Funding rate arbitrage exploits discrepancies in perpetual futures funding rates across different exchanges to generate risk-free profits, while statistical arbitrage relies on identifying price inefficiencies and mean-reverting patterns within correlated asset pairs using quantitative models. Funding rate strategies demand constant monitoring of interest rate differentials and liquidity conditions, contrasting with the data-driven, algorithmic approach of statistical arbitrage that focuses on historical price relationships and statistical indicators. Explore deeper to understand how these distinct arbitrage techniques can enhance your trading strategies and risk management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between funding rate arbitrage and statistical arbitrage is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and optimize profits in crypto and traditional markets. Funding rate arbitrage exploits discrepancies in interest payments between long and short positions on perpetual futures, while statistical arbitrage relies on mathematical models to identify pricing inefficiencies across assets. Properly distinguishing these strategies enables more accurate execution and capital allocation in diverse market conditions. Mastery of each arbitrage type enhances a trader's ability to capitalize on distinct market inefficiencies with tailored risk management approaches.
Comparison Table
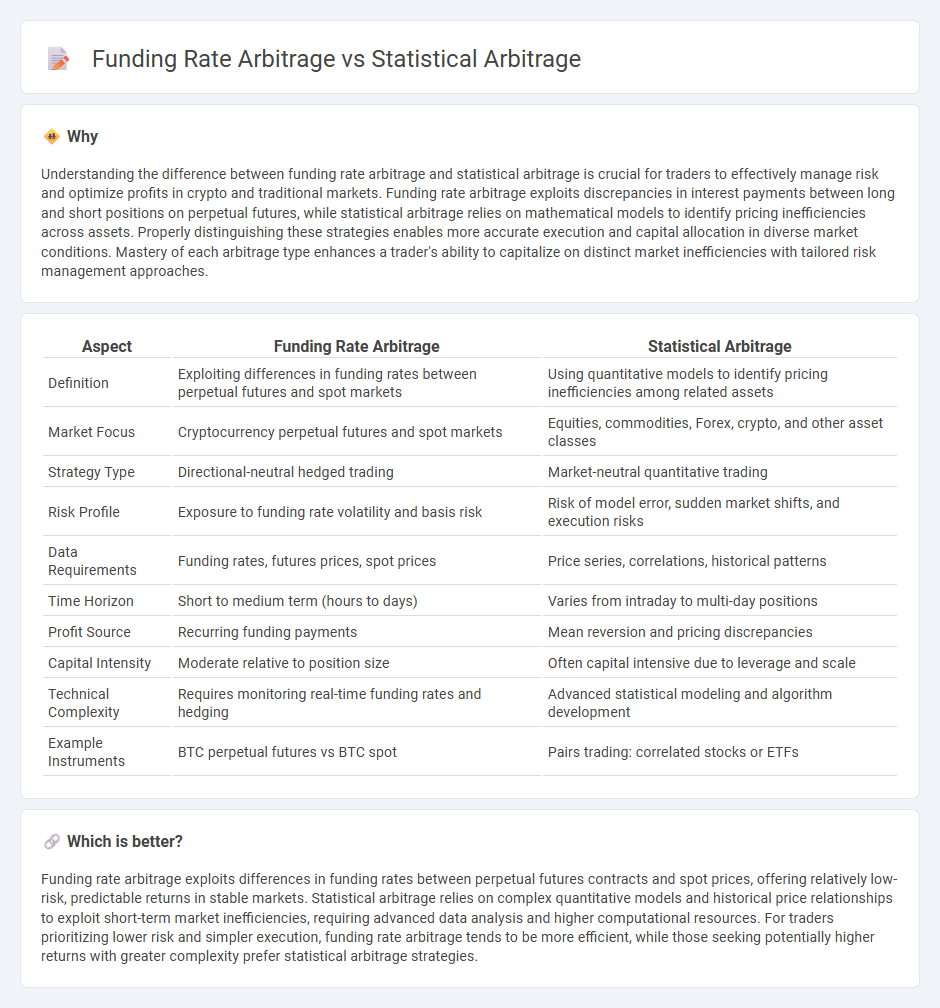
| Aspect | Funding Rate Arbitrage | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting differences in funding rates between perpetual futures and spot markets | Using quantitative models to identify pricing inefficiencies among related assets |
| Market Focus | Cryptocurrency perpetual futures and spot markets | Equities, commodities, Forex, crypto, and other asset classes |
| Strategy Type | Directional-neutral hedged trading | Market-neutral quantitative trading |
| Risk Profile | Exposure to funding rate volatility and basis risk | Risk of model error, sudden market shifts, and execution risks |
| Data Requirements | Funding rates, futures prices, spot prices | Price series, correlations, historical patterns |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term (hours to days) | Varies from intraday to multi-day positions |
| Profit Source | Recurring funding payments | Mean reversion and pricing discrepancies |
| Capital Intensity | Moderate relative to position size | Often capital intensive due to leverage and scale |
| Technical Complexity | Requires monitoring real-time funding rates and hedging | Advanced statistical modeling and algorithm development |
| Example Instruments | BTC perpetual futures vs BTC spot | Pairs trading: correlated stocks or ETFs |
Which is better?
