unpredictable and prone to rapid reversals. Data shows quantitative strategies typically outperform retail flow chasing by exploiting inefficiencies and maintaining disciplined risk management.
Connection
Retail flow chasing leverages real-time data on individual investor behaviors, enabling quantitative trading algorithms to identify and exploit market patterns with higher precision. Quantitative trading models integrate these retail-derived signals to enhance predictive accuracy and optimize trade execution strategies. This synergy improves market liquidity and price discovery by aligning algorithmic decisions with retail market sentiment trends.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Strategies
Quantitative trading leverages advanced algorithmic strategies, employing mathematical models and large datasets to execute trades with precision and speed, minimizing human bias and maximizing efficiency. Retail flow chasing relies on tracking and reacting to retail investor behaviors, often resulting in less predictable outcomes and increased market noise. Explore the intricacies of algorithmic trading versus retail flow chasing to understand their impacts on market dynamics and your trading approach.
Order Flow Analysis
Quantitative trading leverages algorithmic models and statistical methods to analyze large datasets, enabling rapid execution and risk management, while retail flow chasing centers on interpreting order flow data to predict short-term market movements based on retail trader behavior. Order Flow Analysis in quantitative trading involves sophisticated tools to detect patterns in bid-ask dynamics, enhancing predictive accuracy compared to the often reactive retail flow chasing strategies. Explore the nuances of Order Flow Analysis to understand the competitive edges between these trading methodologies.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage leverages quantitative trading techniques, utilizing algorithms and high-frequency data analysis to exploit price inefficiencies across correlated securities, delivering systematic and automated strategies with reduced emotional bias. In contrast, retail flow chasing relies on tracking retail order flows and market sentiment, often resulting in reactive and less data-driven decisions that may lead to higher volatility and risk. Discover how statistical arbitrage outperforms retail flow chasing in precision and profitability by exploring advanced market dynamics.
Source and External Links
Quantitative Trading Firms Explained | Hunter Bond - Quantitative trading firms use mathematical models, statistics, and algorithms to execute trades automatically, focusing on data-driven strategies like high-frequency trading and statistical arbitrage to generate returns.
Quantitative analysis (finance) - Wikipedia - Quantitative trading involves the application of mathematical and statistical methods in finance to identify trading opportunities through patterns and correlations, with major firms like Renaissance Technologies using these techniques.
Self-Study Plan for Becoming a Quantitative Trader - Part I - QuantStart - Quantitative trading requires mastery of forecasting, signal generation, backtesting, and data processing, making quant trading a prestigious, technical, and competitive career path often aided by self-study and experience with algorithmic strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com