Order book imbalance measures the difference between buy and sell orders, revealing market sentiment and potential price movements. Iceberg orders are large trades hidden by splitting into smaller visible portions to minimize market impact. Explore how understanding these concepts can enhance your trading strategies and market analysis.
Why it is important
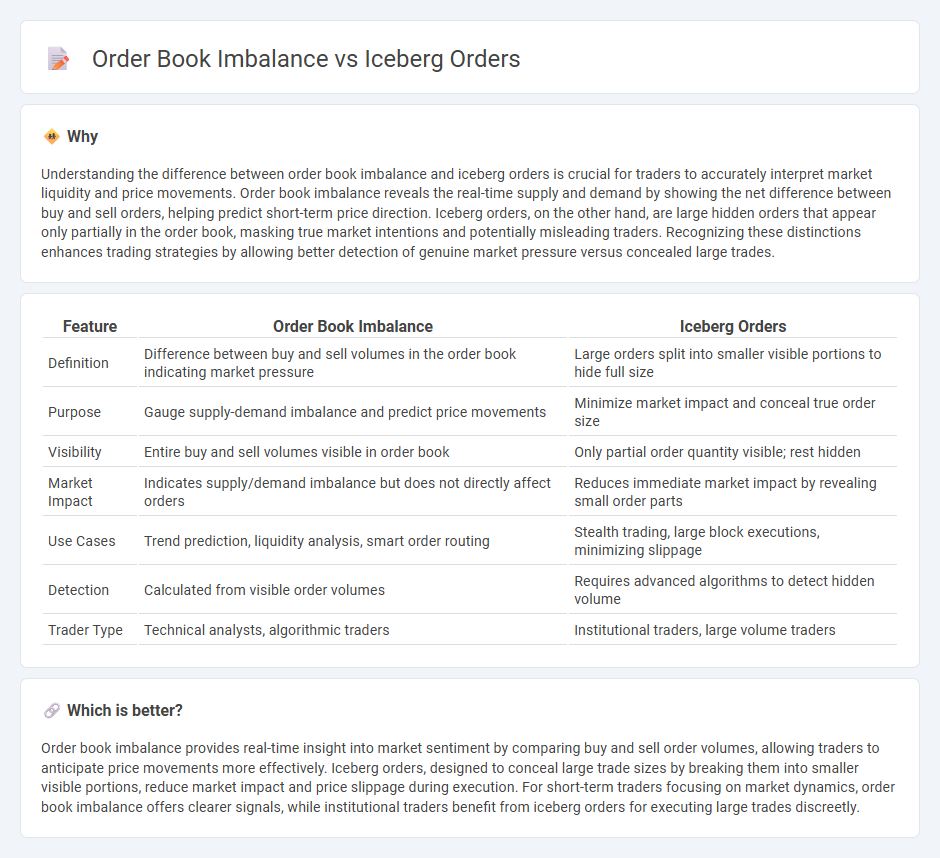
Understanding the difference between order book imbalance and iceberg orders is crucial for traders to accurately interpret market liquidity and price movements. Order book imbalance reveals the real-time supply and demand by showing the net difference between buy and sell orders, helping predict short-term price direction. Iceberg orders, on the other hand, are large hidden orders that appear only partially in the order book, masking true market intentions and potentially misleading traders. Recognizing these distinctions enhances trading strategies by allowing better detection of genuine market pressure versus concealed large trades.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Order Book Imbalance | Iceberg Orders |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Difference between buy and sell volumes in the order book indicating market pressure | Large orders split into smaller visible portions to hide full size |
| Purpose | Gauge supply-demand imbalance and predict price movements | Minimize market impact and conceal true order size |
| Visibility | Entire buy and sell volumes visible in order book | Only partial order quantity visible; rest hidden |
| Market Impact | Indicates supply/demand imbalance but does not directly affect orders | Reduces immediate market impact by revealing small order parts |
| Use Cases | Trend prediction, liquidity analysis, smart order routing | Stealth trading, large block executions, minimizing slippage |
| Detection | Calculated from visible order volumes | Requires advanced algorithms to detect hidden volume |
| Trader Type | Technical analysts, algorithmic traders | Institutional traders, large volume traders |
Which is better?
Order book imbalance provides real-time insight into market sentiment by comparing buy and sell order volumes, allowing traders to anticipate price movements more effectively. Iceberg orders, designed to conceal large trade sizes by breaking them into smaller visible portions, reduce market impact and price slippage during execution. For short-term traders focusing on market dynamics, order book imbalance offers clearer signals, while institutional traders benefit from iceberg orders for executing large trades discreetly.
Connection
Order book imbalance indicates the difference between buy and sell orders at various price levels, revealing market pressure and potential price movements. Iceberg orders, which hide the full size of large trades by splitting them into smaller visible portions, contribute to this imbalance by obscuring true liquidity on the order book. Monitoring the interplay between visible order book imbalances and hidden iceberg orders helps traders better assess market sentiment and execute strategies with reduced market impact.
Key Terms
Hidden Liquidity
Iceberg orders conceal large trade quantities by breaking them into smaller visible orders, minimizing market impact and revealing only a fraction of the total volume, contributing to hidden liquidity. Order book imbalance reflects the disparity between buy and sell orders but may not capture hidden liquidity from iceberg orders, leading to misleading signals about true market depth. Explore how understanding the interplay between iceberg orders and order book imbalance uncovers hidden liquidity and improves trading strategies.
Volume Transparency
Iceberg orders conceal large trade volumes by splitting orders into smaller visible portions, preserving volume transparency challenges in the order book. In contrast, order book imbalance reflects the real-time disparity between buy and sell volumes, offering direct insights into market pressure and potential price movements. Explore deeper into these mechanisms to understand how traders manage volume transparency and market liquidity effectively.
Market Dynamics
Iceberg orders strategically conceal large trade volumes by breaking them into smaller visible chunks, influencing order book depth and liquidity without revealing the full intent, thus impacting market dynamics and price discovery. Order book imbalance, showing the disparity between buy and sell orders, provides insights into potential short-term price movements and trader sentiment but can be distorted by hidden orders like icebergs. Explore further to understand how these elements interact and shape trading strategies in dynamic markets.
Source and External Links
Iceberg Order - Overview, How It Works, and Example - An iceberg order breaks a large buy or sell order into multiple smaller ones, revealing only a small part at a time to avoid market impact and obtain better prices, usually used by institutional traders.
Iceberg Orders - Kraken Support - Iceberg orders show only a small portion of the total order to the market at once, with the rest hidden, allowing large trades without revealing full order size and minimizing market impact.
What are Iceberg Orders? - Bookmap - Iceberg orders split large orders into smaller limit orders to hide total quantity and reduce price impact, helping large investors execute trades without causing sharp price changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com