Airdrop farming involves leveraging cryptocurrency giveaways to accumulate tokens with minimal investment, focusing on identifying and participating in new project launches. Algorithmic trading employs automated systems and mathematical models to execute high-frequency trades, optimizing market opportunities systematically. Explore the advantages and challenges of both strategies to determine which aligns best with your trading goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between airdrop farming and algorithmic trading is crucial for maximizing efficiency in cryptocurrency markets. Airdrop farming involves strategically acquiring free token distributions by participating in specific blockchain networks, while algorithmic trading uses automated systems to execute trades based on predefined criteria and market data. Mastery of both techniques enables traders to diversify risk, optimize portfolio growth, and leverage unique market opportunities. Recognizing the distinct strategies ensures informed decision-making and enhances overall trading profitability.
Comparison Table
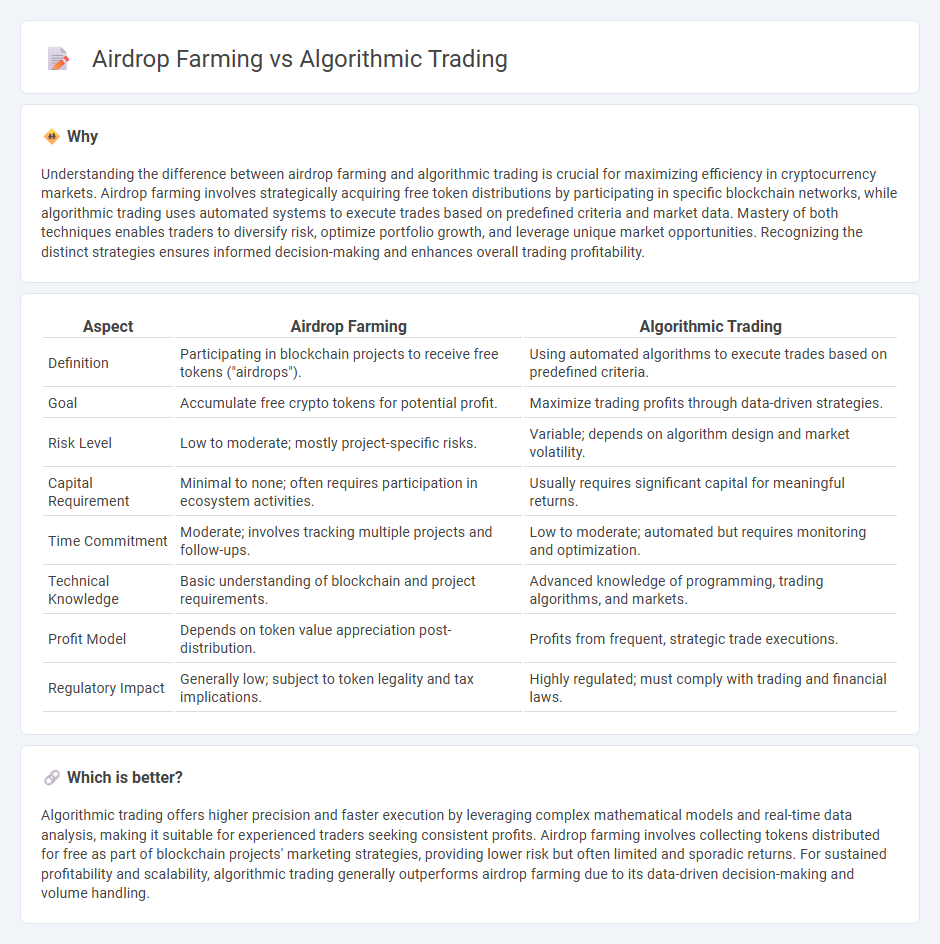
| Aspect | Airdrop Farming | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Participating in blockchain projects to receive free tokens ("airdrops"). | Using automated algorithms to execute trades based on predefined criteria. |
| Goal | Accumulate free crypto tokens for potential profit. | Maximize trading profits through data-driven strategies. |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate; mostly project-specific risks. | Variable; depends on algorithm design and market volatility. |
| Capital Requirement | Minimal to none; often requires participation in ecosystem activities. | Usually requires significant capital for meaningful returns. |
| Time Commitment | Moderate; involves tracking multiple projects and follow-ups. | Low to moderate; automated but requires monitoring and optimization. |
| Technical Knowledge | Basic understanding of blockchain and project requirements. | Advanced knowledge of programming, trading algorithms, and markets. |
| Profit Model | Depends on token value appreciation post-distribution. | Profits from frequent, strategic trade executions. |
| Regulatory Impact | Generally low; subject to token legality and tax implications. | Highly regulated; must comply with trading and financial laws. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic trading offers higher precision and faster execution by leveraging complex mathematical models and real-time data analysis, making it suitable for experienced traders seeking consistent profits. Airdrop farming involves collecting tokens distributed for free as part of blockchain projects' marketing strategies, providing lower risk but often limited and sporadic returns. For sustained profitability and scalability, algorithmic trading generally outperforms airdrop farming due to its data-driven decision-making and volume handling.
Connection
Airdrop farming involves collecting free cryptocurrency tokens distributed by blockchain projects, which can be strategically integrated into algorithmic trading systems to optimize portfolio diversification and enhance trading signals. Algorithmic trading leverages automated strategies to execute trades based on predefined rules, incorporating airdropped assets to exploit market inefficiencies and maximize returns. Combining these techniques enables traders to capitalize on token distribution events while maintaining disciplined, data-driven trading practices.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Trading:
Algorithmic trading employs advanced mathematical models and high-frequency data analysis to execute trades at optimal speeds, minimizing human error and maximizing profit potential in volatile markets. Unlike airdrop farming, which relies on collecting free tokens from blockchain projects, algorithmic trading leverages real-time market signals and automation for strategic investment decisions. Discover more about how algorithmic trading transforms modern financial markets and enhances trading efficiency.
Backtesting
Algorithmic trading relies heavily on backtesting, using historical market data to simulate trading strategies and optimize performance before actual deployment. Airdrop farming, in contrast, has limited application for backtesting since it involves earning crypto tokens through participation incentives rather than trading patterns. Explore more to understand how backtesting shapes strategy efficacy in algorithmic trading versus airdrop farming nuances.
Execution Speed
Algorithmic trading relies on ultra-fast execution speeds to capitalize on market inefficiencies within milliseconds, leveraging advanced algorithms and low-latency infrastructure. Airdrop farming, in contrast, prioritizes prompt claim submissions but often operates on slower blockchain networks, where speed is less critical than participation eligibility and timing. Discover how execution speed impacts these strategies and which offers optimal gains.
Source and External Links
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading involves using computer code and software to open and close trades based on pre-set rules such as price movements, with major strategies including price action, technical analysis, and combination approaches tailored for volatility and risk management in markets.
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - It refers to programmed trading strategies that automate decisions based on conditions, like moving average algorithms that buy or sell when prices cross specific averages, often using tactics like incremental order placement to minimize market impact.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading uses automated pre-programmed instructions including time, price, and volume considerations, and has evolved with machine learning techniques such as deep reinforcement learning and directional change algorithms to adapt dynamically to volatile market conditions and improve trade timing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com