Dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from multiple private trading venues, offering traders enhanced anonymity and reduced market impact compared to traditional exchanges. ECNs facilitate real-time electronic order matching among market participants, promoting transparency and immediate trade execution across public markets. Explore the advantages and use cases of dark pool aggregation versus ECN trading to optimize your market strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark pool aggregation and ECN (Electronic Communication Network) trading is crucial for optimizing trade execution and minimizing market impact. Dark pools allow large orders to be executed privately, reducing price slippage and revealing less information to the market. ECNs offer transparent order matching and real-time pricing, beneficial for retail traders and high-frequency trading strategies. Knowing when to use each platform enhances liquidity access and trading efficiency, ultimately improving portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
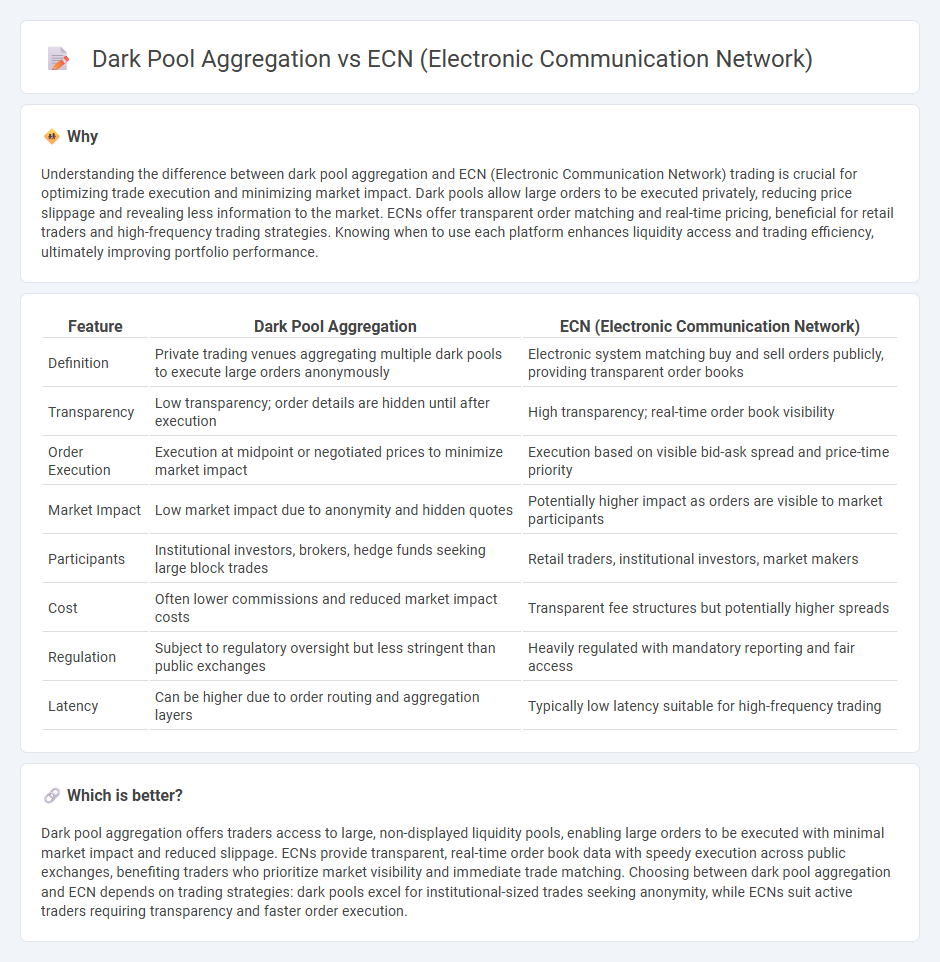
| Feature | Dark Pool Aggregation | ECN (Electronic Communication Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private trading venues aggregating multiple dark pools to execute large orders anonymously | Electronic system matching buy and sell orders publicly, providing transparent order books |
| Transparency | Low transparency; order details are hidden until after execution | High transparency; real-time order book visibility |
| Order Execution | Execution at midpoint or negotiated prices to minimize market impact | Execution based on visible bid-ask spread and price-time priority |
| Market Impact | Low market impact due to anonymity and hidden quotes | Potentially higher impact as orders are visible to market participants |
| Participants | Institutional investors, brokers, hedge funds seeking large block trades | Retail traders, institutional investors, market makers |
| Cost | Often lower commissions and reduced market impact costs | Transparent fee structures but potentially higher spreads |
| Regulation | Subject to regulatory oversight but less stringent than public exchanges | Heavily regulated with mandatory reporting and fair access |
| Latency | Can be higher due to order routing and aggregation layers | Typically low latency suitable for high-frequency trading |
Which is better?
Dark pool aggregation offers traders access to large, non-displayed liquidity pools, enabling large orders to be executed with minimal market impact and reduced slippage. ECNs provide transparent, real-time order book data with speedy execution across public exchanges, benefiting traders who prioritize market visibility and immediate trade matching. Choosing between dark pool aggregation and ECN depends on trading strategies: dark pools excel for institutional-sized trades seeking anonymity, while ECNs suit active traders requiring transparency and faster order execution.
Connection
Dark pool aggregation and Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) are connected through their role in enhancing market liquidity by pooling and matching large, anonymous orders away from public exchanges. ECNs facilitate transparent electronic trading by connecting multiple market participants, while dark pool aggregators consolidate orders from various dark pools to optimize execution prices and reduce market impact. This integration allows traders to access a broader pool of liquidity, improve trade execution quality, and minimize information leakage in high-frequency and institutional trading strategies.
Key Terms
Order Routing
ECNs provide transparent electronic order books that match buyer and seller orders in real-time, while dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from multiple private trading venues to minimize market impact during order execution. Order routing strategies leverage ECNs for visible price discovery but rely on dark pool aggregation to access hidden liquidity pools for large block trades. Explore advanced order routing techniques to optimize trade execution across ECNs and dark pools.
Liquidity Access
ECNs provide transparent, real-time access to multiple market participants, enhancing liquidity discovery through visible order books, whereas dark pool aggregation consolidates hidden liquidity sources to minimize market impact and reduce price slippage. While ECNs offer price improvement and immediate execution by matching public bids and offers, dark pools enable large institutional trades to execute discreetly without exposing orders to the wider market. Explore how the choice between ECN and dark pool aggregation impacts trading strategies and liquidity efficiency.
Trade Transparency
Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) offer real-time trade transparency by displaying order books openly, facilitating price discovery and efficient market access. In contrast, dark pool aggregations execute large blocks of trades anonymously, prioritizing reduced market impact but limiting visibility into price formation. Explore how transparency differences influence trading strategies and market fairness in modern financial markets.
Source and External Links
Electronic communication network - An ECN is a computerized forum that facilitates trading of financial products by matching buy and sell orders electronically without traditional exchanges, typically charging small fees and increasing market competition by offering order matching outside regular exchange hours.
What is an electronic communication network (ECN)? - An ECN is an alternative trading system enabling automated and direct trading between buyers and sellers, often quote-driven, settling trades directly between counterparties rather than via central clearing, widely used in OTC and FX markets.
What is An Electronic Communication Network (ECN)? - ECNs are electronic platforms that allow traders to transact directly with each other anonymously and transparently, automatically matching buy and sell orders in a decentralized manner without intermediaries like brokers or market makers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com