Penny jump and price improvement are key concepts in trading that influence order execution quality and market efficiency. Penny jump refers to the minimum price increment required to outbid an existing order, affecting bid-ask spreads and liquidity. Explore how understanding these mechanisms can optimize trading strategies and enhance execution outcomes.
Why it is important
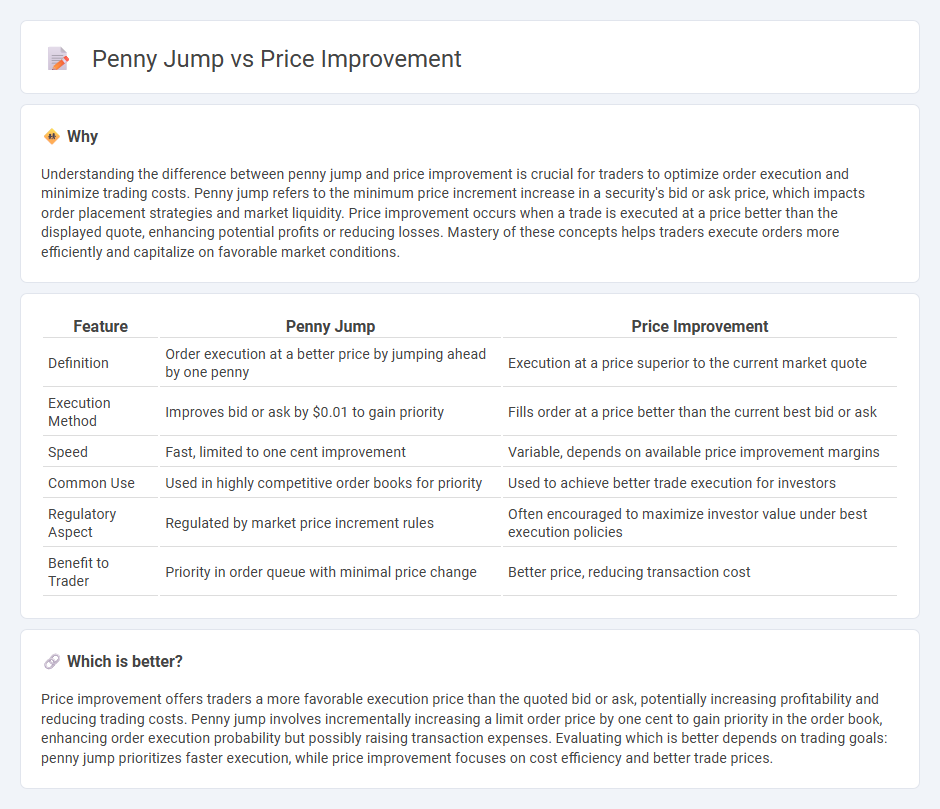
Understanding the difference between penny jump and price improvement is crucial for traders to optimize order execution and minimize trading costs. Penny jump refers to the minimum price increment increase in a security's bid or ask price, which impacts order placement strategies and market liquidity. Price improvement occurs when a trade is executed at a price better than the displayed quote, enhancing potential profits or reducing losses. Mastery of these concepts helps traders execute orders more efficiently and capitalize on favorable market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Penny Jump | Price Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Order execution at a better price by jumping ahead by one penny | Execution at a price superior to the current market quote |
| Execution Method | Improves bid or ask by $0.01 to gain priority | Fills order at a price better than the current best bid or ask |
| Speed | Fast, limited to one cent improvement | Variable, depends on available price improvement margins |
| Common Use | Used in highly competitive order books for priority | Used to achieve better trade execution for investors |
| Regulatory Aspect | Regulated by market price increment rules | Often encouraged to maximize investor value under best execution policies |
| Benefit to Trader | Priority in order queue with minimal price change | Better price, reducing transaction cost |
Which is better?
Price improvement offers traders a more favorable execution price than the quoted bid or ask, potentially increasing profitability and reducing trading costs. Penny jump involves incrementally increasing a limit order price by one cent to gain priority in the order book, enhancing order execution probability but possibly raising transaction expenses. Evaluating which is better depends on trading goals: penny jump prioritizes faster execution, while price improvement focuses on cost efficiency and better trade prices.
Connection
Penny jump occurs when the price of a security increases by one cent, influencing the bid-ask spread and liquidity in trading markets. Price improvement refers to executing trades at prices better than the current quote, often triggered by small price increments like penny jumps. These micro movements enable traders to secure better execution prices, enhancing overall market efficiency and reducing trading costs.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
Price improvement occurs when a trade is executed at a better price than the best bid or ask, narrowing the bid-ask spread and benefiting traders with reduced transaction costs. Penny jump refers to stepping the bid or ask price by a minimum increment, typically one cent, to position a limit order ahead of others within the spread, impacting market liquidity and order priority. Explore in-depth analysis on how price improvement and penny jumps influence bid-ask spread dynamics and trading strategies.
Order Execution
Price improvement occurs when an order is executed at a better price than the best available quote, enhancing trading efficiency and minimizing transaction costs. Penny jump refers to increasing the bid or ask price by one cent to gain priority in order execution, often impacting queue positioning in the order book. Explore the nuances of order execution strategies to optimize trade outcomes and reduce market impact.
Liquidity
Price improvement occurs when an order is executed at a better price than the current best bid or offer, enhancing market liquidity by tightening spreads and increasing trade efficiency. Penny jump, a tactic where traders step ahead by one cent, can fragment liquidity and widen spreads, often disadvantaging resting orders. Explore the impact of these strategies on market depth and order execution quality to optimize trading outcomes.
Source and External Links
Understanding Price Improvement | Charles Schwab - Price improvement occurs when orders execute at better prices than the National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO), resulting in savings per share; for example, buying shares slightly cheaper than the current best quoted price.
Price improvement, tick harmonization & investor benefit - NYSE - Price improvement means getting a better-than-expected trade price, and harmonizing tick sizes across markets could increase investor cost savings by enabling more frequent sub-penny improvements.
Cboe U.S. Equities Exchanges Retail Price Improvement - The Cboe Retail Price Improvement Program allows certain orders to gain price improvements in increments as small as $0.001, with retail orders commonly receiving an average of $0.86 per 100 shares in price improvement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com