Flash loan arbitrage leverages uncollateralized loans to exploit price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges within a single transaction, enabling instantaneous profit without initial capital. Market making involves continuously providing buy and sell orders to enhance liquidity and capture the bid-ask spread over time, relying on strategic order placement and risk management. Explore the core differences and optimal strategies in flash loan arbitrage versus market making to maximize trading efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loan arbitrage and market making is essential for traders to optimize strategy profitability and risk management effectively. Flash loan arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges rapidly using uncollateralized loans, requiring advanced technical expertise and timing precision. Market making involves providing continuous liquidity by simultaneously placing buy and sell orders to earn the bid-ask spread, demanding deep market knowledge and capital commitment. Differentiating these methods enables traders to select approaches aligned with their risk tolerance, capital availability, and market conditions.
Comparison Table
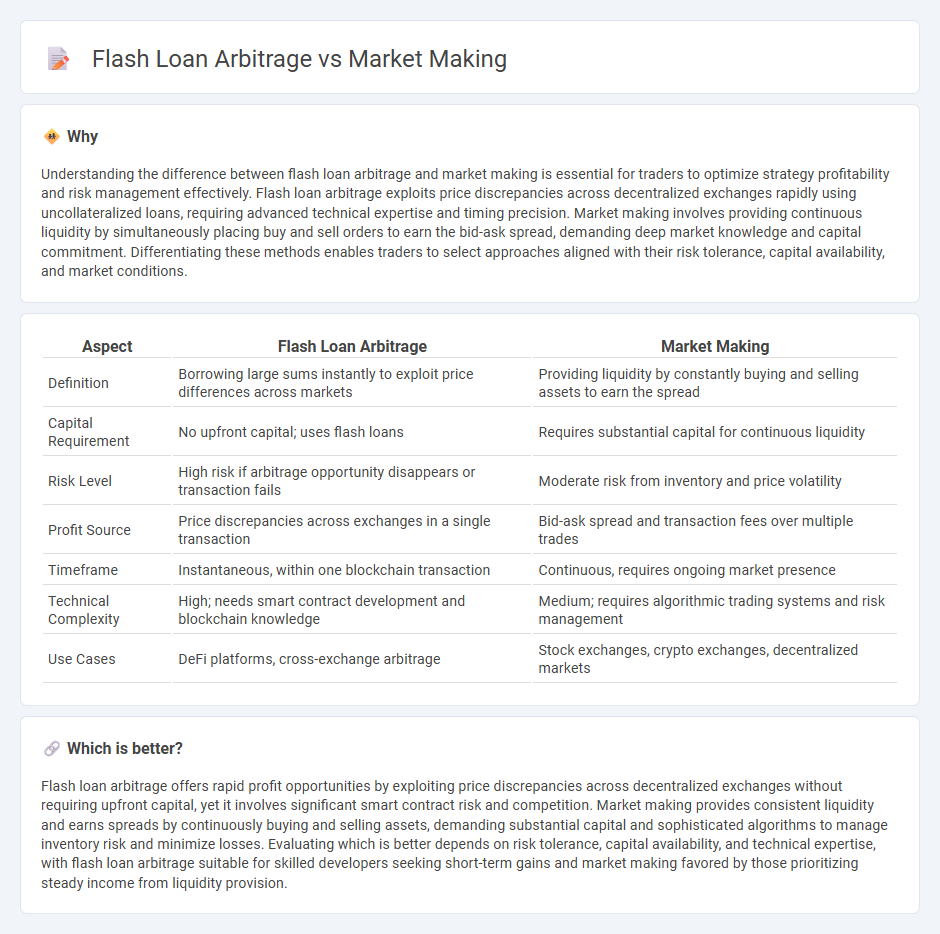
| Aspect | Flash Loan Arbitrage | Market Making |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Borrowing large sums instantly to exploit price differences across markets | Providing liquidity by constantly buying and selling assets to earn the spread |
| Capital Requirement | No upfront capital; uses flash loans | Requires substantial capital for continuous liquidity |
| Risk Level | High risk if arbitrage opportunity disappears or transaction fails | Moderate risk from inventory and price volatility |
| Profit Source | Price discrepancies across exchanges in a single transaction | Bid-ask spread and transaction fees over multiple trades |
| Timeframe | Instantaneous, within one blockchain transaction | Continuous, requires ongoing market presence |
| Technical Complexity | High; needs smart contract development and blockchain knowledge | Medium; requires algorithmic trading systems and risk management |
| Use Cases | DeFi platforms, cross-exchange arbitrage | Stock exchanges, crypto exchanges, decentralized markets |
Which is better?
Flash loan arbitrage offers rapid profit opportunities by exploiting price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges without requiring upfront capital, yet it involves significant smart contract risk and competition. Market making provides consistent liquidity and earns spreads by continuously buying and selling assets, demanding substantial capital and sophisticated algorithms to manage inventory risk and minimize losses. Evaluating which is better depends on risk tolerance, capital availability, and technical expertise, with flash loan arbitrage suitable for skilled developers seeking short-term gains and market making favored by those prioritizing steady income from liquidity provision.
Connection
Flash loan arbitrage leverages instant, uncollateralized loans to exploit price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges, enabling quick profit without upfront capital. Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously placing buy and sell orders to capture bid-ask spreads, stabilizing market prices. Both strategies rely on exploiting short-term price inefficiencies and require advanced algorithmic execution to maximize returns in volatile trading environments.
Key Terms
**Market Making:**
Market making involves continuously providing buy and sell orders on decentralized exchanges to maintain liquidity and capture the bid-ask spread as profit. This strategy relies on deep order book analysis, real-time price monitoring, and efficient risk management to ensure consistent returns. Explore more about market making techniques and how they compare with flash loan arbitrage strategies.
Bid-Ask Spread
Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread as traders buy and sell assets. Flash loan arbitrage exploits temporary price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges, often using borrowed funds without collateral to execute near-instantaneous trades. Explore the detailed mechanisms and strategies of market making and flash loan arbitrage to maximize liquidity provision and arbitrage opportunities.
Liquidity Provision
Market making provides continuous liquidity by placing buy and sell orders to facilitate smoother trading and tighter spreads on exchanges. Flash loan arbitrage leverages temporary, uncollateralized loans to exploit price discrepancies across markets without maintaining ongoing liquidity positions. Explore the nuances of liquidity provision in both strategies to optimize your trading approach.
Source and External Links
Mastering the Market Maker Trading Strategy | EPAM SolutionsHub - Market makers profit by providing liquidity through buying at the bid price and selling at the ask price, managing inventory risk, and analyzing order flow to anticipate market movements while adhering to regulations.
Market Making and Mean Reversion - CIS UPenn - A market maker is an entity that continuously quotes buy and sell prices to profit from the spread while providing liquidity and avoiding large net positions in the instrument traded.
Market Maker - Definition, Role, How They Work - Market makers are firms or individuals that offer simultaneous bids and asks, earning profits from the bid-ask spread and taking on inventory risks to maintain market liquidity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com