Alternative data signals, derived from unconventional sources like social media trends and satellite imagery, offer unique insights beyond traditional market metrics. Quantitative signals rely on statistical and mathematical models analyzing historical price and volume data to identify trading opportunities. Explore how integrating these approaches can enhance your trading strategy.
Why it is important
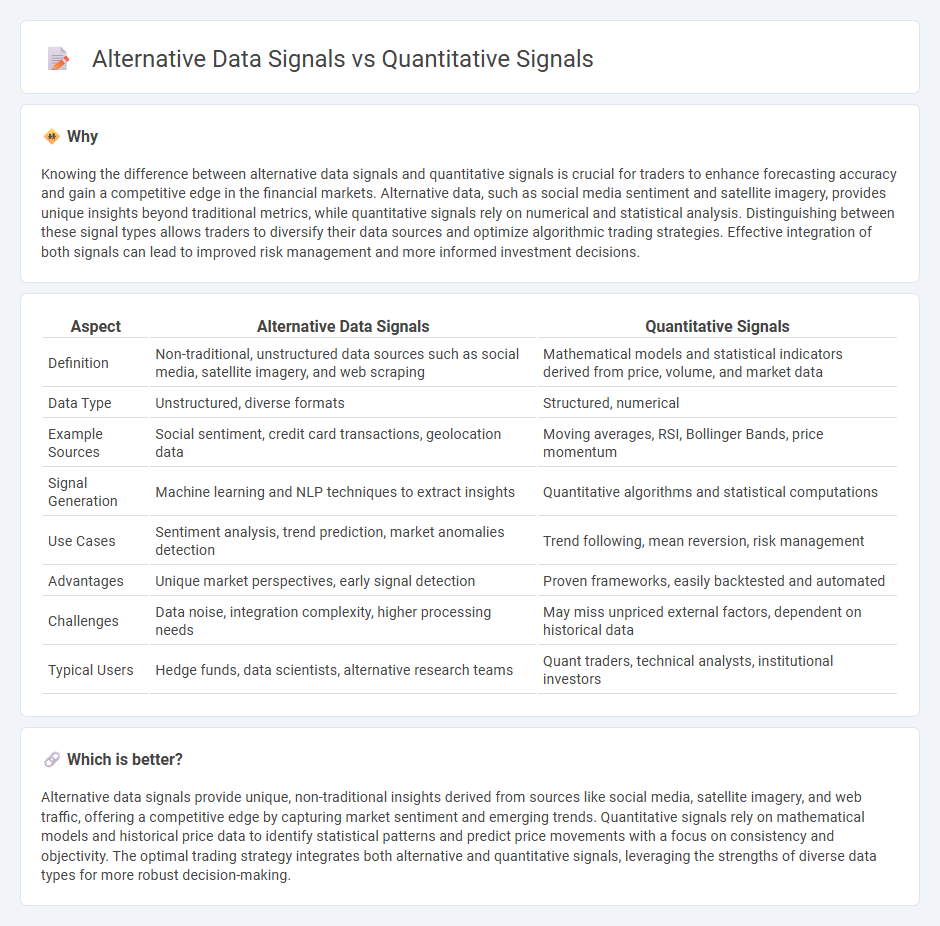
Knowing the difference between alternative data signals and quantitative signals is crucial for traders to enhance forecasting accuracy and gain a competitive edge in the financial markets. Alternative data, such as social media sentiment and satellite imagery, provides unique insights beyond traditional metrics, while quantitative signals rely on numerical and statistical analysis. Distinguishing between these signal types allows traders to diversify their data sources and optimize algorithmic trading strategies. Effective integration of both signals can lead to improved risk management and more informed investment decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alternative Data Signals | Quantitative Signals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-traditional, unstructured data sources such as social media, satellite imagery, and web scraping | Mathematical models and statistical indicators derived from price, volume, and market data |
| Data Type | Unstructured, diverse formats | Structured, numerical |
| Example Sources | Social sentiment, credit card transactions, geolocation data | Moving averages, RSI, Bollinger Bands, price momentum |
| Signal Generation | Machine learning and NLP techniques to extract insights | Quantitative algorithms and statistical computations |
| Use Cases | Sentiment analysis, trend prediction, market anomalies detection | Trend following, mean reversion, risk management |
| Advantages | Unique market perspectives, early signal detection | Proven frameworks, easily backtested and automated |
| Challenges | Data noise, integration complexity, higher processing needs | May miss unpriced external factors, dependent on historical data |
| Typical Users | Hedge funds, data scientists, alternative research teams | Quant traders, technical analysts, institutional investors |
Which is better?
Alternative data signals provide unique, non-traditional insights derived from sources like social media, satellite imagery, and web traffic, offering a competitive edge by capturing market sentiment and emerging trends. Quantitative signals rely on mathematical models and historical price data to identify statistical patterns and predict price movements with a focus on consistency and objectivity. The optimal trading strategy integrates both alternative and quantitative signals, leveraging the strengths of diverse data types for more robust decision-making.
Connection
Alternative data signals provide unstructured and non-traditional information such as social media trends, satellite imagery, and transaction records, which enhance quantitative signals derived from statistical models and financial metrics in trading strategies. The integration of alternative data enriches quantitative models by offering unique insights that improve predictive accuracy and risk management. This synergy enables traders to identify market opportunities faster and optimize portfolio performance with more robust, data-driven decisions.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Models
Quantitative signals leverage structured numerical data such as stock prices, trading volumes, and financial ratios to inform algorithmic models for investment decisions. Alternative data signals incorporate non-traditional sources like satellite imagery, social media sentiment, and web traffic, enhancing predictive accuracy and uncovering hidden market trends. Explore how integrating these data types can optimize algorithmic strategies and improve portfolio performance.
Non-traditional Data Sources
Non-traditional data sources such as satellite imagery, social media sentiment, and web scraping provide unique alternative data signals that complement traditional quantitative signals like financial metrics and market indicators. These alternative data streams enable deeper insights into consumer behavior, supply chain dynamics, and real-time market trends, enhancing predictive analytics and investment strategies. Explore how integrating non-traditional data sources can revolutionize your data-driven decision-making processes.
Signal Generation
Quantitative signals rely on numerical data derived from financial metrics, price movements, and volume trends to generate predictive models for asset performance. Alternative data signals incorporate unconventional datasets such as satellite imagery, social media sentiment, and transaction details, expanding the scope of signal generation beyond traditional financial indicators. Explore how integrating these diverse data sources can enhance signal generation strategies and improve investment decision-making.
Source and External Links
About Trading Signals | SYGNAL - Quantitative signals, or trading signals, are standardized values generated by quantitative models to express how bullish or bearish the model is on a financial instrument, guiding buy, sell, or hold decisions based on the predicted future value of the asset.
Quant signals old and new: Recent Performance and Ideas - Nomura - Quantitative signals often include factors like price momentum, earnings momentum, analysts' recommendations, and valuation ratios, which are combined in models to generate systematic strategies with measurable historical performance.
Quant Alpha Signals - Quantitative Finance Platform - Quantitative signals utilize advanced technology, behavioral analytics, and real-time data to systematically identify market opportunities, generate trading signals, and facilitate risk-adjusted execution for automated and data-driven trading approaches.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com