Trading in modular blockchains leverages specialized layers for scalability, customization, and interoperability, enabling efficient decentralized transactions and asset exchanges. Exchange-traded funds (crypto ETFs) offer investors exposure to a diversified portfolio of cryptocurrencies within traditional market frameworks, combining regulatory oversight with ease of access. Explore how these innovative trading methods shape the future of digital asset investment and portfolio management.
Why it is important
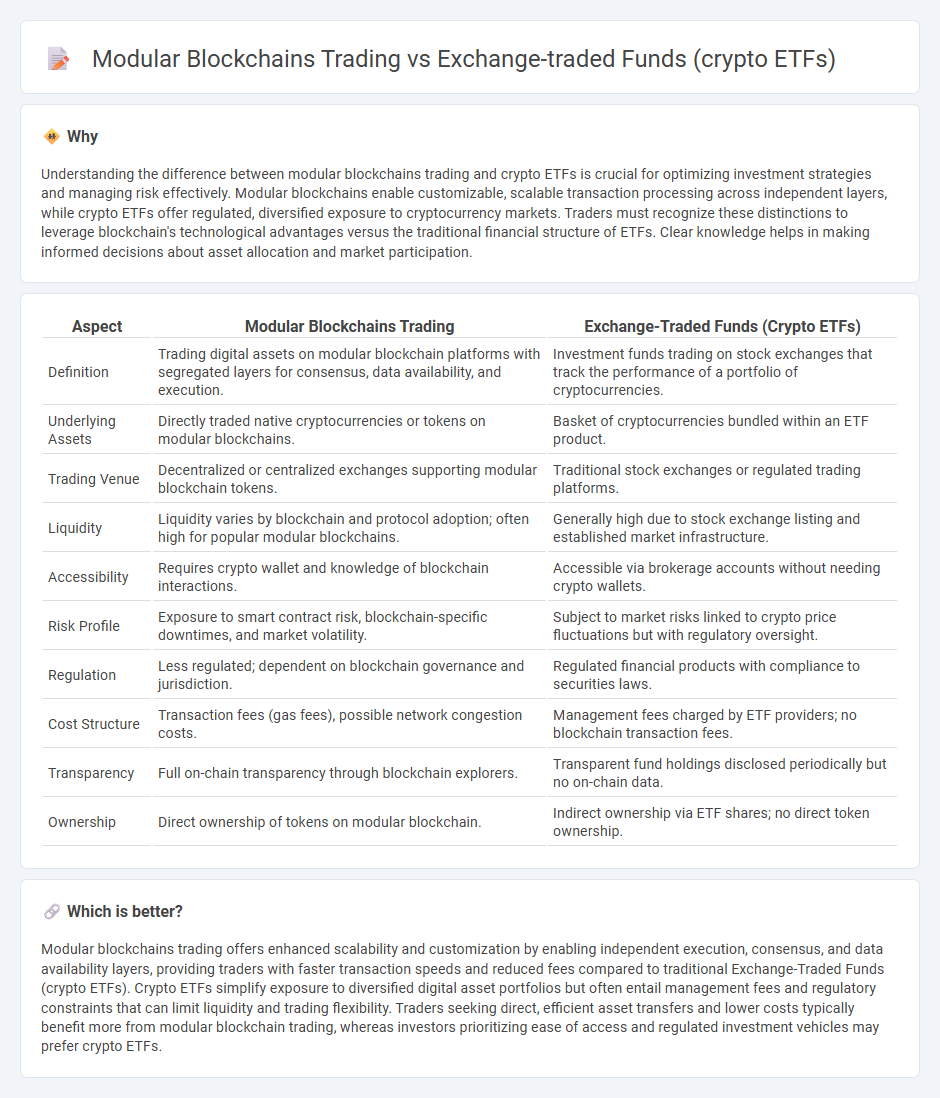
Understanding the difference between modular blockchains trading and crypto ETFs is crucial for optimizing investment strategies and managing risk effectively. Modular blockchains enable customizable, scalable transaction processing across independent layers, while crypto ETFs offer regulated, diversified exposure to cryptocurrency markets. Traders must recognize these distinctions to leverage blockchain's technological advantages versus the traditional financial structure of ETFs. Clear knowledge helps in making informed decisions about asset allocation and market participation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Modular Blockchains Trading | Exchange-Traded Funds (Crypto ETFs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading digital assets on modular blockchain platforms with segregated layers for consensus, data availability, and execution. | Investment funds trading on stock exchanges that track the performance of a portfolio of cryptocurrencies. |
| Underlying Assets | Directly traded native cryptocurrencies or tokens on modular blockchains. | Basket of cryptocurrencies bundled within an ETF product. |
| Trading Venue | Decentralized or centralized exchanges supporting modular blockchain tokens. | Traditional stock exchanges or regulated trading platforms. |
| Liquidity | Liquidity varies by blockchain and protocol adoption; often high for popular modular blockchains. | Generally high due to stock exchange listing and established market infrastructure. |
| Accessibility | Requires crypto wallet and knowledge of blockchain interactions. | Accessible via brokerage accounts without needing crypto wallets. |
| Risk Profile | Exposure to smart contract risk, blockchain-specific downtimes, and market volatility. | Subject to market risks linked to crypto price fluctuations but with regulatory oversight. |
| Regulation | Less regulated; dependent on blockchain governance and jurisdiction. | Regulated financial products with compliance to securities laws. |
| Cost Structure | Transaction fees (gas fees), possible network congestion costs. | Management fees charged by ETF providers; no blockchain transaction fees. |
| Transparency | Full on-chain transparency through blockchain explorers. | Transparent fund holdings disclosed periodically but no on-chain data. |
| Ownership | Direct ownership of tokens on modular blockchain. | Indirect ownership via ETF shares; no direct token ownership. |
Which is better?
Modular blockchains trading offers enhanced scalability and customization by enabling independent execution, consensus, and data availability layers, providing traders with faster transaction speeds and reduced fees compared to traditional Exchange-Traded Funds (crypto ETFs). Crypto ETFs simplify exposure to diversified digital asset portfolios but often entail management fees and regulatory constraints that can limit liquidity and trading flexibility. Traders seeking direct, efficient asset transfers and lower costs typically benefit more from modular blockchain trading, whereas investors prioritizing ease of access and regulated investment vehicles may prefer crypto ETFs.
