Grid trading systematically places buy and sell orders at preset intervals around a fixed price, capitalizing on market volatility to generate profits through repetitive trades. Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued stocks based on fundamental analysis, holding them long-term until their intrinsic value is realized. Explore the differences between grid trading and value investing to determine the strategy best suited to your financial goals.
Why it is important
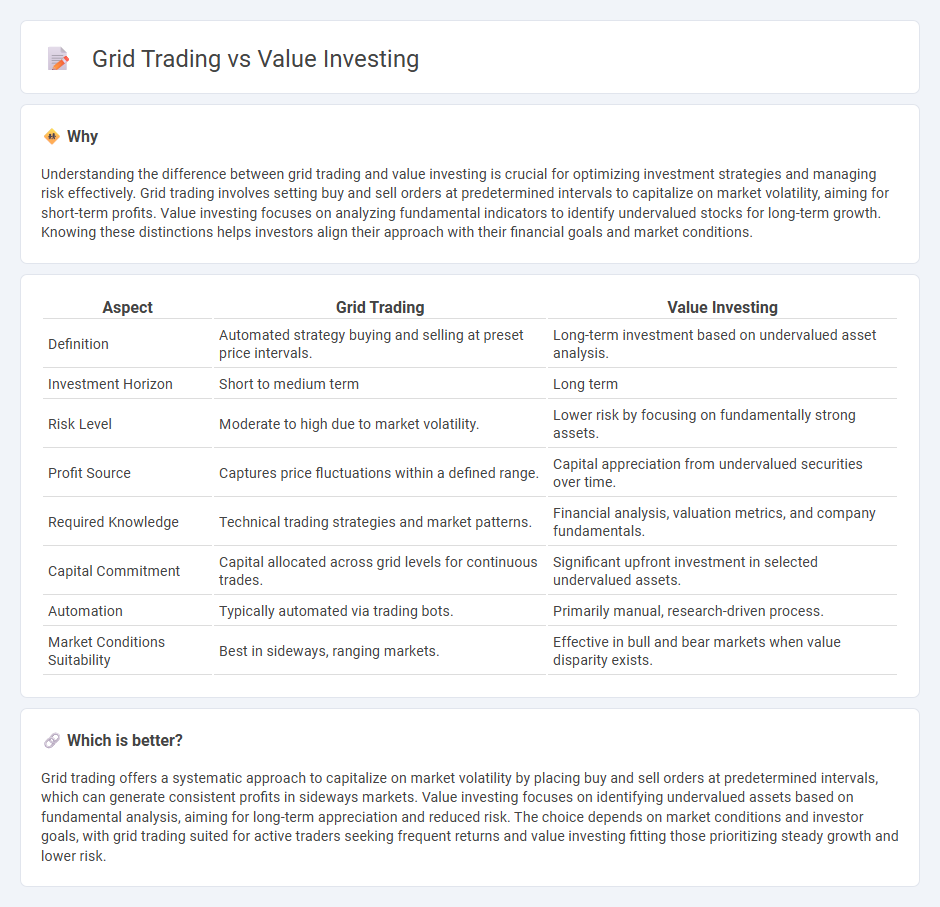
Understanding the difference between grid trading and value investing is crucial for optimizing investment strategies and managing risk effectively. Grid trading involves setting buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals to capitalize on market volatility, aiming for short-term profits. Value investing focuses on analyzing fundamental indicators to identify undervalued stocks for long-term growth. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their approach with their financial goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grid Trading | Value Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated strategy buying and selling at preset price intervals. | Long-term investment based on undervalued asset analysis. |
| Investment Horizon | Short to medium term | Long term |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high due to market volatility. | Lower risk by focusing on fundamentally strong assets. |
| Profit Source | Captures price fluctuations within a defined range. | Capital appreciation from undervalued securities over time. |
| Required Knowledge | Technical trading strategies and market patterns. | Financial analysis, valuation metrics, and company fundamentals. |
| Capital Commitment | Capital allocated across grid levels for continuous trades. | Significant upfront investment in selected undervalued assets. |
| Automation | Typically automated via trading bots. | Primarily manual, research-driven process. |
| Market Conditions Suitability | Best in sideways, ranging markets. | Effective in bull and bear markets when value disparity exists. |
Which is better?
Grid trading offers a systematic approach to capitalize on market volatility by placing buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals, which can generate consistent profits in sideways markets. Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued assets based on fundamental analysis, aiming for long-term appreciation and reduced risk. The choice depends on market conditions and investor goals, with grid trading suited for active traders seeking frequent returns and value investing fitting those prioritizing steady growth and lower risk.
Connection
Grid trading and value investing both rely on systematic approaches to capitalize on market volatility and price discrepancies. Grid trading executes buy and sell orders at predefined intervals, capturing profits from price oscillations, while value investing identifies undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals for long-term gains. Integrating value investing principles into grid trading enhances decision-making by focusing on fundamentally sound assets, reducing risk, and improving overall portfolio performance.
Key Terms
Value Investing:
Value investing involves selecting stocks that appear undervalued based on fundamental analysis, focusing on companies with strong financial health, stable earnings, and intrinsic value below market price. It emphasizes long-term growth by investing in assets with potential for price correction and dividends rather than frequent trades. Discover more insights to master value investing strategies and portfolio management.
Intrinsic Value
Value investing centers on identifying stocks priced below their intrinsic value, leveraging fundamental analysis to evaluate a company's true worth through metrics like earnings, cash flow, and book value. Grid trading, by contrast, is a market-neutral strategy deploying buy and sell orders at regular intervals regardless of intrinsic value, capitalizing on price volatility instead of underlying fundamentals. Explore deeper insights into how intrinsic value drives long-term portfolio growth versus the tactical profit opportunities of grid trading.
Margin of Safety
Value investing emphasizes purchasing securities below their intrinsic value, prioritizing a strong margin of safety to protect against market volatility and investment losses. Grid trading, a systematic strategy involving predefined buy and sell orders, offers less emphasis on fundamental analysis and margin of safety, focusing instead on capitalizing on market fluctuations. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how margin of safety influences these distinct investment approaches.
Source and External Links
Value investing - Wikipedia - Value investing is an investment strategy that involves buying securities considered underpriced based on fundamental analysis, originating with Benjamin Graham and David Dodd, and focusing on buying stocks below their intrinsic value with a margin of safety.
What is value investing? | iShares - BlackRock - Value investing targets stocks that are cheap compared to their real worth using financial metrics like Price to Book and Price to Earnings ratios, and can now be accessed easily through ETFs like the iShares MSCI World ex Australia Value ETF.
Value Investing History | Columbia Business School - Value investing was developed in the 1920s at Columbia Business School by Benjamin Graham and David Dodd, emphasizing estimation of a stock's intrinsic value rather than anticipating price movements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com