Dark pool activity allows institutional investors to execute large trades anonymously, reducing market impact and preventing price slippage often seen in lit exchanges. Direct Market Access (DMA) provides traders with real-time connectivity to order books, enabling faster execution and greater transparency in trade placement. Explore the advantages and risks of dark pools and DMA to optimize your trading strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark pool activity and direct market access (DMA) is crucial for traders to assess market liquidity and price transparency effectively. Dark pools facilitate large-volume trades away from public exchanges, reducing market impact but limiting immediate visibility. DMA enables traders to directly interact with public order books, ensuring real-time execution and full market transparency. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize trade execution strategies and manage risk efficiently in different market environments.
Comparison Table
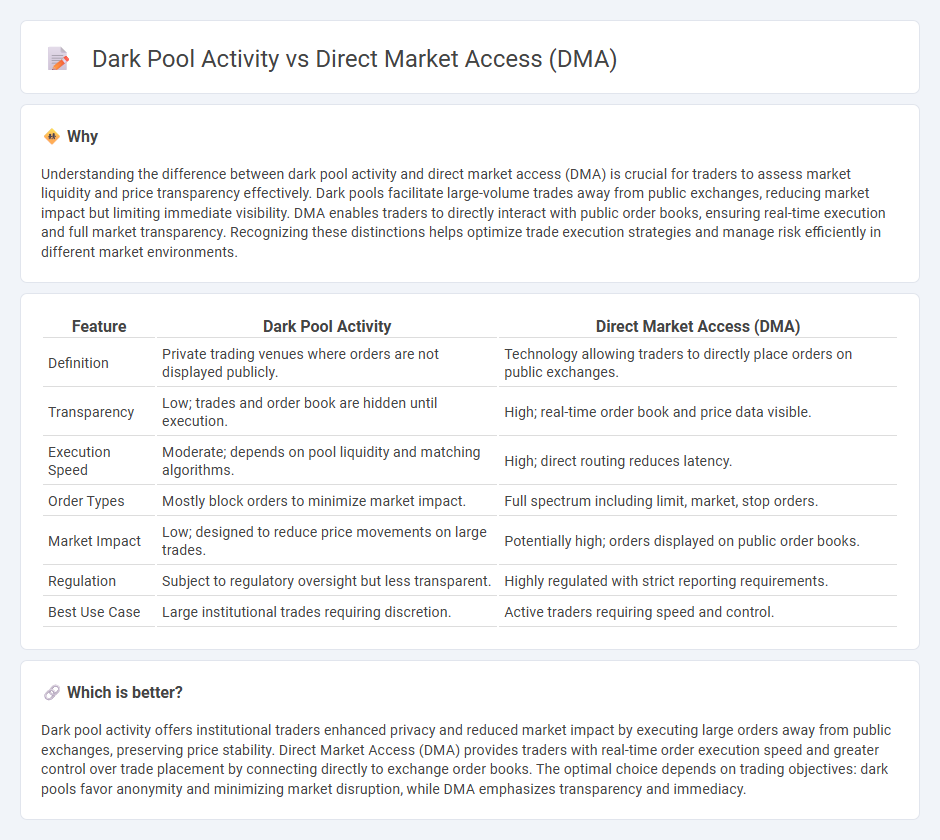
| Feature | Dark Pool Activity | Direct Market Access (DMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private trading venues where orders are not displayed publicly. | Technology allowing traders to directly place orders on public exchanges. |
| Transparency | Low; trades and order book are hidden until execution. | High; real-time order book and price data visible. |
| Execution Speed | Moderate; depends on pool liquidity and matching algorithms. | High; direct routing reduces latency. |
| Order Types | Mostly block orders to minimize market impact. | Full spectrum including limit, market, stop orders. |
| Market Impact | Low; designed to reduce price movements on large trades. | Potentially high; orders displayed on public order books. |
| Regulation | Subject to regulatory oversight but less transparent. | Highly regulated with strict reporting requirements. |
| Best Use Case | Large institutional trades requiring discretion. | Active traders requiring speed and control. |
Which is better?
Dark pool activity offers institutional traders enhanced privacy and reduced market impact by executing large orders away from public exchanges, preserving price stability. Direct Market Access (DMA) provides traders with real-time order execution speed and greater control over trade placement by connecting directly to exchange order books. The optimal choice depends on trading objectives: dark pools favor anonymity and minimizing market disruption, while DMA emphasizes transparency and immediacy.
Connection
Dark pool activity and Direct Market Access (DMA) are interconnected through the facilitation of large, anonymous trades that minimize market impact and enhance liquidity. DMA allows institutional investors to bypass traditional brokers and access dark pools directly, enabling efficient execution of sizable orders away from public order books. This synergy improves trade confidentiality and execution speed, critical factors in high-frequency and algorithmic trading strategies.
Key Terms
Order Routing
Direct Market Access (DMA) enables traders to route orders directly to exchanges, ensuring transparency and speed in execution. Dark pool activity, by contrast, involves routing orders to private exchanges where transactions occur anonymously, minimizing market impact but reducing visibility. Explore the nuances of order routing strategies and their impact on execution quality to optimize trading decisions.
Transparency
Direct Market Access (DMA) provides traders with real-time, transparent access to public order books, enhancing price discovery and market efficiency. Dark pool activity, in contrast, occurs in private trading venues where orders remain undisclosed, reducing market transparency but allowing large trades to be executed with minimal market impact. Explore how transparency differences between DMA and dark pools influence trading strategies and market behavior.
Liquidity
Direct Market Access (DMA) provides traders with real-time access to public exchanges, enhancing liquidity by enabling immediate order execution and price transparency. Dark pool activity, in contrast, offers private trading venues where large orders execute anonymously, potentially reducing market impact but limiting visible liquidity. Explore the nuances of how DMA and dark pools influence market liquidity and trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Direct Market Access (DMA) - Overview, How It Works, Users - DMA is a method of electronic trading that allows investors to execute trades by directly interacting with an electronic order book, bypassing brokers to place orders at their chosen price, often used in equities, fixed income, and derivatives markets and suitable for advanced traders employing strategies like algorithmic trading.
Direct market access - DMA is the electronic trading infrastructure that lets investors directly interact with an exchange's order book using sell-side firms' technology but controlling their own trade execution, evolving from traditional broker-dealer models to provide faster, autonomous order management often integrated with algorithmic trading, though certain types raise regulatory concerns.
What is DMA (Direct Market Access)? - DMA enables traders to send orders directly to a financial exchange's order book without broker intervention, offering faster execution, real-time transparency, and greater control over trades, favored by hedge funds and algorithmic traders for optimizing trading strategies in fast markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com