Funding rate arbitrage exploits differences in funding rates between perpetual futures contracts and spot prices, offering relatively low-risk, predictable returns in stable markets. Statistical arbitrage relies on complex quantitative models and historical price relationships to exploit short-term market inefficiencies, requiring advanced data analysis and higher computational resources. For traders prioritizing lower risk and simpler execution, funding rate arbitrage tends to be more efficient, while those seeking potentially higher returns with greater complexity prefer statistical arbitrage strategies.
Connection
Funding rate arbitrage and statistical arbitrage are connected through their reliance on price inefficiencies across different markets or instruments to generate risk-adjusted returns. Funding rate arbitrage exploits disparities in perpetual futures funding rates relative to spot prices, while statistical arbitrage uses quantitative models to identify and capitalize on short-term price anomalies and mean reversion patterns. Both strategies employ algorithmic trading systems to execute high-frequency trades that aim to profit from temporary market dislocations.
Key Terms
**Statistical Arbitrage:**
Statistical arbitrage leverages quantitative models to exploit price inefficiencies across correlated financial instruments, using historical data and statistical methods to predict and capitalize on mean-reverting behaviors. This strategy involves high-frequency trading and complex algorithms that dynamically adjust positions based on real-time market signals, minimizing risk through diversified pair trades. Explore how statistical arbitrage algorithms can optimize your trading portfolios and enhance market efficiency.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage utilizes mean reversion by identifying price deviations from historical averages, aiming to profit as prices revert to the mean. Funding rate arbitrage exploits discrepancies in crypto derivatives' funding rates, betting on mean reversion in these rates to capture consistent yields. Explore deeper insights into how mean reversion principles drive these arbitrage strategies for optimized trading.
Pairs Trading
Statistical arbitrage in pairs trading involves exploiting mean-reversion patterns between correlated asset prices by dynamically adjusting positions to capitalize on price divergences. Funding rate arbitrage leverages the difference in borrowing costs across perpetual futures contracts to generate riskless profits, often combined with long-short positions on the underlying tokens. Explore detailed strategies and risk considerations behind pairs trading and funding rate arbitrage to enhance your quantitative trading approach.
Source and External Links
Top Statistical Arbitrage Strategies and Their Risks - WunderTrading - Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral, quantitative trading strategy that exploits price discrepancies between related securities using mathematical models, aiming for consistent returns through paired long and short positions and focusing on mean reversion patterns while emphasizing strong risk management.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage (Stat Arb) involves short-term trading of broadly diversified portfolios employing mean reversion and other statistical techniques to exploit small pricing inefficiencies, typically automated to manage high turnover and low-margin trades, and widely used in hedge funds and investment banks.
Statistical Arbitrage in High Frequency Trading Based on Limit Order ... - Statistical arbitrage is defined academically as spreading risk across thousands to millions of trades with very short holding periods, aiming to generate profits from numerous small-arbitrage opportunities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com