Stop hunting exploits common stop-loss placements to trigger premature exits, creating liquidity for larger traders to capitalize on price swings. Order spoofing involves placing fake orders to manipulate market perception and induce false buying or selling pressure without the intent to execute. Discover more about these trading tactics and their impact on market dynamics.
Why it is important
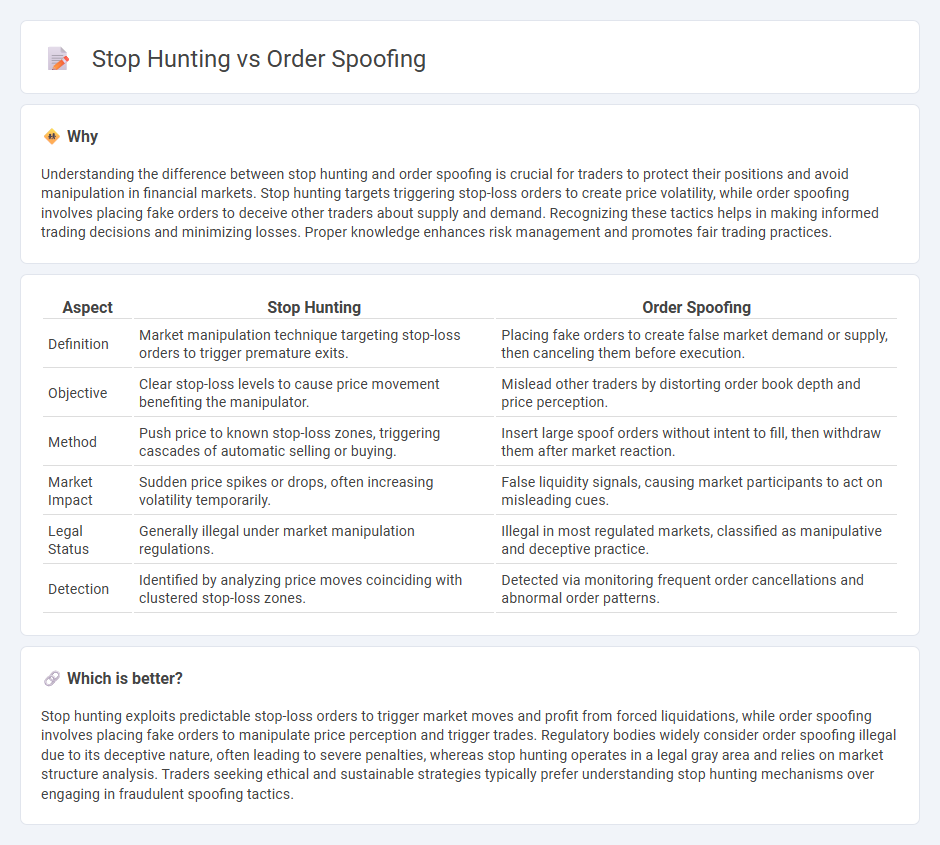
Understanding the difference between stop hunting and order spoofing is crucial for traders to protect their positions and avoid manipulation in financial markets. Stop hunting targets triggering stop-loss orders to create price volatility, while order spoofing involves placing fake orders to deceive other traders about supply and demand. Recognizing these tactics helps in making informed trading decisions and minimizing losses. Proper knowledge enhances risk management and promotes fair trading practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Stop Hunting | Order Spoofing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market manipulation technique targeting stop-loss orders to trigger premature exits. | Placing fake orders to create false market demand or supply, then canceling them before execution. |
| Objective | Clear stop-loss levels to cause price movement benefiting the manipulator. | Mislead other traders by distorting order book depth and price perception. |
| Method | Push price to known stop-loss zones, triggering cascades of automatic selling or buying. | Insert large spoof orders without intent to fill, then withdraw them after market reaction. |
| Market Impact | Sudden price spikes or drops, often increasing volatility temporarily. | False liquidity signals, causing market participants to act on misleading cues. |
| Legal Status | Generally illegal under market manipulation regulations. | Illegal in most regulated markets, classified as manipulative and deceptive practice. |
| Detection | Identified by analyzing price moves coinciding with clustered stop-loss zones. | Detected via monitoring frequent order cancellations and abnormal order patterns. |
Which is better?
Stop hunting exploits predictable stop-loss orders to trigger market moves and profit from forced liquidations, while order spoofing involves placing fake orders to manipulate price perception and trigger trades. Regulatory bodies widely consider order spoofing illegal due to its deceptive nature, often leading to severe penalties, whereas stop hunting operates in a legal gray area and relies on market structure analysis. Traders seeking ethical and sustainable strategies typically prefer understanding stop hunting mechanisms over engaging in fraudulent spoofing tactics.
Connection
Stop hunting and order spoofing are connected through market manipulation techniques that exploit stop-loss orders to trigger price movements. Traders place large spoof orders to create false market signals, causing other participants to activate their stop-losses, which amplifies price volatility. This coordinated strategy manipulates supply and demand dynamics, allowing manipulators to profit from induced price shifts.
Key Terms
Order Spoofing:
Order spoofing manipulates market perception by placing large fake orders to create false demand or supply, influencing price movements without intending to execute those orders. This deceptive strategy misleads traders into making decisions based on inaccurate order book data, often disrupting market transparency. Explore more on how order spoofing impacts trading dynamics and regulatory responses.
Fake Orders
Order spoofing involves placing fake orders with no intention of execution to manipulate market prices, creating false demand or supply signals. Stop hunting targets triggering stop-loss orders by pushing prices to specific levels, often exploiting clusters of stop orders to induce rapid price movements. Explore deeper insights into how fake orders influence trading strategies and market behavior.
Order Book Manipulation
Order spoofing involves placing large, fake orders on the order book to create misleading market sentiment and manipulate prices, commonly used to trigger false supply or demand signals. Stop hunting targets specific stop-loss orders by pushing prices to these levels through aggressive trades, exploiting automatic order executions and causing rapid market moves. Explore more to understand the intricate tactics used in order book manipulation and their impact on trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Spoofing the order book: UK and US regulators take aim - Spoofing is a market manipulation tactic where traders place orders on one side of the order book to falsely create demand or supply, quickly cancel them, and profit from the resulting price movement without ever intending to execute those initial orders.
What is Spoofing in Trading? | Order Book Stock ... - Spoofing involves intentionally placing orders to buy or sell securities and cancelling them before execution, misleading other traders with false signals about supply or demand in the market.
What Is Spoofing in Trading? - SoFi - Spoofing is an illegal trading practice in which orders are placed to manipulate asset prices, then rapidly cancelled, often using algorithms to create a deceptive sense of market activity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com