Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing fees by relying on smart contracts. Cross-chain bridges facilitate asset transfers across different blockchain networks by locking tokens on the source chain and minting equivalents on the target chain, promoting interoperability. Discover how these innovative technologies transform decentralized trading and asset management.
Why it is important
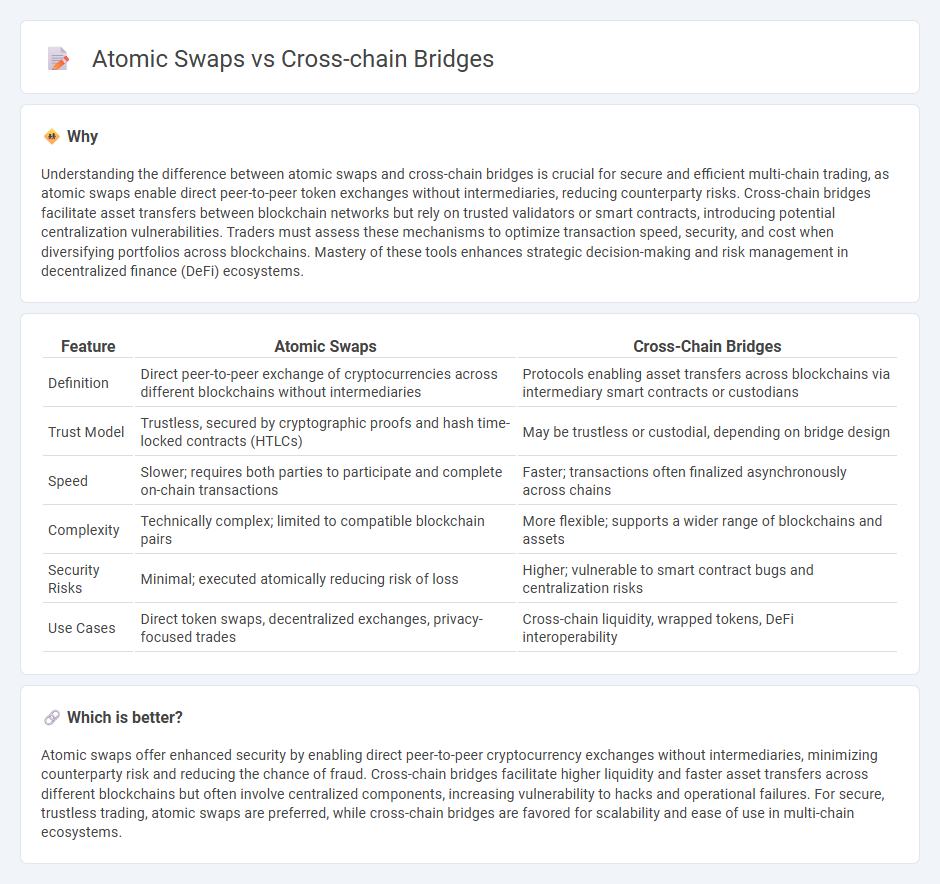
Understanding the difference between atomic swaps and cross-chain bridges is crucial for secure and efficient multi-chain trading, as atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer token exchanges without intermediaries, reducing counterparty risks. Cross-chain bridges facilitate asset transfers between blockchain networks but rely on trusted validators or smart contracts, introducing potential centralization vulnerabilities. Traders must assess these mechanisms to optimize transaction speed, security, and cost when diversifying portfolios across blockchains. Mastery of these tools enhances strategic decision-making and risk management in decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Atomic Swaps | Cross-Chain Bridges |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct peer-to-peer exchange of cryptocurrencies across different blockchains without intermediaries | Protocols enabling asset transfers across blockchains via intermediary smart contracts or custodians |
| Trust Model | Trustless, secured by cryptographic proofs and hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs) | May be trustless or custodial, depending on bridge design |
| Speed | Slower; requires both parties to participate and complete on-chain transactions | Faster; transactions often finalized asynchronously across chains |
| Complexity | Technically complex; limited to compatible blockchain pairs | More flexible; supports a wider range of blockchains and assets |
| Security Risks | Minimal; executed atomically reducing risk of loss | Higher; vulnerable to smart contract bugs and centralization risks |
| Use Cases | Direct token swaps, decentralized exchanges, privacy-focused trades | Cross-chain liquidity, wrapped tokens, DeFi interoperability |
Which is better?
Atomic swaps offer enhanced security by enabling direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, minimizing counterparty risk and reducing the chance of fraud. Cross-chain bridges facilitate higher liquidity and faster asset transfers across different blockchains but often involve centralized components, increasing vulnerability to hacks and operational failures. For secure, trustless trading, atomic swaps are preferred, while cross-chain bridges are favored for scalability and ease of use in multi-chain ecosystems.
Connection
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency transactions across different blockchains without intermediaries, ensuring trustless asset exchanges. Cross-chain bridges facilitate interoperability by allowing assets and data to move seamlessly between distinct blockchain networks, often leveraging atomic swap technology for secure swaps. Both mechanisms enhance liquidity and trading efficiency by enabling decentralized exchanges across multiple blockchain platforms.
Key Terms
Interoperability
Cross-chain bridges facilitate interoperability by enabling direct asset transfers across different blockchain networks, creating seamless connectivity and liquidity between ecosystems. Atomic swaps ensure interoperability through trustless peer-to-peer exchanges, eliminating intermediaries and reducing counterparty risks across chains. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand which method best suits your cross-chain interoperability needs.
Trustlessness
Cross-chain bridges enable asset transfers between different blockchains by relying on intermediary smart contracts or validators, which may introduce varying degrees of trust depending on bridge design. Atomic swaps facilitate direct peer-to-peer exchanges of cryptocurrencies across chains without intermediaries, ensuring true trustlessness by leveraging cryptographic protocols like hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs). Explore further to understand how trustless mechanisms impact decentralized finance and cross-chain interoperability.
Liquidity
Cross-chain bridges facilitate liquidity by allowing direct token transfers across different blockchain networks, enabling seamless asset movement and liquidity pooling. Atomic swaps, while enabling trustless peer-to-peer token exchanges without intermediaries, have limited liquidity impact due to their one-to-one transaction nature and slower execution times. Discover the detailed mechanisms and liquidity comparisons between these two technologies for optimized cross-chain asset management.
Source and External Links
What Is A Cross Chain Bridge? | Chainlink - A cross-chain bridge is a decentralized application enabling asset transfers between blockchains using mechanisms like lock-and-mint, burn-and-mint, or lock-and-unlock, and can facilitate complex cross-chain transactions including token swaps and staking.
Introduction to Cross-Chain Bridges - Chainalysis - Cross-chain bridges enhance blockchain interoperability by securely sharing assets and data across multiple chains, expanding DeFi opportunities, enabling multi-chain DApps, and providing users with more flexibility in blockchain choice.
6 best cross-chain bridges in 2023 - TechTarget - Cross-chain bridges allow exchange of information, cryptocurrencies, or NFTs between blockchains using wrapped tokens or liquidity pools to facilitate movement of value across otherwise siloed blockchain networks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com