Dark pool aggregation consolidates hidden liquidity from private exchanges, enabling traders to access large blocks of shares without impacting market prices. Order book matching operates on transparent public exchanges, pairing buy and sell orders based on price and time priority to ensure fair price discovery. Discover how these mechanisms influence trading strategies and market efficiency.
Why it is important
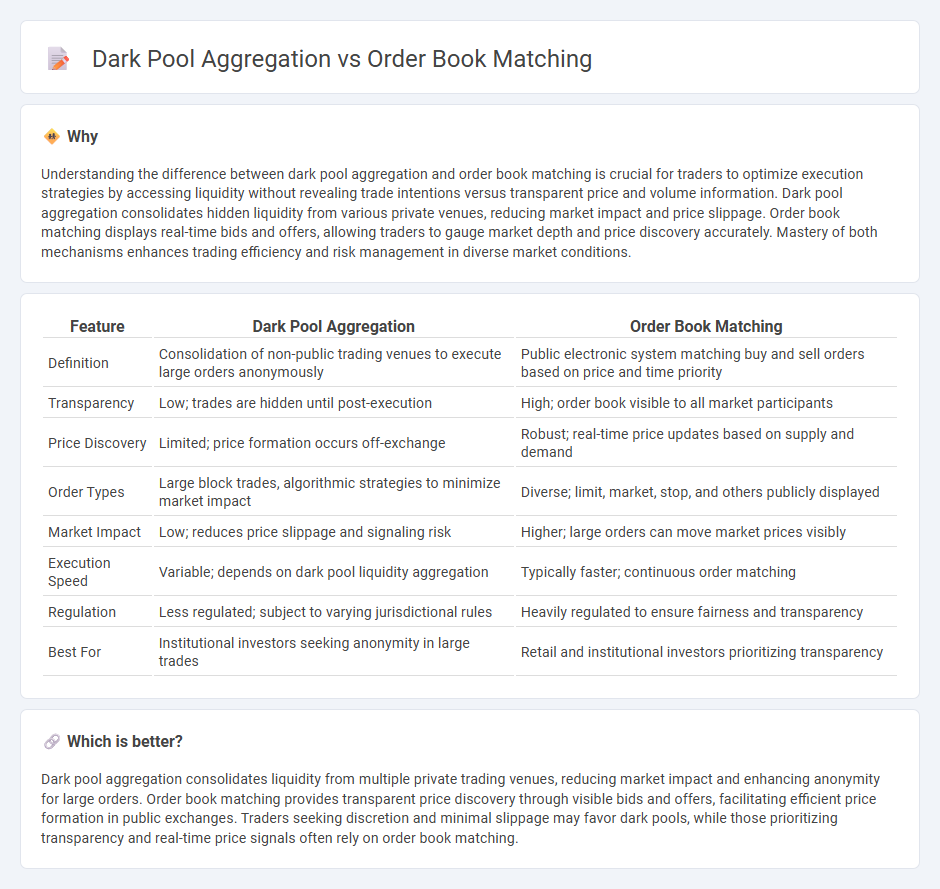
Understanding the difference between dark pool aggregation and order book matching is crucial for traders to optimize execution strategies by accessing liquidity without revealing trade intentions versus transparent price and volume information. Dark pool aggregation consolidates hidden liquidity from various private venues, reducing market impact and price slippage. Order book matching displays real-time bids and offers, allowing traders to gauge market depth and price discovery accurately. Mastery of both mechanisms enhances trading efficiency and risk management in diverse market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dark Pool Aggregation | Order Book Matching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consolidation of non-public trading venues to execute large orders anonymously | Public electronic system matching buy and sell orders based on price and time priority |
| Transparency | Low; trades are hidden until post-execution | High; order book visible to all market participants |
| Price Discovery | Limited; price formation occurs off-exchange | Robust; real-time price updates based on supply and demand |
| Order Types | Large block trades, algorithmic strategies to minimize market impact | Diverse; limit, market, stop, and others publicly displayed |
| Market Impact | Low; reduces price slippage and signaling risk | Higher; large orders can move market prices visibly |
| Execution Speed | Variable; depends on dark pool liquidity aggregation | Typically faster; continuous order matching |
| Regulation | Less regulated; subject to varying jurisdictional rules | Heavily regulated to ensure fairness and transparency |
| Best For | Institutional investors seeking anonymity in large trades | Retail and institutional investors prioritizing transparency |
Which is better?
Dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from multiple private trading venues, reducing market impact and enhancing anonymity for large orders. Order book matching provides transparent price discovery through visible bids and offers, facilitating efficient price formation in public exchanges. Traders seeking discretion and minimal slippage may favor dark pools, while those prioritizing transparency and real-time price signals often rely on order book matching.
Connection
Dark pool aggregation enhances liquidity by consolidating multiple private trading venues, enabling large institutional orders to be executed with minimal market impact. Order book matching systems then integrate this aggregated liquidity to efficiently pair buy and sell orders based on price and time priority. This connection optimizes trade execution by combining hidden liquidity sources with transparent order matching mechanisms, reducing spreads and improving market depth.
Key Terms
**Order Book Matching:**
Order book matching systematically pairs buy and sell orders based on price-time priority, ensuring transparent price discovery and market liquidity. This mechanism enables efficient execution by matching orders directly on public exchanges, reflecting real-time supply and demand. Explore the advantages of order book matching to understand its impact on market transparency and trading efficiency.
Limit Order
Limit orders play a crucial role in both order book matching and dark pool aggregation by specifying the price at which traders are willing to buy or sell assets. Order book matching transparently displays these limit orders, allowing market participants to see the depth and liquidity before executing trades. Explore how limit order strategies impact price discovery and liquidity in various trading venues to enhance your market understanding.
Bid-Ask Spread
Order book matching directly reveals bid-ask spreads through transparent display of buy and sell orders, facilitating efficient price discovery in public exchanges. Dark pool aggregation conceals order sizes and prices, often resulting in narrower visible bid-ask spreads but reduced market transparency and potential price improvement. Explore how these contrasting mechanisms impact liquidity and trading strategies in modern financial markets.
Source and External Links
How does order matching work when I trade alternative assets on Public - Order book matching occurs when bid (buy) and ask (sell) prices equal or cross each other, with matches prioritized first by best price and then by submission time; unmatched orders remain pending on the order book until matched or canceled after 90 days.
Matching principles - Eurex - Orders can be fully or partially matched, with fully matched orders removed from the book and partially matched orders having their executed quantity removed but the remainder staying active, while market orders receive highest priority in the matching process.
Order Matching: Achieving Seamless Trades - BlockApex - An order matching engine pairs buy and sell orders based on algorithms like price-time priority, which matches the highest bids with the lowest asks, prioritizing by price first and then by order time to ensure fair and efficient trade execution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com