High-frequency scalp bots execute rapid trades to capitalize on minimal price fluctuations, leveraging speed and low latency to profit from market microstructure inefficiencies, whereas statistical arbitrage bots rely on complex mathematical models and historical data correlations to identify and exploit price discrepancies across related assets. Both strategies demand robust algorithmic precision and advanced technology infrastructure to manage risks and maximize returns effectively. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand which bot best suits your trading objectives and market conditions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between high-frequency scalp bots and statistical arbitrage bots is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and risk management. High-frequency scalp bots execute numerous trades within milliseconds to profit from small price fluctuations, whereas statistical arbitrage bots use mathematical models to exploit price inefficiencies across correlated assets over longer periods. Traders leveraging the specific strengths of each bot enhance profitability while mitigating market impact and execution risks. Knowledge of their distinct algorithms and market behaviors enables precise alignment with trading goals and financial regulations.
Comparison Table
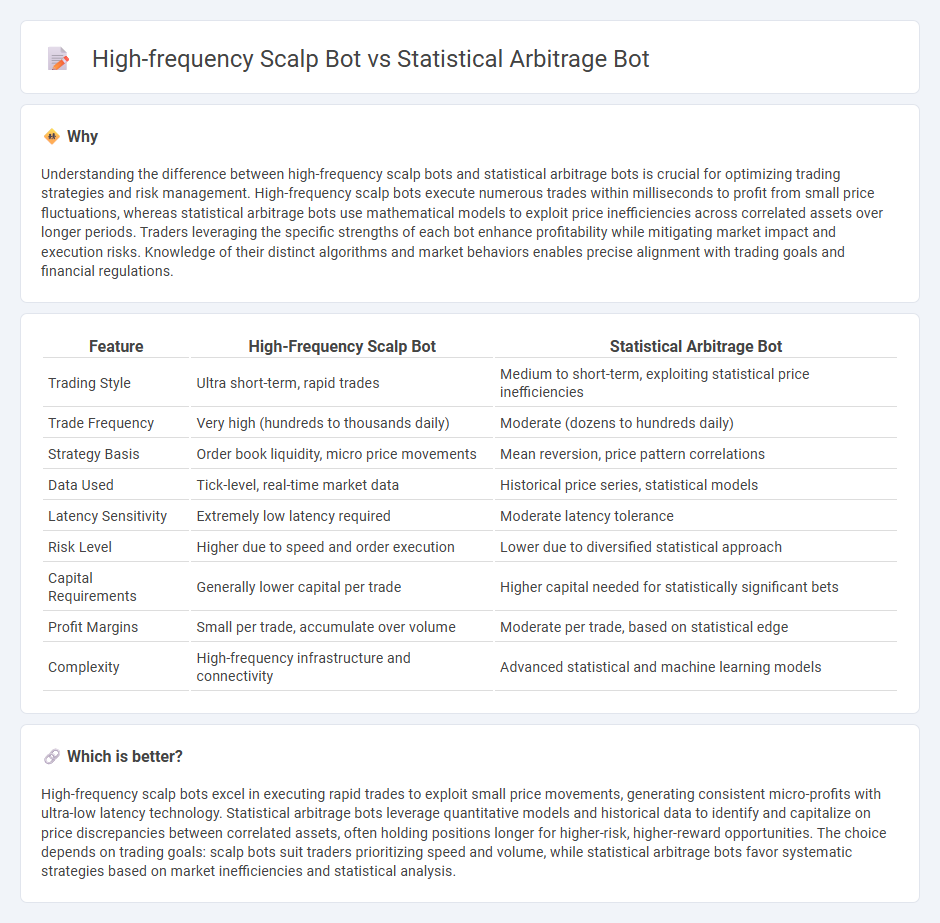
| Feature | High-Frequency Scalp Bot | Statistical Arbitrage Bot |
|---|---|---|
| Trading Style | Ultra short-term, rapid trades | Medium to short-term, exploiting statistical price inefficiencies |
| Trade Frequency | Very high (hundreds to thousands daily) | Moderate (dozens to hundreds daily) |
| Strategy Basis | Order book liquidity, micro price movements | Mean reversion, price pattern correlations |
| Data Used | Tick-level, real-time market data | Historical price series, statistical models |
| Latency Sensitivity | Extremely low latency required | Moderate latency tolerance |
| Risk Level | Higher due to speed and order execution | Lower due to diversified statistical approach |
| Capital Requirements | Generally lower capital per trade | Higher capital needed for statistically significant bets |
| Profit Margins | Small per trade, accumulate over volume | Moderate per trade, based on statistical edge |
| Complexity | High-frequency infrastructure and connectivity | Advanced statistical and machine learning models |
Which is better?
