Flash loans enable instant, unsecured borrowing of large cryptocurrency amounts, leveraging arbitrage or collateral swapping within a single transaction to maximize profit. Algorithmic trading employs automated strategies based on mathematical models and real-time data to execute trades at optimal prices and speeds. Explore the intricacies of flash loans versus algorithmic trading to enhance your trading strategies and outcomes.
Why it is important
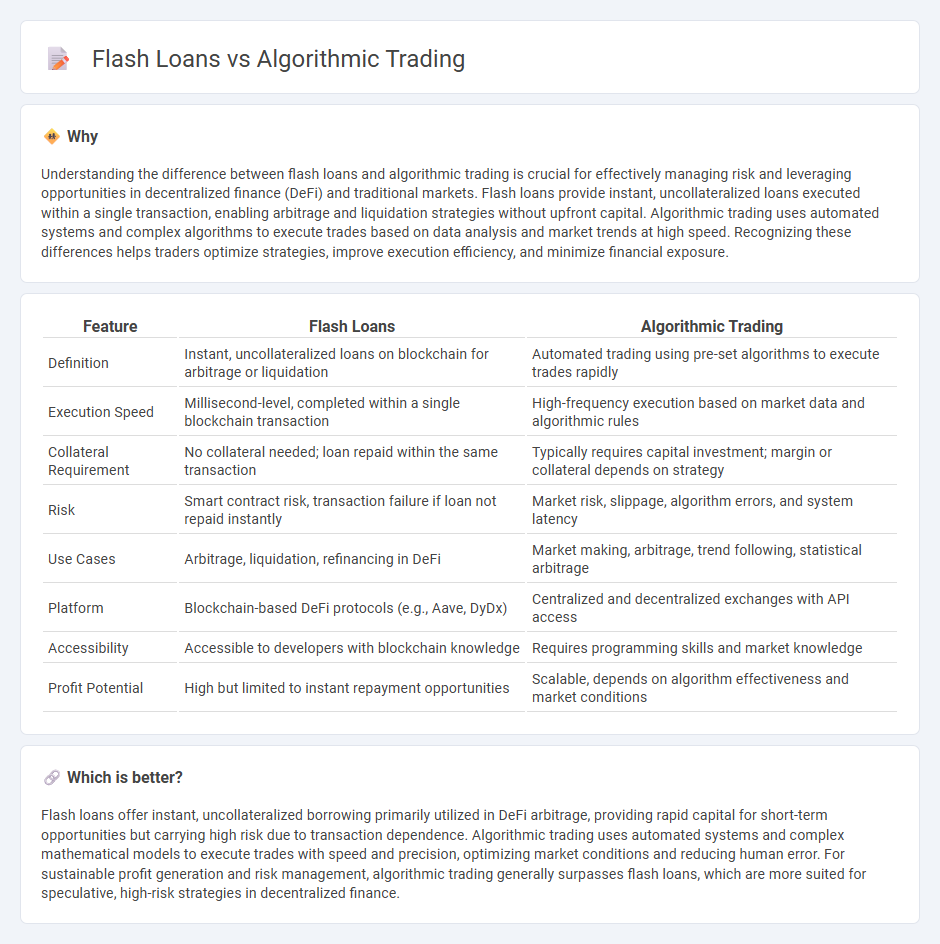
Understanding the difference between flash loans and algorithmic trading is crucial for effectively managing risk and leveraging opportunities in decentralized finance (DeFi) and traditional markets. Flash loans provide instant, uncollateralized loans executed within a single transaction, enabling arbitrage and liquidation strategies without upfront capital. Algorithmic trading uses automated systems and complex algorithms to execute trades based on data analysis and market trends at high speed. Recognizing these differences helps traders optimize strategies, improve execution efficiency, and minimize financial exposure.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Flash Loans | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant, uncollateralized loans on blockchain for arbitrage or liquidation | Automated trading using pre-set algorithms to execute trades rapidly |
| Execution Speed | Millisecond-level, completed within a single blockchain transaction | High-frequency execution based on market data and algorithmic rules |
| Collateral Requirement | No collateral needed; loan repaid within the same transaction | Typically requires capital investment; margin or collateral depends on strategy |
| Risk | Smart contract risk, transaction failure if loan not repaid instantly | Market risk, slippage, algorithm errors, and system latency |
| Use Cases | Arbitrage, liquidation, refinancing in DeFi | Market making, arbitrage, trend following, statistical arbitrage |
| Platform | Blockchain-based DeFi protocols (e.g., Aave, DyDx) | Centralized and decentralized exchanges with API access |
| Accessibility | Accessible to developers with blockchain knowledge | Requires programming skills and market knowledge |
| Profit Potential | High but limited to instant repayment opportunities | Scalable, depends on algorithm effectiveness and market conditions |
Which is better?
Flash loans offer instant, uncollateralized borrowing primarily utilized in DeFi arbitrage, providing rapid capital for short-term opportunities but carrying high risk due to transaction dependence. Algorithmic trading uses automated systems and complex mathematical models to execute trades with speed and precision, optimizing market conditions and reducing human error. For sustainable profit generation and risk management, algorithmic trading generally surpasses flash loans, which are more suited for speculative, high-risk strategies in decentralized finance.
Connection
Flash loans enable traders to borrow vast amounts of capital instantly without collateral, facilitating rapid arbitrage opportunities exploited by algorithmic trading systems. Algorithmic trading leverages these instant, large-volume loans to execute complex, high-frequency strategies that capitalize on price discrepancies across decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. This synergy enhances market efficiency but also introduces risks like flash loan attacks, highlighting the importance of robust smart contract security in trading ecosystems.
Key Terms
**Algorithmic Trading:**
Algorithmic trading leverages advanced mathematical models and high-frequency data analysis to execute large volumes of trades at speeds impossible for human traders, aiming to maximize profit through precise timing and pattern recognition. It integrates complex algorithms within financial markets to exploit inefficiencies, often utilized by hedge funds, investment banks, and proprietary trading firms. Explore more about how algorithmic trading transforms market strategies and risk management.
Quantitative Strategies
Algorithmic trading utilizes complex mathematical models and quantitative strategies to execute trades at high speed, relying on historical data and real-time market analysis to optimize profitability. Flash loans, a DeFi innovation, enable the borrowing of large sums of cryptocurrency without collateral, exploiting arbitrage and liquidation opportunities within a single transaction block. Explore the nuances of these advanced financial methods to enhance your understanding of cutting-edge quantitative trading approaches.
Backtesting
Backtesting in algorithmic trading involves simulating trading strategies on historical data to evaluate performance and risk before deployment, ensuring robust algorithms that adapt to market conditions. In contrast, flash loans, a DeFi innovation, lack traditional backtesting frameworks due to their instantaneous, uncollateralized nature, relying on real-time execution and arbitrage opportunities within blockchain transactions. Explore how backtesting methodologies enhance algorithmic strategy development and contrast with the unique dynamics of flash loan utilization.
Source and External Links
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading uses computer codes and software to automatically open and close trades based on preset rules like price movement, with main strategies including price action, technical analysis, and a combination of both, often used for high-frequency trading and risk management.
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - Algorithmic trading involves trading decisions executed by computers based on programmed rules, such as moving average strategies, allowing traders to implement large trades in batches to minimize market price impact.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading executes orders using automated pre-programmed instructions and has evolved to incorporate machine learning techniques like deep reinforcement learning and directional change algorithms for better adaptability and precision in volatile markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com