Pair trading involves simultaneously buying and selling two correlated assets to exploit price discrepancies while minimizing market risk. Quantitative trading employs mathematical models and algorithms to analyze large datasets, identify trading opportunities, and execute orders systematically. Discover more about how these strategies harness data and analysis to optimize investment performance.
Why it is important
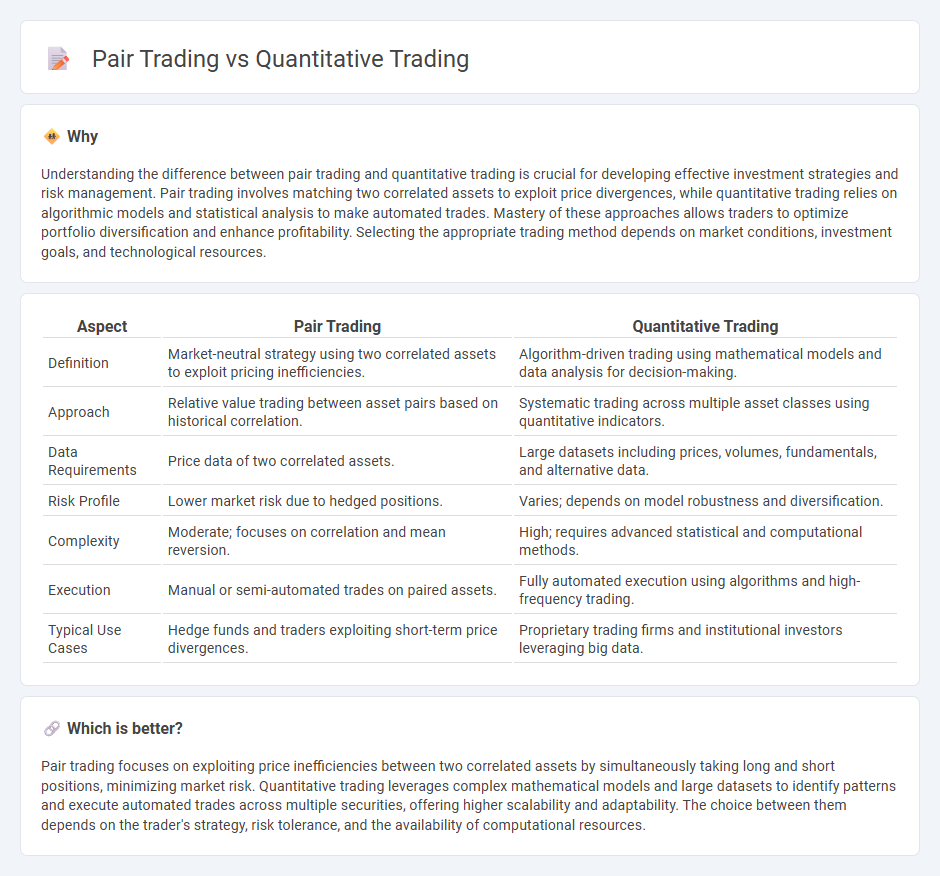
Understanding the difference between pair trading and quantitative trading is crucial for developing effective investment strategies and risk management. Pair trading involves matching two correlated assets to exploit price divergences, while quantitative trading relies on algorithmic models and statistical analysis to make automated trades. Mastery of these approaches allows traders to optimize portfolio diversification and enhance profitability. Selecting the appropriate trading method depends on market conditions, investment goals, and technological resources.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Pair Trading | Quantitative Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-neutral strategy using two correlated assets to exploit pricing inefficiencies. | Algorithm-driven trading using mathematical models and data analysis for decision-making. |
| Approach | Relative value trading between asset pairs based on historical correlation. | Systematic trading across multiple asset classes using quantitative indicators. |
| Data Requirements | Price data of two correlated assets. | Large datasets including prices, volumes, fundamentals, and alternative data. |
| Risk Profile | Lower market risk due to hedged positions. | Varies; depends on model robustness and diversification. |
| Complexity | Moderate; focuses on correlation and mean reversion. | High; requires advanced statistical and computational methods. |
| Execution | Manual or semi-automated trades on paired assets. | Fully automated execution using algorithms and high-frequency trading. |
| Typical Use Cases | Hedge funds and traders exploiting short-term price divergences. | Proprietary trading firms and institutional investors leveraging big data. |
Which is better?
Pair trading focuses on exploiting price inefficiencies between two correlated assets by simultaneously taking long and short positions, minimizing market risk. Quantitative trading leverages complex mathematical models and large datasets to identify patterns and execute automated trades across multiple securities, offering higher scalability and adaptability. The choice between them depends on the trader's strategy, risk tolerance, and the availability of computational resources.
Connection
Pair trading and quantitative trading are connected through their reliance on statistical and mathematical models to identify trading opportunities. Pair trading uses quantitative techniques to analyze correlated asset pairs, aiming to exploit price divergences for profit. Quantitative trading frameworks enhance pair trading strategies by automating data analysis, risk management, and execution processes.
Key Terms
**Quantitative Trading:**
Quantitative trading leverages mathematical models, algorithms, and statistical techniques to identify trading opportunities based on data-driven analysis across various asset classes, including equities, commodities, and forex. This approach utilizes high-frequency data, machine learning, and historical price patterns to execute trades automatically with minimal human intervention, optimizing for risk-adjusted returns. Discover more about the advantages and methodologies of quantitative trading and how it contrasts with pair trading strategies.
Algorithmic Models
Quantitative trading leverages advanced algorithmic models to analyze vast datasets and execute high-frequency trades across diverse assets, enhancing market efficiency and minimizing human biases. Pair trading, a subset of quantitative strategies, involves identifying correlated asset pairs and exploiting price divergences through mean-reversion algorithms, typically used in equity markets. Explore more about algorithmic models' role in optimizing these trading strategies and boosting financial portfolio performance.
Backtesting
Quantitative trading uses statistical models and algorithms to identify and execute trades across various assets, emphasizing backtesting to validate strategy performance over historical data. Pair trading, a market-neutral strategy, involves simultaneously buying one asset and selling a correlated counterpart, with backtesting crucial for assessing the spread's mean reversion and risk parameters. Explore detailed methodologies and best practices for backtesting to optimize both quantitative and pair trading strategies effectively.
Source and External Links
Quantitative Trader Courses: How to Become a Quantitative Trader - Quantitative trading involves using mathematical models and automated trading strategies, often employing price and volume data, to identify profitable trading opportunities and reduce emotion-based decisions through high-frequency trading automation.
How To Become a Quantitative Trader in 4 Steps (With Skills) - Indeed - Quantitative traders use mathematical computations and algorithmic trading software to analyze large data sets, develop innovative strategies, and capitalize on fast-changing market opportunities with creativity and continuous innovation.
Quantitative analysis (finance) - Wikipedia - Quantitative trading is a subset of quantitative finance applying mathematical and statistical methods to trading, including algorithmic and high-frequency trading, often implemented by "quants" working on derivative pricing, risk management, and investment management at firms like Renaissance Technologies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com