Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing transaction fees. Synthetic assets replicate the value of real-world assets through smart contracts, offering broad market exposure without owning the underlying asset. Explore the nuances of atomic swaps versus synthetic assets to optimize your trading strategies.
Why it is important
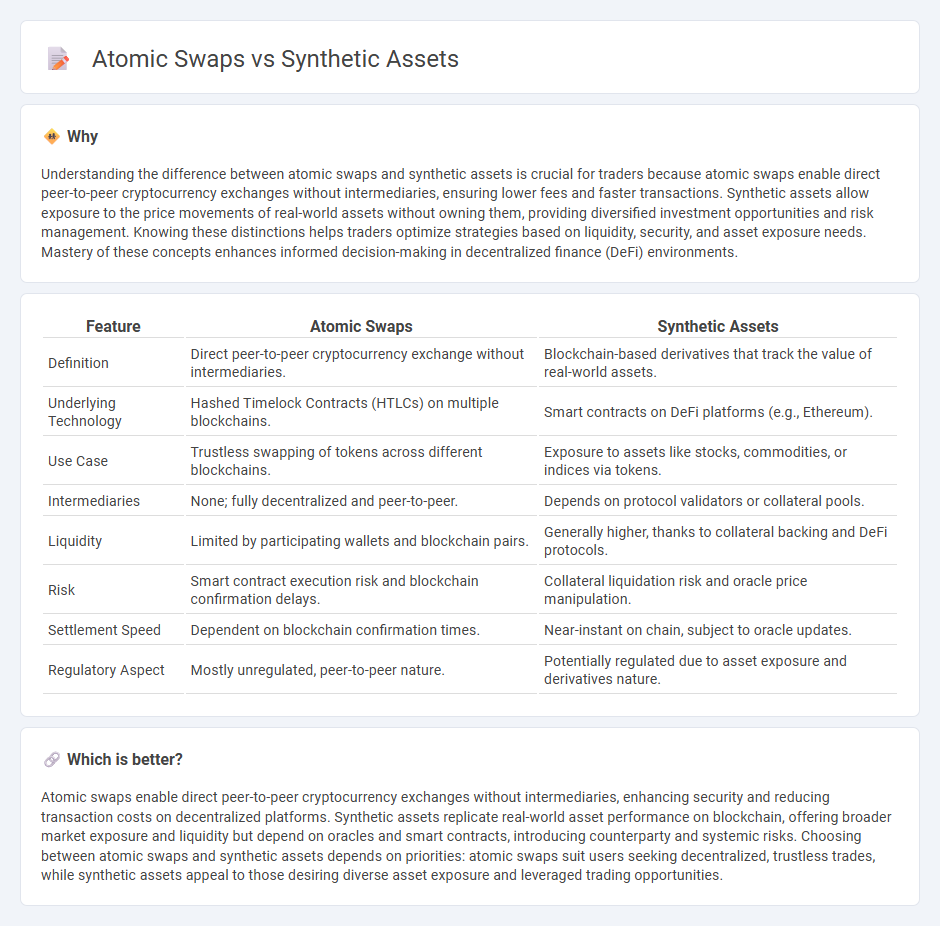
Understanding the difference between atomic swaps and synthetic assets is crucial for traders because atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, ensuring lower fees and faster transactions. Synthetic assets allow exposure to the price movements of real-world assets without owning them, providing diversified investment opportunities and risk management. Knowing these distinctions helps traders optimize strategies based on liquidity, security, and asset exposure needs. Mastery of these concepts enhances informed decision-making in decentralized finance (DeFi) environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Atomic Swaps | Synthetic Assets |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchange without intermediaries. | Blockchain-based derivatives that track the value of real-world assets. |
| Underlying Technology | Hashed Timelock Contracts (HTLCs) on multiple blockchains. | Smart contracts on DeFi platforms (e.g., Ethereum). |
| Use Case | Trustless swapping of tokens across different blockchains. | Exposure to assets like stocks, commodities, or indices via tokens. |
| Intermediaries | None; fully decentralized and peer-to-peer. | Depends on protocol validators or collateral pools. |
| Liquidity | Limited by participating wallets and blockchain pairs. | Generally higher, thanks to collateral backing and DeFi protocols. |
| Risk | Smart contract execution risk and blockchain confirmation delays. | Collateral liquidation risk and oracle price manipulation. |
| Settlement Speed | Dependent on blockchain confirmation times. | Near-instant on chain, subject to oracle updates. |
| Regulatory Aspect | Mostly unregulated, peer-to-peer nature. | Potentially regulated due to asset exposure and derivatives nature. |
Which is better?
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing transaction costs on decentralized platforms. Synthetic assets replicate real-world asset performance on blockchain, offering broader market exposure and liquidity but depend on oracles and smart contracts, introducing counterparty and systemic risks. Choosing between atomic swaps and synthetic assets depends on priorities: atomic swaps suit users seeking decentralized, trustless trades, while synthetic assets appeal to those desiring diverse asset exposure and leveraged trading opportunities.
Connection
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, facilitating seamless cross-chain asset transfers essential for synthetic asset trading. Synthetic assets replicate the value of real-world assets on blockchain networks, relying on atomic swaps to maintain liquidity and diversify trading pairs across different blockchains. This connection enhances decentralized finance by allowing users to efficiently trade a broad range of tokenized assets while reducing counterparty risk and transaction costs.
Key Terms
Derivatives
Synthetic assets replicate the value of traditional financial instruments using blockchain technology, enabling exposure to derivatives without owning the underlying asset. Atomic swaps facilitate direct, trustless exchange of cryptocurrencies across different blockchains, streamlining derivative trading without intermediaries. Explore the intricacies of synthetic assets and atomic swaps to deepen your understanding of decentralized derivatives.
Cross-chain
Synthetic assets enable exposure to cross-chain tokens without directly holding the underlying assets, facilitating seamless trading and liquidity across multiple blockchain networks through tokenized derivatives. Atomic swaps offer trustless, peer-to-peer exchange of cryptocurrencies across different chains by utilizing smart contracts that execute simultaneous transactions, minimizing counterparty risk. Explore the technical intricacies and real-world applications of synthetic assets versus atomic swaps in cross-chain ecosystems to understand their impact on decentralized finance.
Interoperability
Synthetic assets enable seamless interoperability by representing real-world assets on blockchain platforms, allowing users to trade derivatives without needing the underlying asset. Atomic swaps facilitate direct peer-to-peer exchange of different cryptocurrencies across distinct blockchains without intermediaries, promoting cross-chain interoperability at the protocol level. Explore deeper insights into how these technologies enhance decentralized finance and cross-chain interactions.
Source and External Links
Unlocking Crypto Synthetic Assets: Explained - LCX - Synthetic assets are blockchain-based financial instruments designed to mimic the value and behavior of real-world assets like stocks, commodities, or currencies, created mainly through smart contracts on DeFi platforms without owning the underlying asset.
Crypto synthetic assets, explained - Cointelegraph - Synthetic assets are digital instruments on blockchain that replicate the performance of traditional assets, enabling investors to access diverse markets without intermediaries but requiring careful understanding due to their complexity and risks.
Synthetic Asset Definition - CoinMarketCap - Synthetic assets, or "synths," are tokenized derivatives on blockchain that allow trading and investment exposure to assets without owning them, offering enhanced security and traceability compared to traditional derivatives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com