Delta neutral strategy aims to balance positive and negative deltas to minimize directional risk in trading, often using combinations of options and underlying assets. Options selling, or writing, involves collecting premiums by selling call or put options, benefiting primarily from time decay and volatility changes. Explore the nuances of these trading approaches to enhance your portfolio management techniques.
Why it is important
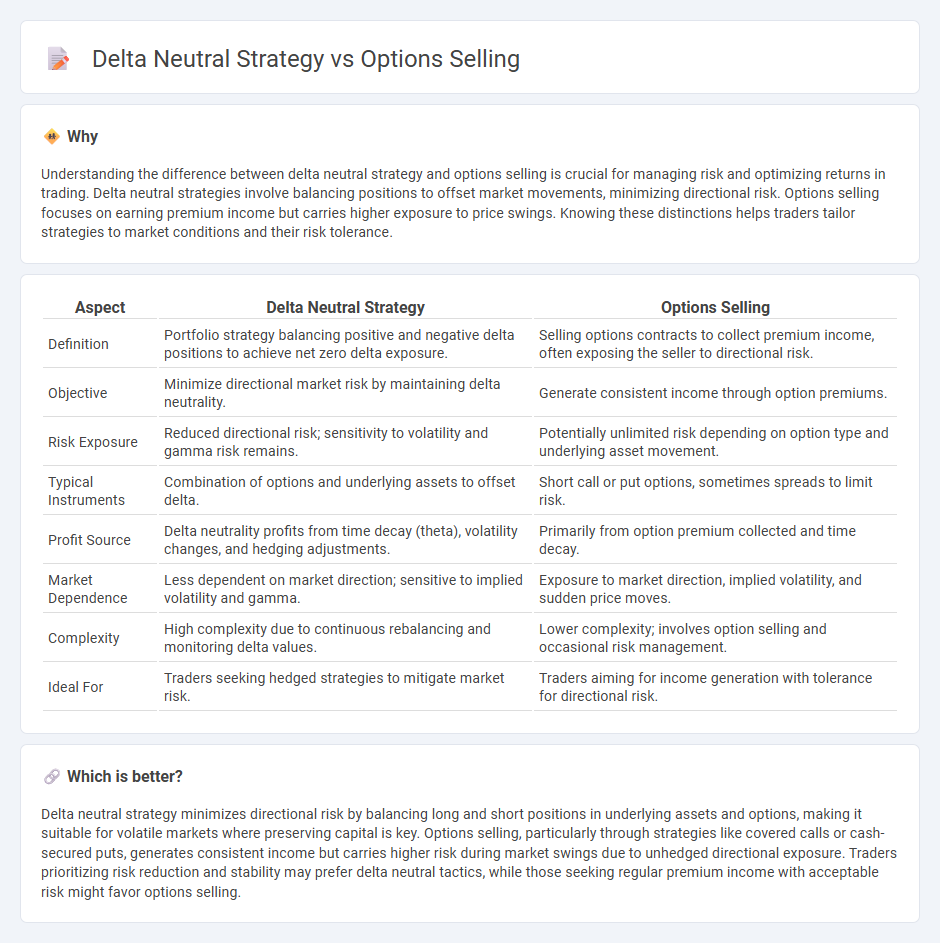
Understanding the difference between delta neutral strategy and options selling is crucial for managing risk and optimizing returns in trading. Delta neutral strategies involve balancing positions to offset market movements, minimizing directional risk. Options selling focuses on earning premium income but carries higher exposure to price swings. Knowing these distinctions helps traders tailor strategies to market conditions and their risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta Neutral Strategy | Options Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Portfolio strategy balancing positive and negative delta positions to achieve net zero delta exposure. | Selling options contracts to collect premium income, often exposing the seller to directional risk. |
| Objective | Minimize directional market risk by maintaining delta neutrality. | Generate consistent income through option premiums. |
| Risk Exposure | Reduced directional risk; sensitivity to volatility and gamma risk remains. | Potentially unlimited risk depending on option type and underlying asset movement. |
| Typical Instruments | Combination of options and underlying assets to offset delta. | Short call or put options, sometimes spreads to limit risk. |
| Profit Source | Delta neutrality profits from time decay (theta), volatility changes, and hedging adjustments. | Primarily from option premium collected and time decay. |
| Market Dependence | Less dependent on market direction; sensitive to implied volatility and gamma. | Exposure to market direction, implied volatility, and sudden price moves. |
| Complexity | High complexity due to continuous rebalancing and monitoring delta values. | Lower complexity; involves option selling and occasional risk management. |
| Ideal For | Traders seeking hedged strategies to mitigate market risk. | Traders aiming for income generation with tolerance for directional risk. |
Which is better?
Delta neutral strategy minimizes directional risk by balancing long and short positions in underlying assets and options, making it suitable for volatile markets where preserving capital is key. Options selling, particularly through strategies like covered calls or cash-secured puts, generates consistent income but carries higher risk during market swings due to unhedged directional exposure. Traders prioritizing risk reduction and stability may prefer delta neutral tactics, while those seeking regular premium income with acceptable risk might favor options selling.
Connection
Delta neutral strategy involves creating an options position where the overall delta is zero, minimizing exposure to price movements of the underlying asset. Options selling generates premium income, which can be used to offset potential losses in maintaining delta neutrality. This connection allows traders to profit from time decay while managing directional risk effectively.
Key Terms
Premium
Options selling generates consistent income by capturing option premiums, leveraging time decay and market volatility to profit from the erosion of option value. Delta neutral strategy balances option positions with underlying assets to minimize directional risk while seeking to profit from changes in implied volatility and time decay. Explore detailed insights on how premium dynamics influence these strategies to optimize your options trading approach.
Hedging
Options selling generates premium income by taking on directional risk, often requiring active management to mitigate potential losses during adverse market moves. Delta neutral strategies maintain a balanced portfolio by offsetting positive and negative delta positions, aiming to hedge market exposure and minimize price fluctuations. Explore more about how these approaches optimize risk management and enhance portfolio stability.
Gamma
Options selling involves collecting premium while managing exposure to Gamma risk, which measures the rate of change of Delta in an option's price. A delta neutral strategy aims to hedge Delta exposure, often resulting in higher Gamma sensitivity, requiring frequent adjustments to maintain neutrality and control risk. Explore the nuances of Gamma impact on these strategies to optimize your options trading approach.
Source and External Links
From zero to hero: selling options - Saxo Bank - Selling options involves either selling call options (profiting if the stock stays below the strike price plus premium) or put options (profiting if the stock does not drop below the strike price minus premium), enabling income through premiums with defined risks if the stock price moves unfavorably.
How to sell calls and puts - Fidelity Investments - Selling options generates current income by receiving premiums, with sellers having the obligation to buy or sell the underlying security if exercised, and involves strategies such as covered calls where options are sold on stocks already owned to earn extra income.
Buying and selling options through Vanguard Brokerage - Options trading includes selling to open (writing) calls or puts to earn premiums by giving the buyer rights to buy or sell an asset later, albeit with significant risks and requiring prior brokerage approval to trade.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com