High-frequency scalp bots excel in executing rapid trades to exploit small price movements, generating consistent micro-profits with ultra-low latency technology. Statistical arbitrage bots leverage quantitative models and historical data to identify and capitalize on price discrepancies between correlated assets, often holding positions longer for higher-risk, higher-reward opportunities. The choice depends on trading goals: scalp bots suit traders prioritizing speed and volume, while statistical arbitrage bots favor systematic strategies based on market inefficiencies and statistical analysis.
Connection
High-frequency scalp bots and statistical arbitrage bots both utilize algorithmic trading strategies to exploit short-term market inefficiencies and price discrepancies. While high-frequency scalp bots focus on rapid, small-profit trades by capturing bid-ask spread fluctuations, statistical arbitrage bots analyze historical price data and correlations to identify mispriced assets for arbitrage opportunities. Both rely on advanced quantitative models, low-latency data feeds, and automated execution to maximize trading performance in highly liquid markets.
Key Terms
**Statistical Arbitrage Bot:**
Statistical arbitrage bots exploit pricing inefficiencies across correlated assets by leveraging advanced statistical models and historical data to identify mean-reverting opportunities. These bots execute trades over longer horizons compared to high-frequency scalp bots, relying on quantitative algorithms that analyze market trends and asset correlations to generate consistent returns with reduced noise. To understand how statistical arbitrage bots optimize trading strategies and risk management, explore deeper insights here.
Mean Reversion
A statistical arbitrage bot leverages mean reversion by identifying price divergences from historical averages and executing trades expecting prices to revert to the mean, utilizing quantitative models and historical data analysis. A high-frequency scalp bot targets rapid, small price movements, often exploiting very short-term inefficiencies without relying heavily on mean reversion, focusing instead on speed and order flow information. Explore deeper insights on how these bot strategies uniquely capitalize on market dynamics and mean reversion principles.
Cointegration
Statistical arbitrage bots leverage cointegration to identify pairs of cryptocurrencies whose price movements maintain a stable long-term relationship, enabling profitable mean-reversion trades. High-frequency scalp bots prioritize rapid, short-term price fluctuations and typically do not rely on cointegration, focusing instead on executing numerous trades with minimal holding times. Explore the nuances of cointegration in automated trading strategies to understand their impact on bot performance and profitability.
Source and External Links
What Is a Statistical Arbitrage Crypto Bot? - WunderTrading - A statistical arbitrage crypto bot is an automated trading system that uses complex mathematical models to identify and exploit price inefficiencies between cryptocurrencies by testing cointegration, calculating spreads, backtesting rigorously, and managing risk before deployment.
Best Crypto Arbitrage Bots in 2025: Full Guide - CrustLab - Statistical arbitrage bots use algorithms and historical data to forecast price movements and identify crypto arbitrage opportunities by predicting future price differences across exchanges using statistical models and advanced trading algorithms.
Statistical Arbitrage: Strategies, Examples, and Risks - dYdX - Statistical arbitrage identifies temporary price inefficiencies between digital assets linked by cointegration, exploiting deviations from typical price relationships through rapid, algorithmic high-frequency trading to profit from mean reversion.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com