Algorithmic arbitrage leverages high-frequency trading algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across multiple markets with speed and precision, capturing small profits from inefficiencies. Merger arbitrage focuses on the risk and reward of trading stocks involved in announced mergers or acquisitions, aiming to profit from the spread between the current market price and the deal price. Discover more about these distinct trading strategies and their roles in modern financial markets.
Why it is important
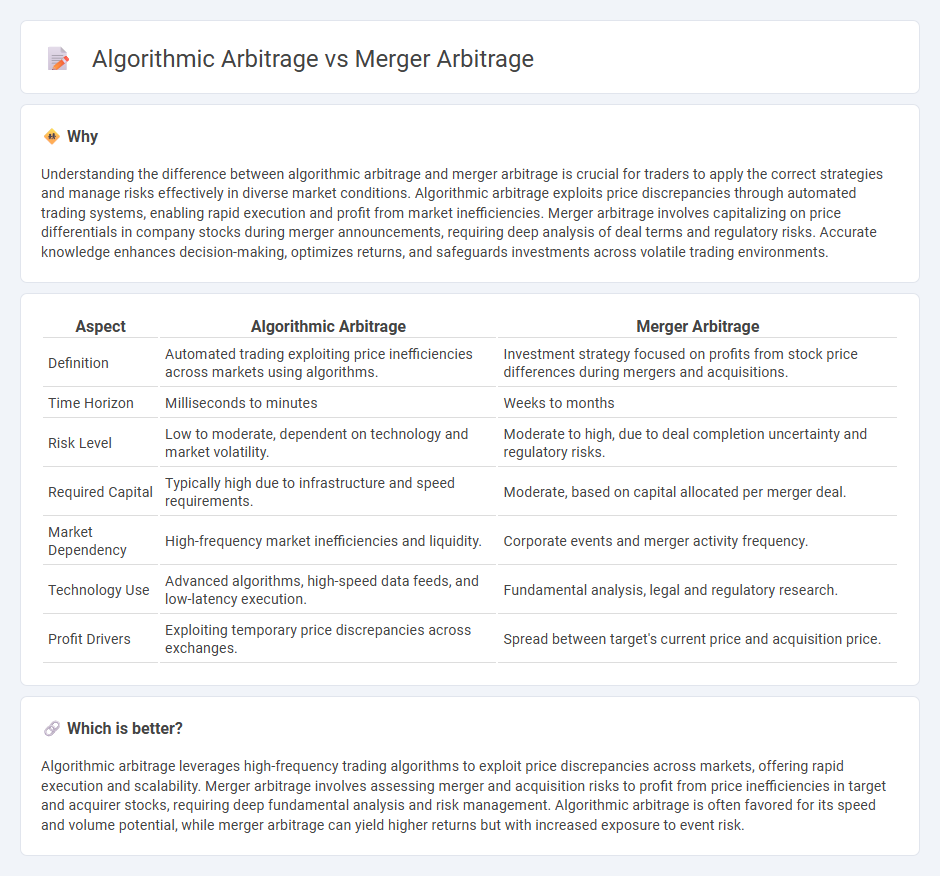
Understanding the difference between algorithmic arbitrage and merger arbitrage is crucial for traders to apply the correct strategies and manage risks effectively in diverse market conditions. Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies through automated trading systems, enabling rapid execution and profit from market inefficiencies. Merger arbitrage involves capitalizing on price differentials in company stocks during merger announcements, requiring deep analysis of deal terms and regulatory risks. Accurate knowledge enhances decision-making, optimizes returns, and safeguards investments across volatile trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Arbitrage | Merger Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading exploiting price inefficiencies across markets using algorithms. | Investment strategy focused on profits from stock price differences during mergers and acquisitions. |
| Time Horizon | Milliseconds to minutes | Weeks to months |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate, dependent on technology and market volatility. | Moderate to high, due to deal completion uncertainty and regulatory risks. |
| Required Capital | Typically high due to infrastructure and speed requirements. | Moderate, based on capital allocated per merger deal. |
| Market Dependency | High-frequency market inefficiencies and liquidity. | Corporate events and merger activity frequency. |
| Technology Use | Advanced algorithms, high-speed data feeds, and low-latency execution. | Fundamental analysis, legal and regulatory research. |
| Profit Drivers | Exploiting temporary price discrepancies across exchanges. | Spread between target's current price and acquisition price. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic arbitrage leverages high-frequency trading algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across markets, offering rapid execution and scalability. Merger arbitrage involves assessing merger and acquisition risks to profit from price inefficiencies in target and acquirer stocks, requiring deep fundamental analysis and risk management. Algorithmic arbitrage is often favored for its speed and volume potential, while merger arbitrage can yield higher returns but with increased exposure to event risk.
Connection
Algorithmic arbitrage leverages automated trading systems to exploit price discrepancies between securities, while merger arbitrage focuses on profiting from price movements related to corporate merger announcements. Both strategies rely on identifying inefficiencies in market pricing driven by corporate events, using quantitative models and real-time data analysis. Integration of algorithmic techniques enhances the speed and precision of merger arbitrage execution, improving opportunities for risk-adjusted returns.
Key Terms
Merger Arbitrage:
Merger arbitrage involves exploiting price discrepancies during corporate mergers or acquisitions, where investors buy target company shares and short acquiree shares to capture spread profits. This strategy demands deep understanding of deal terms, regulatory risks, and timing to anticipate successful deal closures and potential legal hurdles. Explore how merger arbitrage can diversify your investment portfolio and capitalize on event-driven opportunities.
Target Price Spread
Merger arbitrage targets price spreads arising from announced corporate mergers or acquisitions, exploiting discrepancies between the acquisition price and the current market price of the target company's stock. Algorithmic arbitrage employs automated trading algorithms to capitalize on tiny, short-term price inefficiencies across various markets, often executed at high frequency. Explore deeper insights on how these strategies differ in risk profiles and execution by learning more about target price spread dynamics.
Deal Risk
Merger arbitrage involves investing in the stocks of companies involved in mergers or acquisitions, with key deal risks including regulatory approval, deal termination, and financing uncertainties that may impact expected returns. Algorithmic arbitrage leverages automated systems to exploit price discrepancies across markets with minimal human intervention, but it faces risks such as technological failures, market volatility, and execution delays. Explore how deal risk influences strategy selection and risk management in arbitrage approaches.
Source and External Links
Merger arbitrage: Process, examples, types, and risks - Merger arbitrage is an event-driven investing strategy focusing on buying the target company's stock below its expected value post-merger, involving research, understanding agreements, analyzing risk/reward, and monitoring the deal, with risks including deal failure and regulatory issues; it mainly involves cash and in-stock mergers.
An Introduction to Merger Arbitrage - Merger arbitrage is an absolute return strategy investing in companies involved in pending mergers, profiting from the discount between the target's current stock price and the acquisition offer, with key types including stock-for-stock, cash, and mixed consideration mergers.
Risk arbitrage - Merger arbitrage, also called risk arbitrage, involves buying the target's stock and potentially short-selling the acquirer's stock in stock mergers, aiming to profit as the target price approaches the offered price upon deal completion, with spread size reflecting the risk of deal failure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com