Order book imbalance measures the difference between buy and sell orders, serving as a key indicator of market sentiment and potential price movement. Price impact refers to the effect that executing large trades has on the asset's market price, often influenced by the current order book structure. Explore the intricate relationship between order book imbalance and price impact to enhance trading strategies and market analysis.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between order book imbalance and price impact is crucial for traders to optimize trade execution and minimize market slippage. Order book imbalance reflects the real-time supply and demand levels by comparing buy and sell orders at various price points. Price impact measures the effect of a trade on the asset's price, indicating potential shifts due to trade volume relative to market liquidity. Accurate interpretation of both metrics enables traders to anticipate market movements and implement strategic order placements.
Comparison Table
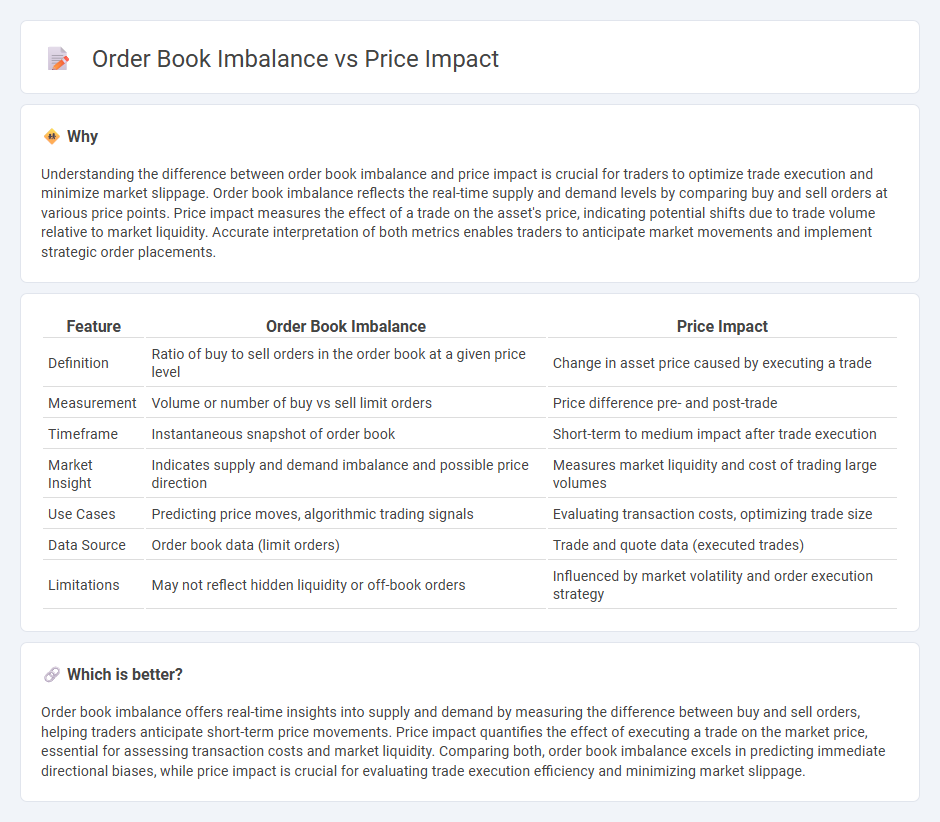
| Feature | Order Book Imbalance | Price Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of buy to sell orders in the order book at a given price level | Change in asset price caused by executing a trade |
| Measurement | Volume or number of buy vs sell limit orders | Price difference pre- and post-trade |
| Timeframe | Instantaneous snapshot of order book | Short-term to medium impact after trade execution |
| Market Insight | Indicates supply and demand imbalance and possible price direction | Measures market liquidity and cost of trading large volumes |
| Use Cases | Predicting price moves, algorithmic trading signals | Evaluating transaction costs, optimizing trade size |
| Data Source | Order book data (limit orders) | Trade and quote data (executed trades) |
| Limitations | May not reflect hidden liquidity or off-book orders | Influenced by market volatility and order execution strategy |
Which is better?
Order book imbalance offers real-time insights into supply and demand by measuring the difference between buy and sell orders, helping traders anticipate short-term price movements. Price impact quantifies the effect of executing a trade on the market price, essential for assessing transaction costs and market liquidity. Comparing both, order book imbalance excels in predicting immediate directional biases, while price impact is crucial for evaluating trade execution efficiency and minimizing market slippage.
Connection
Order book imbalance, reflecting the disparity between buy and sell orders at various price levels, directly influences price impact by signaling potential shifts in supply and demand dynamics. A higher buy order volume relative to sell orders typically leads to upward price pressure, causing more significant price impact when executing trades. Traders use order book imbalance data to anticipate price movements and optimize order execution strategies to minimize adverse price impact.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Price impact reflects the change in an asset's price resulting from a trade, directly linked to liquidity levels present in the order book. Order book imbalance measures the difference between buy and sell orders, indicating potential price movements influenced by liquidity depth and distribution. Explore detailed analyses on how liquidity shapes price impact and order book dynamics.
Bid-Ask Spread
Price impact measures how executing large trades shifts asset prices, influenced by order book imbalance reflecting the difference between bid and ask volumes. A narrow bid-ask spread typically signals high liquidity and low price impact, while a wider spread indicates potential price volatility due to supply-demand disparity. Explore the intricate relationship between price impact, order book imbalance, and bid-ask spread dynamics to optimize trading strategies.
Market Depth
Price impact measures how a trade affects asset price, directly linked to market depth reflected in the order book imbalance--the difference between buy and sell orders at various price levels. Higher market depth, indicated by a balanced order book, typically reduces price impact by absorbing large trades with minimal price fluctuation. Explore deeper insights on how market depth dynamics influence price impact and trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Understanding price impact and slippage - Price impact is the effect a trade has on the market price of an asset, measuring the price change caused by the trade, influenced by factors such as liquidity, order book depth, and order size, with larger trades causing more significant price changes.
What is price impact? - Price impact occurs when a large order consumes available liquidity at multiple price levels, pushing the market price against the trader and resulting in fewer tokens received, especially in low-liquidity or volatile markets.
Price Impact Definition - Price impact describes how an incoming trade changes the asset's price by exhausting available orders in the order book, with price movement extent depending on trading pair liquidity, and it is a critical factor for traders on less liquid markets or with large trades.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com