Tape reading focuses on analyzing real-time order flow and price movement to make short-term trading decisions, leveraging Level 2 market data and time and sales information. Position trading relies on longer-term chart patterns, fundamental analysis, and trend identification to hold trades over days, weeks, or months. Explore the key differences and strategies behind tape reading and position trading to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
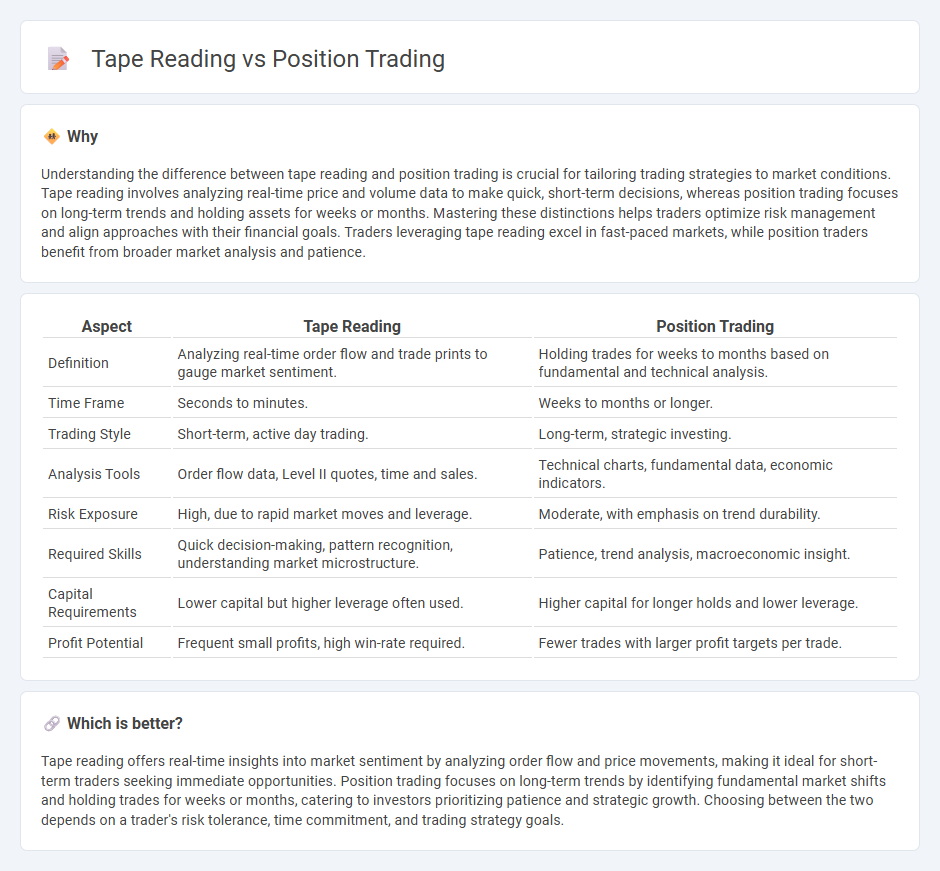
Understanding the difference between tape reading and position trading is crucial for tailoring trading strategies to market conditions. Tape reading involves analyzing real-time price and volume data to make quick, short-term decisions, whereas position trading focuses on long-term trends and holding assets for weeks or months. Mastering these distinctions helps traders optimize risk management and align approaches with their financial goals. Traders leveraging tape reading excel in fast-paced markets, while position traders benefit from broader market analysis and patience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tape Reading | Position Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzing real-time order flow and trade prints to gauge market sentiment. | Holding trades for weeks to months based on fundamental and technical analysis. |
| Time Frame | Seconds to minutes. | Weeks to months or longer. |
| Trading Style | Short-term, active day trading. | Long-term, strategic investing. |
| Analysis Tools | Order flow data, Level II quotes, time and sales. | Technical charts, fundamental data, economic indicators. |
| Risk Exposure | High, due to rapid market moves and leverage. | Moderate, with emphasis on trend durability. |
| Required Skills | Quick decision-making, pattern recognition, understanding market microstructure. | Patience, trend analysis, macroeconomic insight. |
| Capital Requirements | Lower capital but higher leverage often used. | Higher capital for longer holds and lower leverage. |
| Profit Potential | Frequent small profits, high win-rate required. | Fewer trades with larger profit targets per trade. |
Which is better?
Tape reading offers real-time insights into market sentiment by analyzing order flow and price movements, making it ideal for short-term traders seeking immediate opportunities. Position trading focuses on long-term trends by identifying fundamental market shifts and holding trades for weeks or months, catering to investors prioritizing patience and strategic growth. Choosing between the two depends on a trader's risk tolerance, time commitment, and trading strategy goals.
Connection
Tape reading provides real-time market data by analyzing the time and sales ticker, helping position traders identify entry and exit points based on order flow and volume patterns. Position trading relies on long-term market trends, using insights from tape reading to confirm momentum and validate trade setups. This combination enhances decision-making by blending short-term market sentiment with longer-term strategic positioning.
Key Terms
**Position Trading:**
Position trading involves holding securities for extended periods, ranging from weeks to months, to capitalize on major market trends and fundamental analysis. This strategy relies heavily on technical indicators and economic data to identify optimal entry and exit points, minimizing reaction to short-term market fluctuations. Explore deeper insights on how position trading can enhance long-term portfolio growth.
Trend Analysis
Position trading relies heavily on long-term trend analysis, using moving averages and macroeconomic indicators to identify sustained market directions. Tape reading focuses on real-time order flow and volume patterns to gauge short-term momentum and price action shifts. Explore detailed strategies to master both methods and enhance trading precision.
Holding Period
Position trading involves holding assets for weeks to months, capitalizing on long-term market trends, while tape reading focuses on short-term price movements by analyzing real-time order flow and volume. This fundamental difference in holding period dictates distinct strategies: position trading relies on macroeconomic factors and technical indicators, whereas tape reading depends on immediate market sentiment and liquidity dynamics. Explore the nuances of these approaches to enhance your trading strategy and align it with your time horizon preferences.
Source and External Links
A guide to position trading: definition, examples and ... - Position trading is a style that seeks to identify and benefit from ongoing trends, holding positions typically over weeks to months, using strategies such as trend trading, breakout trading, and pullback trading focused on riding the larger market movements rather than short-term fluctuations.
Position Trading 101: A Beginner's Guide With Examples - Position trading is a medium- to long-term active trading strategy where traders hold positions from weeks to months to ride market trends, aiming for substantial profits by timing entries and exits better than simple buy-and-hold investing, including both long and short positions.
Position Trading Strategy: How To Use It - Position trading involves holding securities for months or even years to capture larger price moves, differing from day or swing trading by its longer timeframe, reduced trading frequency, and potential for lower transaction costs while allowing speculation on market downturns via short selling.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com