Flash loans enable traders to borrow large amounts of cryptocurrency instantly and without collateral, exploiting arbitrage opportunities within a single transaction block. Short selling involves borrowing assets to sell them at a high price, aiming to repurchase them later at a lower price to profit from declining markets. Explore more about how these strategies impact modern trading dynamics and risk management.
Why it is important
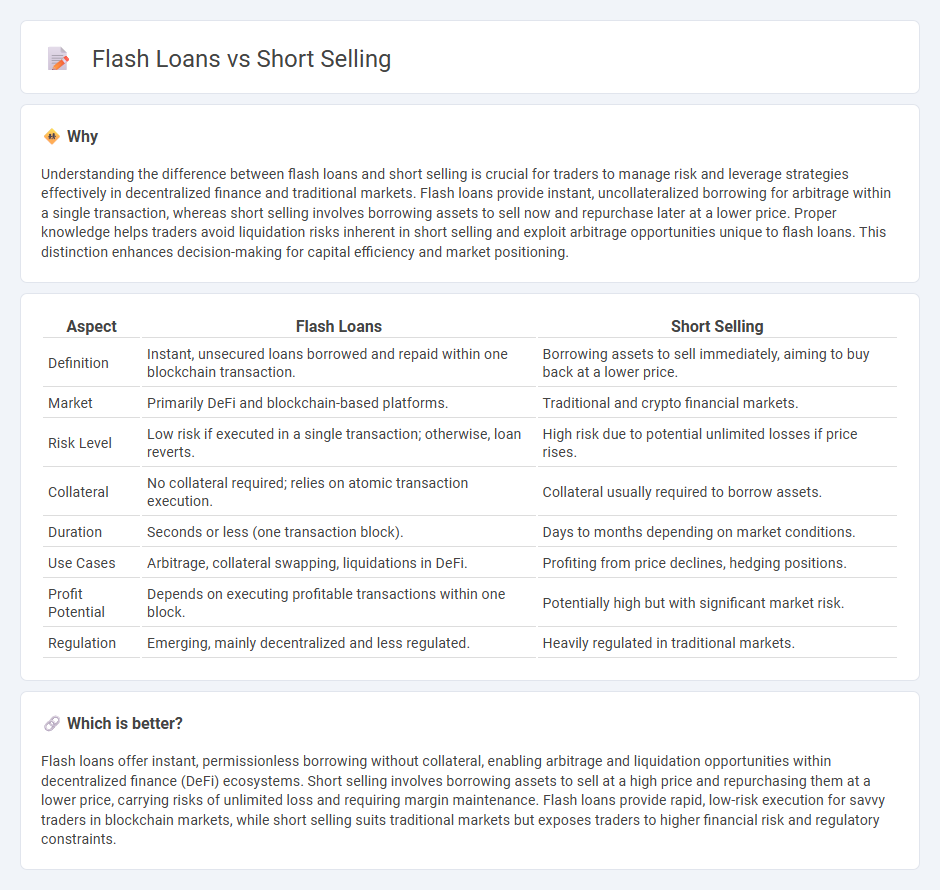
Understanding the difference between flash loans and short selling is crucial for traders to manage risk and leverage strategies effectively in decentralized finance and traditional markets. Flash loans provide instant, uncollateralized borrowing for arbitrage within a single transaction, whereas short selling involves borrowing assets to sell now and repurchase later at a lower price. Proper knowledge helps traders avoid liquidation risks inherent in short selling and exploit arbitrage opportunities unique to flash loans. This distinction enhances decision-making for capital efficiency and market positioning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flash Loans | Short Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant, unsecured loans borrowed and repaid within one blockchain transaction. | Borrowing assets to sell immediately, aiming to buy back at a lower price. |
| Market | Primarily DeFi and blockchain-based platforms. | Traditional and crypto financial markets. |
| Risk Level | Low risk if executed in a single transaction; otherwise, loan reverts. | High risk due to potential unlimited losses if price rises. |
| Collateral | No collateral required; relies on atomic transaction execution. | Collateral usually required to borrow assets. |
| Duration | Seconds or less (one transaction block). | Days to months depending on market conditions. |
| Use Cases | Arbitrage, collateral swapping, liquidations in DeFi. | Profiting from price declines, hedging positions. |
| Profit Potential | Depends on executing profitable transactions within one block. | Potentially high but with significant market risk. |
| Regulation | Emerging, mainly decentralized and less regulated. | Heavily regulated in traditional markets. |
Which is better?
Flash loans offer instant, permissionless borrowing without collateral, enabling arbitrage and liquidation opportunities within decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems. Short selling involves borrowing assets to sell at a high price and repurchasing them at a lower price, carrying risks of unlimited loss and requiring margin maintenance. Flash loans provide rapid, low-risk execution for savvy traders in blockchain markets, while short selling suits traditional markets but exposes traders to higher financial risk and regulatory constraints.
Connection
Flash loans enable traders to borrow large sums of cryptocurrency without collateral for a very short time, facilitating complex trading strategies like short selling. By using flash loans, traders can quickly borrow assets, sell them at a high price, and repurchase them at a lower price to profit from market declines. This seamless execution boosts market liquidity and enables more efficient price discovery in decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
Key Terms
Leverage
Short selling involves borrowing assets to sell them, expecting to buy them back later at a lower price, effectively leveraging market downturns for profit. Flash loans provide instant, uncollateralized leverage within a single transaction, enabling complex arbitrage and liquidation strategies without traditional borrowing constraints. Explore how these leverage mechanisms impact decentralized finance by diving deeper into their unique dynamics.
Collateral
Short selling requires posting collateral to borrow and sell assets, ensuring risk coverage and lender protection throughout the trade. Flash loans operate without collateral by leveraging atomic transactions on blockchain platforms, enabling instant borrowing and repayment within one block. Discover how collateral dynamics shape the risks and advantages of short selling and flash loans.
Arbitrage
Short selling exploits price declines by borrowing and selling assets to repurchase them later at lower prices, capturing arbitrage opportunities during market inefficiencies. Flash loans enable instant, unsecured borrowing of large sums within a single transaction, facilitating arbitrage by exploiting price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges without initial capital. Discover how these powerful strategies leverage market dynamics for profitable arbitrage in evolving financial ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Short Sales - Short selling involves selling a stock you do not own, borrowed from someone else, expecting the stock price to fall so you can buy it back cheaper and make a profit; if the price rises, you incur a loss.
Short selling explained with examples | IG International - Short selling is borrowing shares and immediately selling them on the market with the intention to repurchase at a lower price, profiting from the difference minus fees; losses occur if the price rises instead.
Short (finance) - The short seller borrows shares and sells them, hoping the price falls, then buys them back to return to the lender; short selling carries theoretically unlimited losses because share prices can rise indefinitely.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com