Flash loan arbitrage exploits instantaneous, uncollateralized loans to capitalize on price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges, enabling traders to execute risk-free profits within a single transaction block. Mean reversion strategies rely on statistical analysis, anticipating that asset prices will revert to their historical average, thus allowing traders to buy undervalued assets and sell overvalued ones based on historical price patterns. Discover more about these dynamic trading strategies and how they can optimize your portfolio performance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loan arbitrage and mean reversion is crucial for traders to apply appropriate risk management and maximize profit potential. Flash loan arbitrage involves exploiting temporary price discrepancies across decentralized finance platforms using uncollateralized loans, which demands high technical skill and precision timing. Mean reversion trading relies on the statistical assumption that asset prices will return to their historical average, requiring robust historical data analysis and patience. Knowing these distinctions helps traders design effective strategies tailored to market conditions and capital availability.
Comparison Table
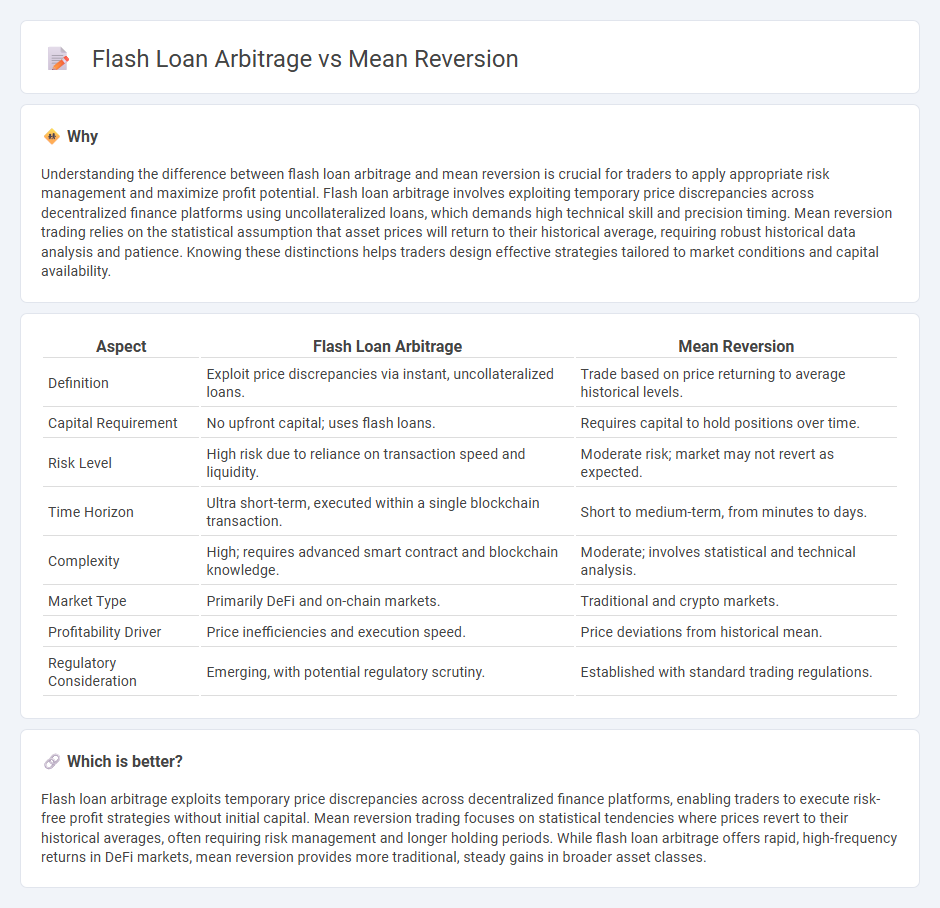
| Aspect | Flash Loan Arbitrage | Mean Reversion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploit price discrepancies via instant, uncollateralized loans. | Trade based on price returning to average historical levels. |
| Capital Requirement | No upfront capital; uses flash loans. | Requires capital to hold positions over time. |
| Risk Level | High risk due to reliance on transaction speed and liquidity. | Moderate risk; market may not revert as expected. |
| Time Horizon | Ultra short-term, executed within a single blockchain transaction. | Short to medium-term, from minutes to days. |
| Complexity | High; requires advanced smart contract and blockchain knowledge. | Moderate; involves statistical and technical analysis. |
| Market Type | Primarily DeFi and on-chain markets. | Traditional and crypto markets. |
| Profitability Driver | Price inefficiencies and execution speed. | Price deviations from historical mean. |
| Regulatory Consideration | Emerging, with potential regulatory scrutiny. | Established with standard trading regulations. |
Which is better?
Flash loan arbitrage exploits temporary price discrepancies across decentralized finance platforms, enabling traders to execute risk-free profit strategies without initial capital. Mean reversion trading focuses on statistical tendencies where prices revert to their historical averages, often requiring risk management and longer holding periods. While flash loan arbitrage offers rapid, high-frequency returns in DeFi markets, mean reversion provides more traditional, steady gains in broader asset classes.
Connection
Flash loan arbitrage exploits temporary price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges by borrowing large sums without collateral, profiting from rapid trades before loan repayment. Mean reversion strategies assume asset prices will revert to their historical averages, identifying overvalued or undervalued conditions ideal for arbitrage opportunities. Combining flash loan arbitrage with mean reversion enables traders to capitalize on transient deviations from mean prices, maximizing returns in decentralized finance markets.
Key Terms
Price Deviation
Mean reversion trading capitalizes on price deviations by anticipating that asset prices will return to their historical average, exploiting temporary mispricings for profit. Flash loan arbitrage leverages instantaneous, unsecured loans to capitalize on price discrepancies across different decentralized exchanges before the prices converge. Explore the detailed mechanics and strategies behind these techniques to enhance your trading insights.
Temporal Opportunity
Mean reversion strategies capitalize on price deviations from historical averages, leveraging temporal stability for profitable trades over medium to long intervals. Flash loan arbitrage exploits instantaneous market inefficiencies using uncollateralized loans, capitalizing on opportunities that exist only for milliseconds within decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. Explore deeper insights into the temporal dynamics distinguishing these strategies to optimize your trading approach.
Automated Execution
Mean reversion trading strategies exploit price deviations from historical averages to capitalize on expected reversals, using automated execution to rapidly detect and act on these statistical patterns. Flash loan arbitrage leverages decentralized finance protocols, utilizing instantly borrowed capital without collateral to execute simultaneous trades across different exchanges for risk-free profits, all coordinated by smart contracts for seamless automation. Explore how these distinct automated execution methodologies optimize profitability in high-frequency and blockchain-based trading environments.
Source and External Links
Mean Reversion Strategies: Introduction, Trading ... - Mean reversion is a financial theory stating asset prices and returns tend to revert to their long-term average, with trading strategies based on buying when price falls below the mean and selling when it rises above it, using moving averages to identify the mean and deviations for trade signals.
Mean reversion (finance) - Mean reversion assumes asset prices converge to their average price over time, guiding buy-sell timing by identifying deviations from historical averages and predicting price movements back toward these averages.
Mean Reversion - Overview, Trading, Impact of Catalysts - Mean reversion theory suggests asset prices move toward a long-term mean, allowing traders to develop strategies that profit by buying below and selling above this average based on statistical analysis and market catalysts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com