Option selling wheel strategy involves selling cash-secured puts and covered calls to generate consistent income while potentially acquiring stocks at a discount. Protective put strategy focuses on purchasing puts to hedge against downside risk in an existing stock position, preserving capital during market downturns. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which option strategy aligns with your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between option selling wheel and protective put strategies is crucial for managing risk and maximizing returns in trading. The option selling wheel involves selling cash-secured puts and covered calls to generate consistent income, while a protective put provides downside protection by purchasing put options on owned stocks. Traders can better align their strategies with market conditions and investment goals by distinguishing these approaches. Proper knowledge mitigates potential losses and enhances portfolio performance through tailored risk management.
Comparison Table
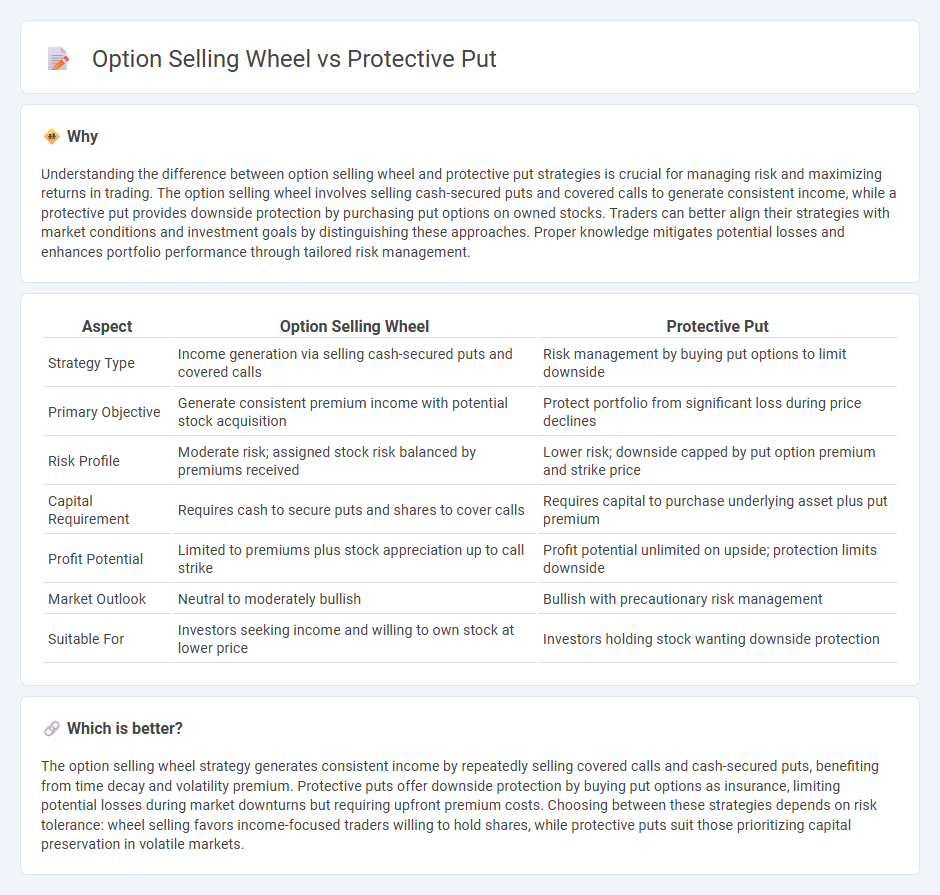
| Aspect | Option Selling Wheel | Protective Put |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy Type | Income generation via selling cash-secured puts and covered calls | Risk management by buying put options to limit downside |
| Primary Objective | Generate consistent premium income with potential stock acquisition | Protect portfolio from significant loss during price declines |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk; assigned stock risk balanced by premiums received | Lower risk; downside capped by put option premium and strike price |
| Capital Requirement | Requires cash to secure puts and shares to cover calls | Requires capital to purchase underlying asset plus put premium |
| Profit Potential | Limited to premiums plus stock appreciation up to call strike | Profit potential unlimited on upside; protection limits downside |
| Market Outlook | Neutral to moderately bullish | Bullish with precautionary risk management |
| Suitable For | Investors seeking income and willing to own stock at lower price | Investors holding stock wanting downside protection |
Which is better?
The option selling wheel strategy generates consistent income by repeatedly selling covered calls and cash-secured puts, benefiting from time decay and volatility premium. Protective puts offer downside protection by buying put options as insurance, limiting potential losses during market downturns but requiring upfront premium costs. Choosing between these strategies depends on risk tolerance: wheel selling favors income-focused traders willing to hold shares, while protective puts suit those prioritizing capital preservation in volatile markets.
Connection
Option selling wheel strategy involves selling cash-secured puts and covered calls to generate income while acquiring stock, whereas the protective put strategy uses put options to hedge against potential downside in stock holdings. Both strategies incorporate options to manage risk and enhance returns, linking the income-focused wheel approach with the downside protection of protective puts. Investors often combine aspects of these methods to balance income generation with risk mitigation in their trading portfolios.
Key Terms
Hedging
Protective puts offer a direct hedging strategy by allowing investors to limit downside risk through buying put options, providing insurance against price drops in the underlying asset. Option selling wheel, involving selling cash-secured puts and covered calls, generates income and manages risk but exposes investors to potential downside if the stock declines significantly. Explore the nuances of these hedging techniques to optimize your portfolio protection and income strategies.
Premium income
Protective puts offer downside protection by allowing investors to hedge positions at the cost of paying premiums, which can reduce overall income but limit losses. The option selling wheel strategy maximizes premium income through repeated selling of options, prioritizing consistent cash flow while accepting higher risk exposure. Explore deeper insights into balancing risk and reward with these strategies for premium income optimization.
Assignment
Protective puts involve buying a put option to hedge against potential downside risk in a stock position, minimizing losses if the stock price declines. Option selling wheel strategies focus on generating income through repeated selling of puts and calls, but carry a higher risk of stock assignment, which requires careful management. To understand how assignment impacts these strategies and optimize your risk-reward balance, explore more detailed insights.
Source and External Links
Protective Put - Definition, Example, Scenarios - A protective put is an options strategy combining a long stock position with a purchased put option to limit downside risk while retaining upside potential, effectively acting as insurance against stock price drops.
Protective Put Strategy: Definition, How It Works & Examples - This strategy allows investors to safeguard their stock investments by buying a put option as a form of insurance, ensuring they can sell shares at the put's strike price if the stock price declines, while still benefiting if the stock appreciates.
Protective Put (Married Put) - The protective put sets a floor price for a stock, limiting downside risk during temporary price dips without sacrificing upside gains, and is used by bullish investors concerned about short-term declines or needing to insure the stock value for specific timeframes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com