Connection
Modular blockchains enhance trading efficiency by enabling specialized layers that handle transaction processing, consensus, and data availability separately, thus optimizing blockchain scalability and speed for crypto assets. Exchange-traded funds (crypto ETFs) leverage this improved infrastructure to offer diversified exposure to digital assets with increased liquidity and reduced volatility. Integrating modular blockchain technology supports more transparent and secure ETF operations, facilitating broader adoption and seamless trading across decentralized and traditional financial platforms.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Crypto ETFs offer high liquidity through established exchanges, enabling effortless buying and selling of diversified crypto assets without managing individual tokens. Modular blockchains trading allows for targeted liquidity within specific layers, optimizing transaction speed and scalability by separating consensus, execution, and data availability. Explore how liquidity dynamics differ between these investment models to enhance your trading strategy.
Custody
Crypto ETFs simplify asset management by offering regulated access to a diversified portfolio of digital currencies, reducing the complexity of custody through third-party institutions. Modular blockchains trading enhances custody by segregating transaction execution, settlement, and consensus layers, providing increased security and customization for digital asset storage. Explore the differences in custody solutions to optimize your digital investment strategy.
Interoperability
Crypto ETFs provide investors diversified exposure to multiple cryptocurrency assets without direct blockchain interaction, optimizing risk through traditional market mechanisms. Modular blockchain trading enhances interoperability by separating consensus, execution, and data availability, enabling seamless asset transfers and decentralized finance growth across chains. Explore how interoperability breakthroughs in modular blockchains can transform crypto trading beyond ETF structures.
Source and External Links
A comprehensive guide to crypto ETFs - Saxo Bank - Crypto ETFs are exchange-traded funds that provide investors with direct exposure to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin by tracking their market price without the need to manage digital wallets, offering a bridge between traditional ETFs and the crypto market.
What Is a Crypto ETF? Everything to Know - Crypto ETFs allow investors to buy shares that track cryptocurrencies, providing accessibility, diversification, and liquidity benefits, while also carrying risks such as tracking errors, regulatory changes, and market volatility.
What is a Bitcoin Futures ETF? | CFTC - Bitcoin futures ETFs give investors exposure to the price movements of bitcoin futures contracts rather than the spot price of bitcoin itself, involving complexities like roll premiums and potential discrepancies between futures and spot prices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com