Statistical arbitrage involves using quantitative models to identify and exploit price inefficiencies between correlated assets, typically executing numerous trades to capture small, consistent profits. Liquidity provision, on the other hand, focuses on placing buy and sell orders to facilitate market transactions, earning returns primarily through the bid-ask spread while managing inventory risk. Explore the key differences and strategic advantages of these trading approaches to enhance your market strategies.
Why it is important
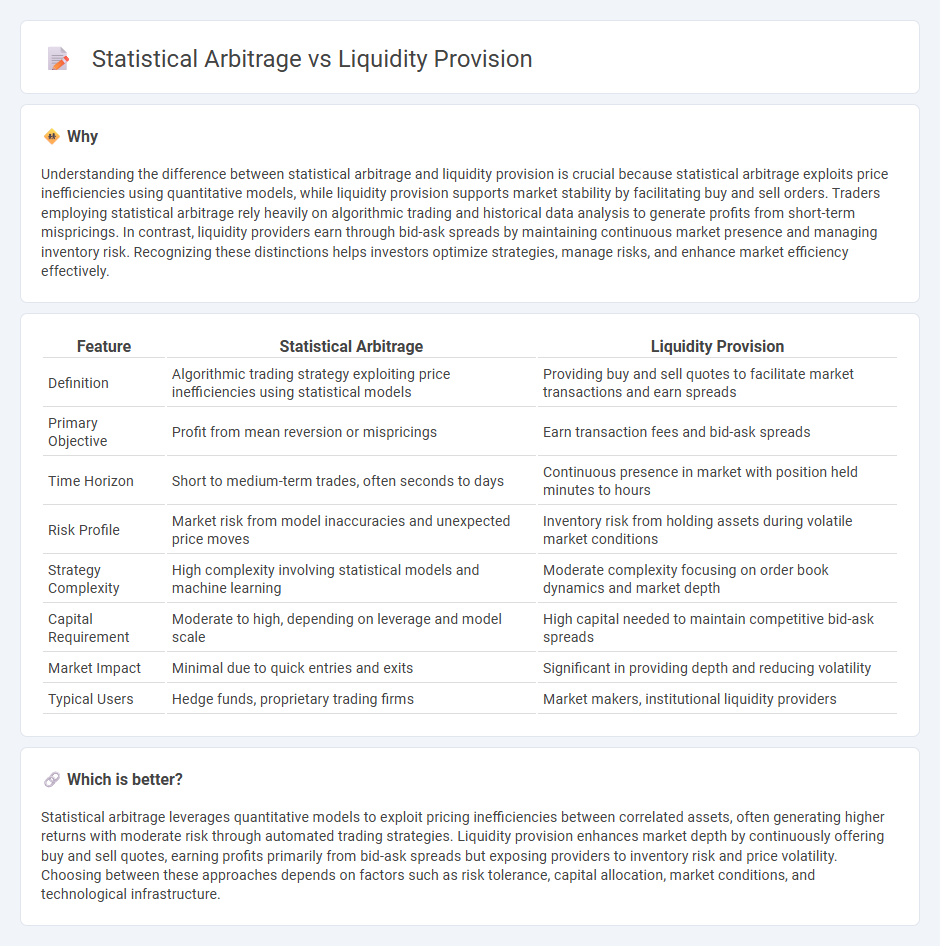
Understanding the difference between statistical arbitrage and liquidity provision is crucial because statistical arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies using quantitative models, while liquidity provision supports market stability by facilitating buy and sell orders. Traders employing statistical arbitrage rely heavily on algorithmic trading and historical data analysis to generate profits from short-term mispricings. In contrast, liquidity providers earn through bid-ask spreads by maintaining continuous market presence and managing inventory risk. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors optimize strategies, manage risks, and enhance market efficiency effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Statistical Arbitrage | Liquidity Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Algorithmic trading strategy exploiting price inefficiencies using statistical models | Providing buy and sell quotes to facilitate market transactions and earn spreads |
| Primary Objective | Profit from mean reversion or mispricings | Earn transaction fees and bid-ask spreads |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium-term trades, often seconds to days | Continuous presence in market with position held minutes to hours |
| Risk Profile | Market risk from model inaccuracies and unexpected price moves | Inventory risk from holding assets during volatile market conditions |
| Strategy Complexity | High complexity involving statistical models and machine learning | Moderate complexity focusing on order book dynamics and market depth |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate to high, depending on leverage and model scale | High capital needed to maintain competitive bid-ask spreads |
| Market Impact | Minimal due to quick entries and exits | Significant in providing depth and reducing volatility |
| Typical Users | Hedge funds, proprietary trading firms | Market makers, institutional liquidity providers |
Which is better?
Statistical arbitrage leverages quantitative models to exploit pricing inefficiencies between correlated assets, often generating higher returns with moderate risk through automated trading strategies. Liquidity provision enhances market depth by continuously offering buy and sell quotes, earning profits primarily from bid-ask spreads but exposing providers to inventory risk and price volatility. Choosing between these approaches depends on factors such as risk tolerance, capital allocation, market conditions, and technological infrastructure.
Connection
Statistical arbitrage and liquidity provision are interconnected through their reliance on market inefficiencies and real-time data analysis. Statistical arbitrage exploits price discrepancies by executing high-frequency trades, which inherently contributes to market liquidity by increasing trade volume and tightening bid-ask spreads. Liquidity providers, in turn, benefit from these frequent trades as they earn the spread while facilitating smoother market operations and enhancing price discovery.
Key Terms
Liquidity Provision:
Liquidity provision involves continuously posting buy and sell orders on a trading platform to facilitate market efficiency and tighten bid-ask spreads, enhancing overall market liquidity. Market makers and algorithms engage in this strategy to earn profits from the bid-ask spread while managing inventory risk and price volatility. Explore how liquidity provision strategies optimize trading costs and improve market stability in dynamic financial environments.
Bid-Ask Spread
Liquidity provision involves placing limit orders to capture the bid-ask spread by supplying market depth and reducing transaction costs for other traders. Statistical arbitrage exploits price discrepancies using quantitative models, often trading around the bid-ask spread to profit from mean-reverting patterns rather than directly capturing it. Explore detailed strategies and risk profiles to understand how each approach leverages the bid-ask spread for optimal returns.
Market Maker
Market makers provide liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, ensuring smooth market operations and tighter bid-ask spreads, while statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models to exploit price inefficiencies across correlated assets for profit. The primary role of a market maker centers on risk management and inventory control, balancing supply and demand in real-time, contrasting with the strategy-driven position-taking in statistical arbitrage. Explore the distinct mechanisms and advantages of market making in enhancing market stability and efficiency.
Source and External Links
Remarks on liquidity provision and on the economic ... - Liquidity provision is a fundamental central bank role, where the Federal Reserve acts as a liquidity backstop by lending against good collateral to ensure financial stability, reassure the public, and support smooth market functioning during stress periods.
DeFi Basics: Liquidity Provision - In decentralized finance (DeFi), liquidity provision involves users depositing paired crypto tokens into liquidity pools on protocols to enable token swaps, earning fees for providing access to tradable assets.
Liquidity Provision: How Does it Work? - Liquidity providers in crypto and forex markets include major banks and brokers who supply buy/sell quotes, enabling smooth trading by aggregating liquidity sources to offer competitive pricing and tight spreads.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com