Volatility harvesting involves exploiting price fluctuations to generate consistent returns by rebalancing a diversified portfolio, while carry trade seeks profit from interest rate differentials between currencies or assets. This strategy taps into market inefficiencies for steady gains, contrasting with carry trade's reliance on borrowing low-yield assets to invest in higher-yield ones. Explore further to understand how these strategies can optimize your trading performance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between volatility harvesting and carry trade is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risk effectively. Volatility harvesting capitalizes on market fluctuations to generate returns through rebalancing, while carry trade involves profiting from interest rate differentials between currencies. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders select appropriate instruments and timing to maximize gains. Proper knowledge minimizes exposure to adverse market conditions and enhances portfolio stability.
Comparison Table
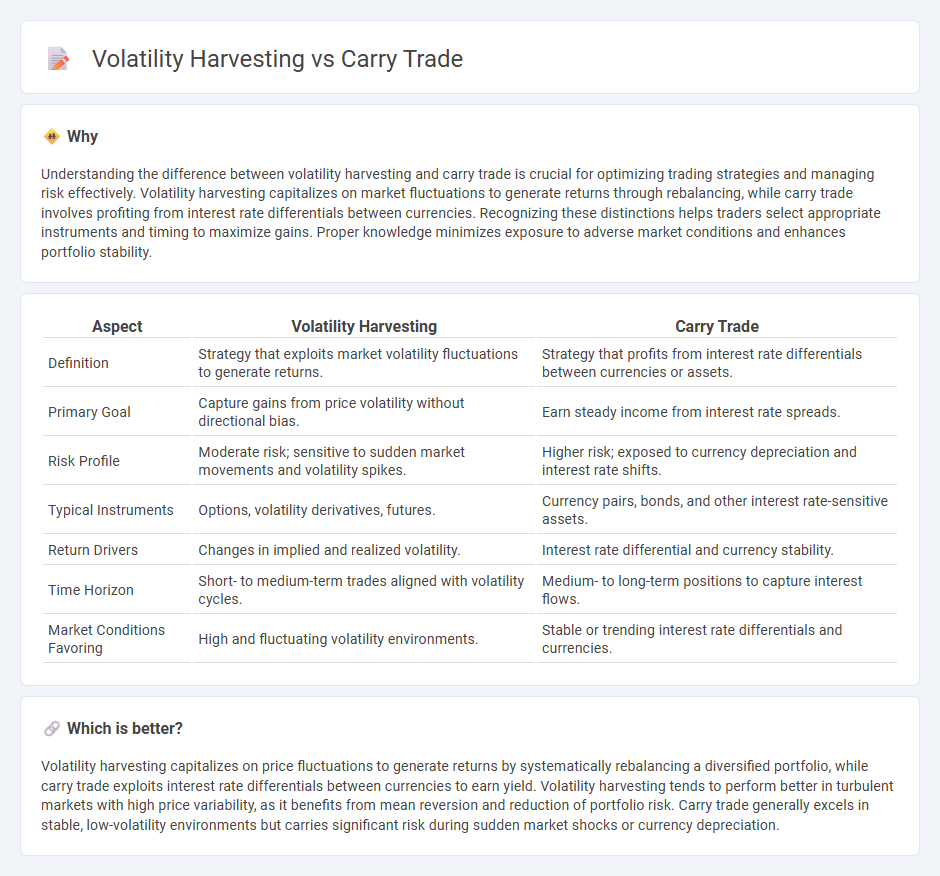
| Aspect | Volatility Harvesting | Carry Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy that exploits market volatility fluctuations to generate returns. | Strategy that profits from interest rate differentials between currencies or assets. |
| Primary Goal | Capture gains from price volatility without directional bias. | Earn steady income from interest rate spreads. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk; sensitive to sudden market movements and volatility spikes. | Higher risk; exposed to currency depreciation and interest rate shifts. |
| Typical Instruments | Options, volatility derivatives, futures. | Currency pairs, bonds, and other interest rate-sensitive assets. |
| Return Drivers | Changes in implied and realized volatility. | Interest rate differential and currency stability. |
| Time Horizon | Short- to medium-term trades aligned with volatility cycles. | Medium- to long-term positions to capture interest flows. |
| Market Conditions Favoring | High and fluctuating volatility environments. | Stable or trending interest rate differentials and currencies. |
Which is better?
Volatility harvesting capitalizes on price fluctuations to generate returns by systematically rebalancing a diversified portfolio, while carry trade exploits interest rate differentials between currencies to earn yield. Volatility harvesting tends to perform better in turbulent markets with high price variability, as it benefits from mean reversion and reduction of portfolio risk. Carry trade generally excels in stable, low-volatility environments but carries significant risk during sudden market shocks or currency depreciation.
Connection
Volatility harvesting and carry trade are connected through their exploitation of market fluctuations and interest rate differentials to generate profits. Volatility harvesting capitalizes on frequent price oscillations by systematically rebalancing portfolios, while carry trade benefits from borrowing in low-interest currencies to invest in higher-yield assets. Both strategies rely on market dynamics and risk management techniques to optimize returns in varying financial environments.
Key Terms
Interest Rate Differential
Interest rate differential drives carry trade by exploiting higher-yielding currencies against lower-yielding counterparts to generate consistent returns. Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations and rebalancing strategies to capture gains from price variability rather than relying solely on interest rates. Explore how these strategies uniquely harness interest rate differentials and market dynamics to optimize investment outcomes.
Currency Risk
Carry trade exploits interest rate differentials between currencies to generate returns, exposing investors to significant currency risk due to potential exchange rate fluctuations. Volatility harvesting leverages currency volatility to enhance portfolio returns by strategically rebalancing positions, effectively managing currency risk through systematic adjustments. Explore the detailed mechanisms and risk management strategies of carry trade and volatility harvesting to optimize currency investment outcomes.
Mean Reversion
Carry trade strategies capitalize on interest rate differentials between currencies, generating steady returns that tend to revert to the mean over time due to economic cycles and monetary policy adjustments. Volatility harvesting exploits fluctuations in asset price volatility by rebalancing portfolios, capturing gains during periods of mean-reverting variance in market volatility. Discover how integrating mean reversion principles can enhance risk-adjusted returns in both carry trade and volatility harvesting approaches.
Source and External Links
What is a carry trade? - A carry trade is an investment strategy where an investor borrows money in a currency with a low interest rate and invests in another currency (or asset) offering a higher interest rate to profit from the interest differential, though it carries significant risk if exchange rates move unfavorably.
Carry (investment) - The carry of an asset is the return from holding it (if positive) or the cost of holding it (if negative); a carry trade involves earning the spread between borrowing a low-carry asset and lending a high-carry one, but unlike arbitrage, it only profits if market conditions do not change against the trade.
The Currency Carry Trade: Is It Still Viable? - The currency carry trade is profitable as long as the extra interest earned on the high-yield currency is not offset by its depreciation, and while theory suggests markets should nullify this profit, empirical evidence has shown the strategy can be consistently profitable over time.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com