Retail flow chasing involves traders following the momentum generated by individual investors' buying or selling patterns, often leading to increased volatility and rapid price changes. Liquidity provision focuses on offering buy and sell orders to stabilize markets, improve trade execution, and narrow bid-ask spreads, benefiting overall market efficiency. Explore the dynamics between retail flow chasing and liquidity provision to enhance your trading strategies.
Why it is important
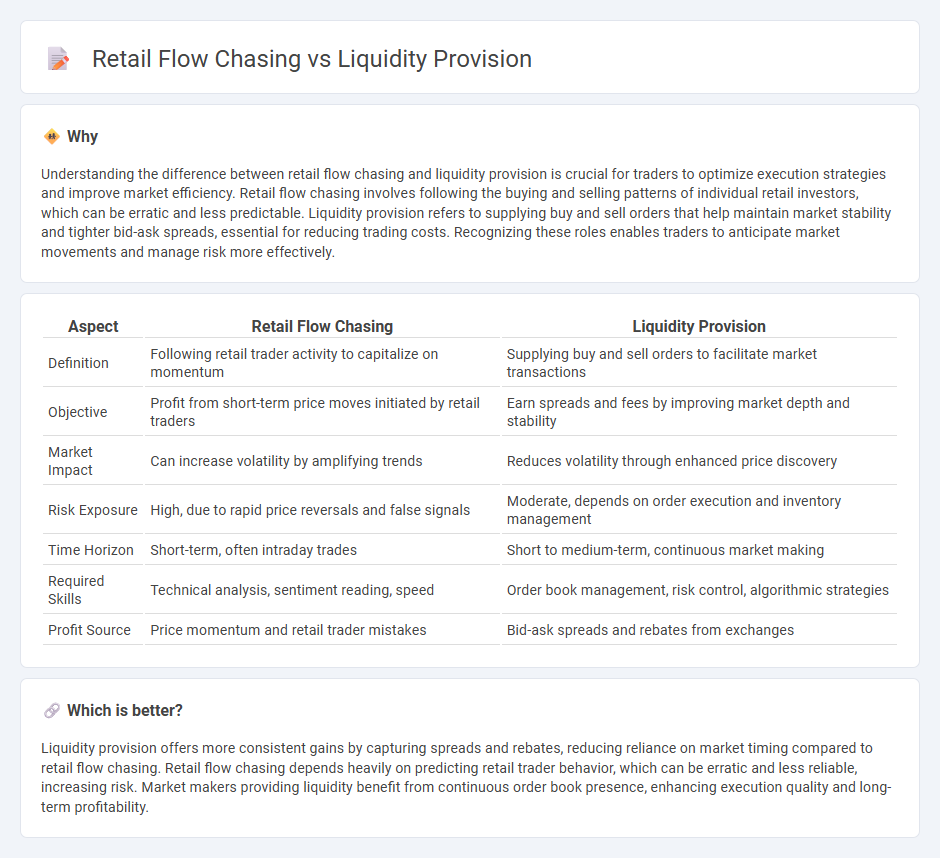
Understanding the difference between retail flow chasing and liquidity provision is crucial for traders to optimize execution strategies and improve market efficiency. Retail flow chasing involves following the buying and selling patterns of individual retail investors, which can be erratic and less predictable. Liquidity provision refers to supplying buy and sell orders that help maintain market stability and tighter bid-ask spreads, essential for reducing trading costs. Recognizing these roles enables traders to anticipate market movements and manage risk more effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Retail Flow Chasing | Liquidity Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Following retail trader activity to capitalize on momentum | Supplying buy and sell orders to facilitate market transactions |
| Objective | Profit from short-term price moves initiated by retail traders | Earn spreads and fees by improving market depth and stability |
| Market Impact | Can increase volatility by amplifying trends | Reduces volatility through enhanced price discovery |
| Risk Exposure | High, due to rapid price reversals and false signals | Moderate, depends on order execution and inventory management |
| Time Horizon | Short-term, often intraday trades | Short to medium-term, continuous market making |
| Required Skills | Technical analysis, sentiment reading, speed | Order book management, risk control, algorithmic strategies |
| Profit Source | Price momentum and retail trader mistakes | Bid-ask spreads and rebates from exchanges |
Which is better?
Liquidity provision offers more consistent gains by capturing spreads and rebates, reducing reliance on market timing compared to retail flow chasing. Retail flow chasing depends heavily on predicting retail trader behavior, which can be erratic and less reliable, increasing risk. Market makers providing liquidity benefit from continuous order book presence, enhancing execution quality and long-term profitability.
Connection
Retail flow chasing involves market participants reacting to retail investor order patterns, creating predictable price movements. Liquidity provision capitalizes on these movements by supplying or absorbing orders, enhancing market depth and efficiency. This dynamic interaction stabilizes price fluctuations while offering profit opportunities for liquidity providers.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
Liquidity provision involves market makers posting buy and sell orders to maintain tight bid-ask spreads, enhancing market efficiency and reducing trading costs. Retail flow chasing typically leads to wider spreads as brokers adjust quotes to manage order imbalances caused by individual investor demand. Explore the dynamics of bid-ask spreads in market microstructure to understand how liquidity and retail flows shape price formation.
Order Book Depth
Order Book Depth plays a crucial role in distinguishing liquidity provision from retail flow chasing by revealing the volume of buy and sell orders at various price levels, indicating market liquidity and potential price stability. Liquidity providers contribute to deeper order books by placing substantial limit orders, facilitating smoother transactions and reducing spread volatility, whereas retail flow chasers react to existing order flows, often causing rapid fluctuations in order book depth and price movements. Explore how understanding order book depth can improve trading strategies and risk management.
Slippage
Liquidity provision minimizes slippage by ensuring ample market depth through continuous buy and sell orders, stabilizing asset prices during large trades. Retail flow chasing often results in higher slippage, as market makers struggle to match unpredictable retail order volumes, leading to price impacts unfavorable to traders. Discover how optimizing liquidity strategies can reduce slippage and improve trade execution efficiency.
Source and External Links
Liquidity Provision - Liquidity provision refers to financial institutions acting as intermediaries in securities markets to improve liquidity by increasing market depth and trading volumes, essential for investors and issuers alike.
DeFi Basics: Liquidity Provision - In decentralized finance (DeFi), liquidity provision involves users depositing cryptocurrencies into liquidity pools in protocols to facilitate token swaps on decentralized exchanges, earning fees as rewards.
Liquidity Provision by the Federal Reserve - Central banks provide liquidity to mitigate financial crises by supplying cash or equivalents, balancing between liquidity needs and economic efficiency through mechanisms like open market operations and lending facilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com