Funding rate arbitrage exploits discrepancies between perpetual futures funding rates and spot prices for risk-free profit, capitalizing on rate imbalances in crypto markets. Basis trading involves capturing the spread between futures contracts and underlying asset prices, leveraging predictable convergence at contract maturity to generate returns. Explore more to understand how these strategies optimize trading performance.
Why it is important
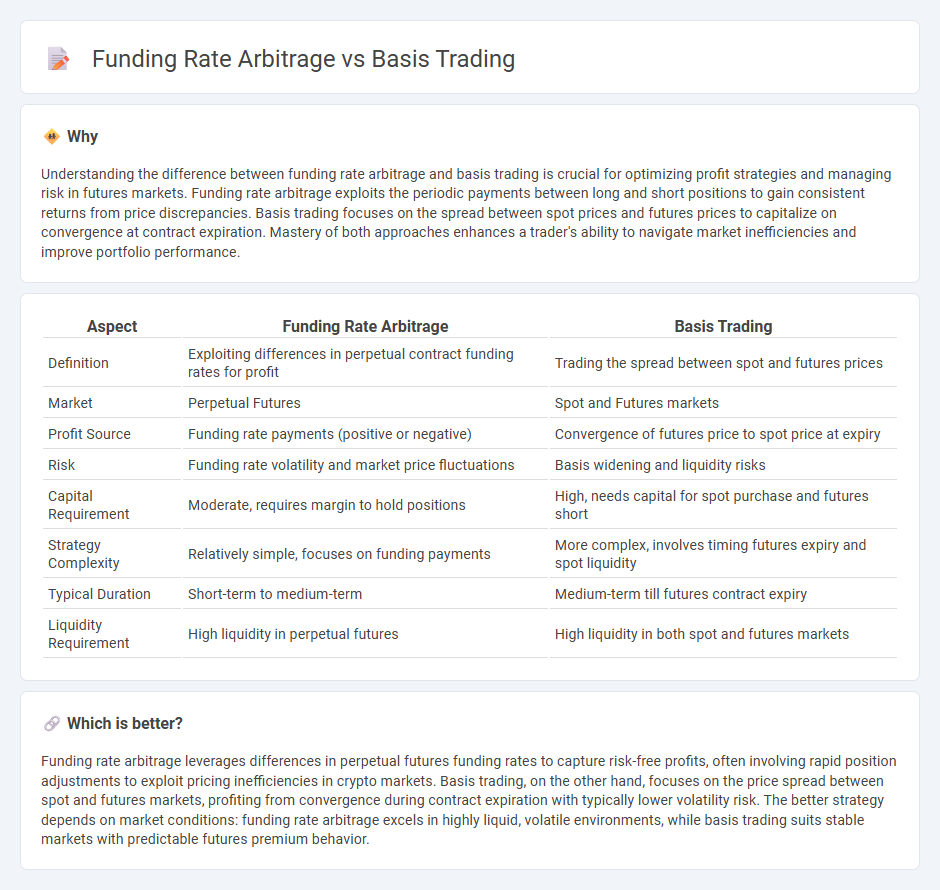
Understanding the difference between funding rate arbitrage and basis trading is crucial for optimizing profit strategies and managing risk in futures markets. Funding rate arbitrage exploits the periodic payments between long and short positions to gain consistent returns from price discrepancies. Basis trading focuses on the spread between spot prices and futures prices to capitalize on convergence at contract expiration. Mastery of both approaches enhances a trader's ability to navigate market inefficiencies and improve portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Funding Rate Arbitrage | Basis Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting differences in perpetual contract funding rates for profit | Trading the spread between spot and futures prices |
| Market | Perpetual Futures | Spot and Futures markets |
| Profit Source | Funding rate payments (positive or negative) | Convergence of futures price to spot price at expiry |
| Risk | Funding rate volatility and market price fluctuations | Basis widening and liquidity risks |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate, requires margin to hold positions | High, needs capital for spot purchase and futures short |
| Strategy Complexity | Relatively simple, focuses on funding payments | More complex, involves timing futures expiry and spot liquidity |
| Typical Duration | Short-term to medium-term | Medium-term till futures contract expiry |
| Liquidity Requirement | High liquidity in perpetual futures | High liquidity in both spot and futures markets |
Which is better?
Funding rate arbitrage leverages differences in perpetual futures funding rates to capture risk-free profits, often involving rapid position adjustments to exploit pricing inefficiencies in crypto markets. Basis trading, on the other hand, focuses on the price spread between spot and futures markets, profiting from convergence during contract expiration with typically lower volatility risk. The better strategy depends on market conditions: funding rate arbitrage excels in highly liquid, volatile environments, while basis trading suits stable markets with predictable futures premium behavior.
Connection
Funding rate arbitrage exploits differences in perpetual futures funding payments, while basis trading focuses on the price spread between spot and futures markets. Both strategies rely on price inefficiencies in cryptocurrency derivatives to generate risk-adjusted returns. By simultaneously managing spot and futures positions, traders capitalize on mispricings influenced by funding rates and basis deviations.
Key Terms
Spot-Futures Price Difference
Basis trading exploits the price difference between spot and futures markets to generate profits by buying the undervalued asset and selling the overvalued counterpart, capitalizing on the convergence at contract maturity. Funding rate arbitrage involves capturing gains from periodic funding payments between perpetual futures and spot markets, typically by holding opposing positions to benefit from positive or negative rates. Explore detailed strategies and market conditions that influence these techniques to master spot-futures price difference trading.
Funding Payments
Basis trading involves exploiting the price difference between a futures contract and the underlying asset, while funding rate arbitrage targets the periodic payments exchanged between long and short positions in perpetual swaps. Funding payments are critical in funding rate arbitrage as traders capitalize on discrepancies to earn risk-free profits by simultaneously holding opposite positions in spot and derivatives markets. Explore deeper strategies and risk factors behind funding payments in cryptocurrency markets to enhance your arbitrage tactics.
Convergence
Basis trading exploits the price difference between a futures contract and its underlying spot asset, aiming for convergence as the contract approaches maturity, where the futures price aligns with the spot price. Funding rate arbitrage involves profiting from periodic payments between longs and shorts in perpetual futures, relying on the funding rate to offset position costs while maintaining market neutrality. Explore detailed strategies and risk factors to master convergence in derivatives trading.
Source and External Links
Basis trading - Wikipedia - Basis trading is a financial strategy that involves taking opposite positions in a spot asset and a related derivative, typically a futures contract, to profit from price convergence over time, with the price difference called the basis (spot price minus futures price) and is used in various asset classes including commodities, fixed income, and equities.
Basis Trading - Overview, How It Works, Leverage - Basis trading is an arbitrage strategy where traders exploit mispricing between a financial instrument and its derivative by holding long and short positions, often using leverage, to profit from the basis while managing risks.
What is Basis Trading and How Does it Affect the Treasury Bond Market? - In the treasury market, basis trading refers to buying Treasury bonds and simultaneously selling related futures contracts to profit from the price differential between the bonds and futures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com