Quantitative signals utilize mathematical models and statistical techniques to analyze market data patterns, enabling traders to make data-driven decisions based on empirical evidence. Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's intrinsic value by examining financial statements, economic indicators, and industry conditions, providing insights into long-term investment potential. Explore more to understand how combining both approaches can enhance trading strategies and optimize portfolio performance.
Why it is important
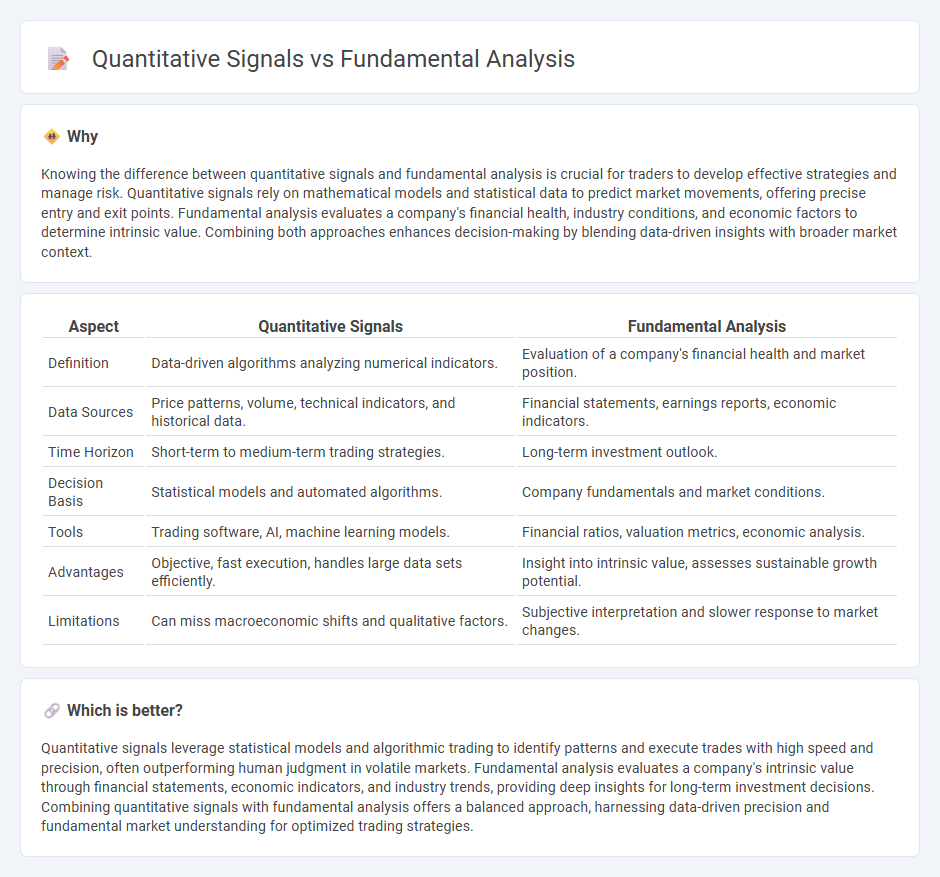
Knowing the difference between quantitative signals and fundamental analysis is crucial for traders to develop effective strategies and manage risk. Quantitative signals rely on mathematical models and statistical data to predict market movements, offering precise entry and exit points. Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's financial health, industry conditions, and economic factors to determine intrinsic value. Combining both approaches enhances decision-making by blending data-driven insights with broader market context.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Signals | Fundamental Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data-driven algorithms analyzing numerical indicators. | Evaluation of a company's financial health and market position. |
| Data Sources | Price patterns, volume, technical indicators, and historical data. | Financial statements, earnings reports, economic indicators. |
| Time Horizon | Short-term to medium-term trading strategies. | Long-term investment outlook. |
| Decision Basis | Statistical models and automated algorithms. | Company fundamentals and market conditions. |
| Tools | Trading software, AI, machine learning models. | Financial ratios, valuation metrics, economic analysis. |
| Advantages | Objective, fast execution, handles large data sets efficiently. | Insight into intrinsic value, assesses sustainable growth potential. |
| Limitations | Can miss macroeconomic shifts and qualitative factors. | Subjective interpretation and slower response to market changes. |
Which is better?
Quantitative signals leverage statistical models and algorithmic trading to identify patterns and execute trades with high speed and precision, often outperforming human judgment in volatile markets. Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's intrinsic value through financial statements, economic indicators, and industry trends, providing deep insights for long-term investment decisions. Combining quantitative signals with fundamental analysis offers a balanced approach, harnessing data-driven precision and fundamental market understanding for optimized trading strategies.
Connection
Quantitative signals use mathematical models and statistical techniques to identify trading opportunities, while fundamental analysis evaluates a company's financial health, market position, and economic factors. Integrating quantitative signals with fundamental analysis enhances decision-making by combining data-driven patterns with intrinsic value assessments. This hybrid approach improves the accuracy of forecasts and helps investors manage risk more effectively.
Key Terms
**Fundamental Analysis:**
Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's intrinsic value by examining financial statements, management quality, industry position, and economic factors, providing a comprehensive view beyond mere price movements. It involves assessing earnings, revenue growth, profit margins, and debt levels to determine long-term investment potential. Explore more to understand how fundamental analysis guides strategic investment decisions.
Earnings Reports
Earnings reports are crucial in fundamental analysis, providing insights into a company's financial health through revenue, net income, and earnings per share metrics. Quantitative signals utilize these financial data points to generate algorithm-driven investment decisions, emphasizing statistical patterns and market trends. Explore how combining both approaches can enhance your investment strategy.
Balance Sheet
Fundamental analysis emphasizes the evaluation of a company's balance sheet to assess financial health by examining key components such as assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. Quantitative signals utilize statistical models and algorithms to analyze balance sheet metrics, identifying patterns and trends that inform investment decisions. Explore in-depth methodologies and practical applications to enhance your understanding of balance sheet analysis in financial markets.
Source and External Links
Fundamental Analysis - Corporate Finance Institute - Fundamental analysis evaluates the intrinsic value of a security by examining macroeconomic and microeconomic factors, using financial statements and economic data to guide investment decisions by comparing intrinsic value with market price.
What is fundamental analysis? How to assess value in trading | Saxo - Fundamental analysis determines an asset's intrinsic value by examining its core fundamentals and ignoring market sentiment and price movements, helping traders identify overvalued or undervalued assets.
Fundamental analysis - Wikipedia - This method analyzes economic conditions, industry trends, and company financials to find the intrinsic true value of a stock, which guides buying, holding, or selling decisions based on whether the market price deviates from this value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com