Dark pool activity involves private, non-public trading venues where large institutional investors execute trades anonymously to minimize market impact and avoid revealing their intentions. Pre-market trading occurs on electronic exchanges before the regular market hours, allowing investors to react to overnight news and adjust positions early. Explore the differences between these trading environments to enhance your market strategy.
Why it is important
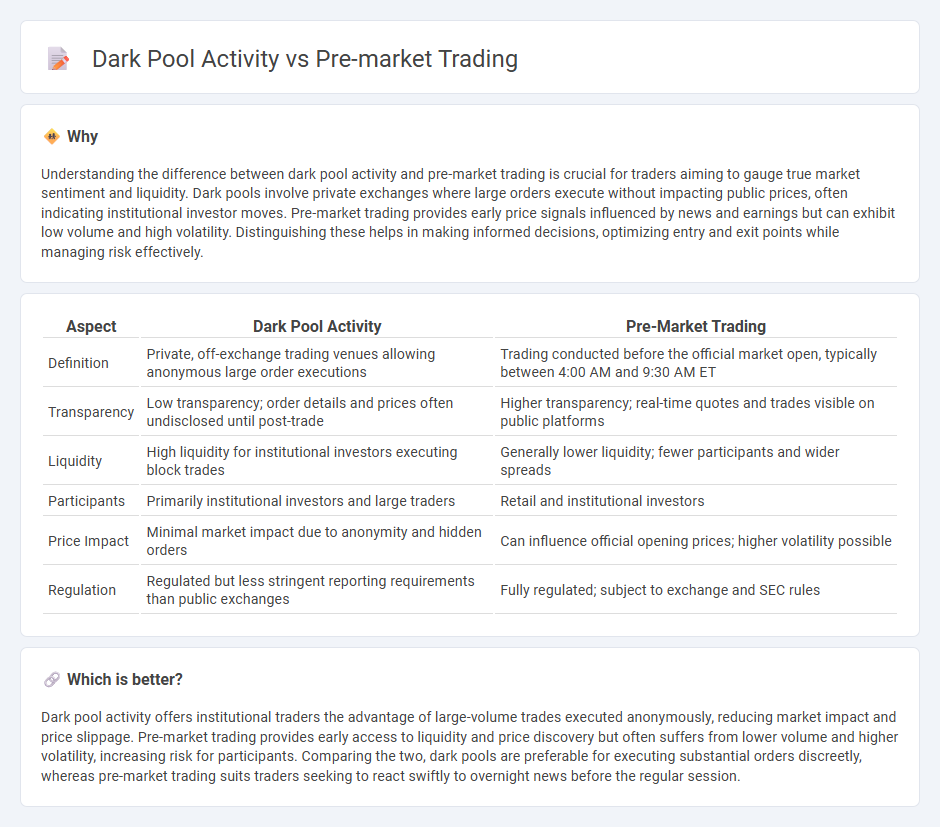
Understanding the difference between dark pool activity and pre-market trading is crucial for traders aiming to gauge true market sentiment and liquidity. Dark pools involve private exchanges where large orders execute without impacting public prices, often indicating institutional investor moves. Pre-market trading provides early price signals influenced by news and earnings but can exhibit low volume and high volatility. Distinguishing these helps in making informed decisions, optimizing entry and exit points while managing risk effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pool Activity | Pre-Market Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private, off-exchange trading venues allowing anonymous large order executions | Trading conducted before the official market open, typically between 4:00 AM and 9:30 AM ET |
| Transparency | Low transparency; order details and prices often undisclosed until post-trade | Higher transparency; real-time quotes and trades visible on public platforms |
| Liquidity | High liquidity for institutional investors executing block trades | Generally lower liquidity; fewer participants and wider spreads |
| Participants | Primarily institutional investors and large traders | Retail and institutional investors |
| Price Impact | Minimal market impact due to anonymity and hidden orders | Can influence official opening prices; higher volatility possible |
| Regulation | Regulated but less stringent reporting requirements than public exchanges | Fully regulated; subject to exchange and SEC rules |
Which is better?
Dark pool activity offers institutional traders the advantage of large-volume trades executed anonymously, reducing market impact and price slippage. Pre-market trading provides early access to liquidity and price discovery but often suffers from lower volume and higher volatility, increasing risk for participants. Comparing the two, dark pools are preferable for executing substantial orders discreetly, whereas pre-market trading suits traders seeking to react swiftly to overnight news before the regular session.
Connection
Dark pool activity and pre-market trading are interconnected through their roles in providing liquidity and facilitating large order executions outside regular market hours. Dark pools enable institutional investors to trade significant volumes anonymously, often influencing price discovery before the official market open. Pre-market trading reflects this activity, as price movements and volume changes in these sessions frequently stem from dark pool transactions processed overnight.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Pre-market trading provides early liquidity and price discovery before regular market hours, often reflecting institutional investor sentiment and news impact. Dark pool activity involves large, non-public trades executed to minimize market impact and maintain confidentiality, contributing significantly to overall market liquidity but with less transparency. Explore detailed analyses of liquidity dynamics in pre-market and dark pool environments to enhance your trading strategies.
Transparency
Pre-market trading offers greater transparency by operating on regulated exchanges where prices and volumes are publicly available, unlike dark pool activity which occurs in private venues with limited disclosure to reduce market impact and prevent front-running. Dark pools enable large institutional investors to execute sizable trades anonymously, minimizing the risk of price slippage but sacrificing transparency for market participants. Explore the nuances of pre-market trading and dark pool dynamics to better understand their roles in market efficiency and investor protection.
Order Execution
Pre-market trading and dark pool activity distinctly impact order execution dynamics; pre-market trading provides price discovery and liquidity outside regular hours, while dark pools enable large block trades with reduced market impact and anonymity. Order execution in pre-market may face higher volatility and lower volume, whereas dark pool transactions prioritize confidentiality and minimal market signaling. Explore detailed strategies to optimize order execution across these trading environments.
Source and External Links
Pre-market Trading: What is It and How to Trade? | IG International - Pre-market trading is the process of buying and selling stocks before the regular market hours begin, typically starting as early as 4am ET in the US, allowing traders to react to overnight news with lower liquidity and more constraints than during normal hours.
Understanding Pre-Market and After-Hours Trading - TD Bank - Pre-market trading in the US usually occurs between 8 am and 9:20 am ET on weekdays and allows investors to trade outside regular hours, but with less volume, limited liquidity, and potentially higher volatility.
Pre-Market Stock Quote Data - Nasdaq - Nasdaq pre-market trading runs from 4:00 to 9:30 a.m. ET with voluntary participation by market makers and ECNs, often resulting in lower liquidity and faster price changes, so investors are advised to use limit orders during this session.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com