Microstructure trading focuses on the detailed analysis of order flows, bid-ask spreads, and market depth to exploit inefficiencies within milliseconds to minutes. Scalping involves executing numerous rapid trades to capture small price movements, relying heavily on speed and precision. Explore more to understand which strategy suits your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Why it is important
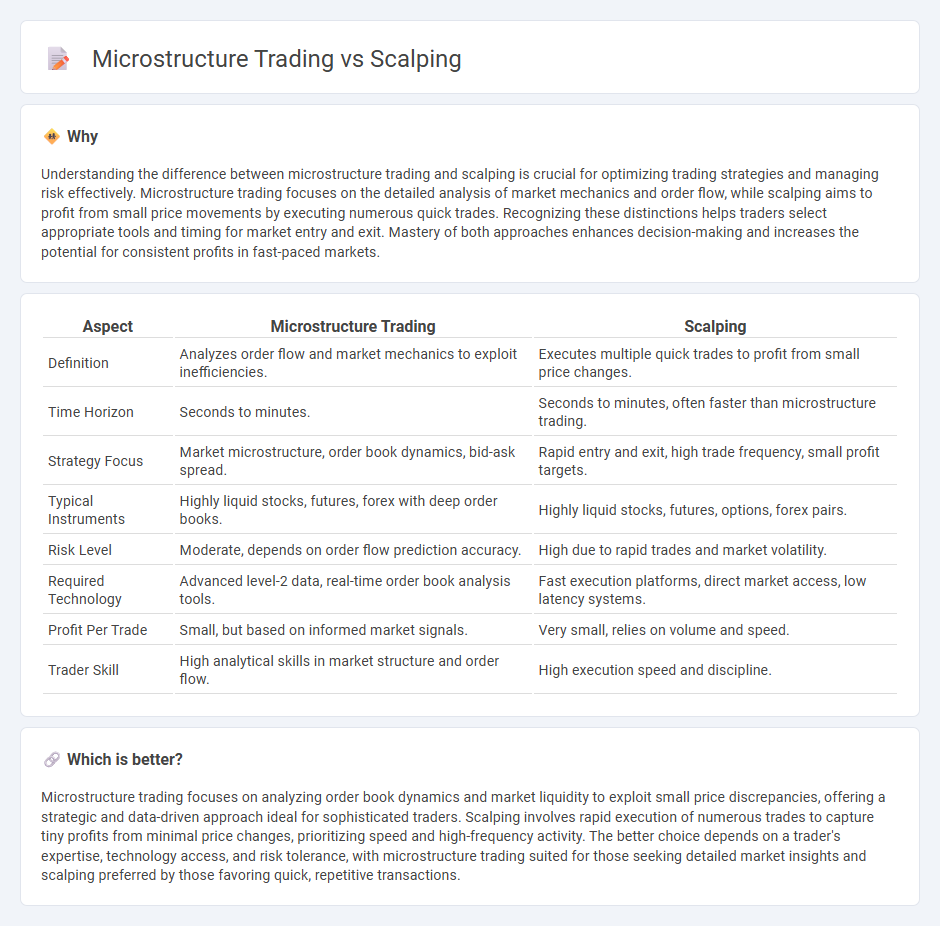
Understanding the difference between microstructure trading and scalping is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risk effectively. Microstructure trading focuses on the detailed analysis of market mechanics and order flow, while scalping aims to profit from small price movements by executing numerous quick trades. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders select appropriate tools and timing for market entry and exit. Mastery of both approaches enhances decision-making and increases the potential for consistent profits in fast-paced markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Trading | Scalping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes order flow and market mechanics to exploit inefficiencies. | Executes multiple quick trades to profit from small price changes. |
| Time Horizon | Seconds to minutes. | Seconds to minutes, often faster than microstructure trading. |
| Strategy Focus | Market microstructure, order book dynamics, bid-ask spread. | Rapid entry and exit, high trade frequency, small profit targets. |
| Typical Instruments | Highly liquid stocks, futures, forex with deep order books. | Highly liquid stocks, futures, options, forex pairs. |
| Risk Level | Moderate, depends on order flow prediction accuracy. | High due to rapid trades and market volatility. |
| Required Technology | Advanced level-2 data, real-time order book analysis tools. | Fast execution platforms, direct market access, low latency systems. |
| Profit Per Trade | Small, but based on informed market signals. | Very small, relies on volume and speed. |
| Trader Skill | High analytical skills in market structure and order flow. | High execution speed and discipline. |
Which is better?
Microstructure trading focuses on analyzing order book dynamics and market liquidity to exploit small price discrepancies, offering a strategic and data-driven approach ideal for sophisticated traders. Scalping involves rapid execution of numerous trades to capture tiny profits from minimal price changes, prioritizing speed and high-frequency activity. The better choice depends on a trader's expertise, technology access, and risk tolerance, with microstructure trading suited for those seeking detailed market insights and scalping preferred by those favoring quick, repetitive transactions.
Connection
Microstructure trading focuses on the analysis of order flow, bid-ask spreads, and market liquidity, which are critical elements for successful scalping strategies that rely on quick, small-profit trades. Scalping exploits microstructure inefficiencies by executing rapid trades to capitalize on tiny price movements within highly liquid assets. Understanding market microstructure enables scalpers to optimize entry and exit points, minimize slippage, and manage transaction costs effectively.
Key Terms
Order Book
Order book analysis plays a crucial role in both scalping and microstructure trading, offering insights into supply-demand dynamics and price movements at a granular level. Scalpers exploit rapid changes in order book liquidity to execute quick trades for small profits, while microstructure traders assess order book depth, order flow imbalance, and hidden liquidity to predict short-term price trends. Explore more strategies and tools to master order book dynamics and enhance your trading precision.
Bid-Ask Spread
Scalping exploits small price movements by rapidly buying and selling assets, aiming to capture profits within the bid-ask spread, while microstructure trading analyzes the intricate components of market liquidity and order flow impacting spread dynamics. The bid-ask spread serves as a critical indicator of transaction costs and market efficiency, directly influencing the profitability of high-frequency strategies such as scalping. Explore further insights into how bid-ask spread intricacies shape advanced trading techniques.
Execution Latency
Execution latency critically impacts both scalping and microstructure trading, determining the speed at which trades are executed and profits realized. High-frequency trading algorithms in scalping demand ultra-low latency environments, often measured in microseconds, to capitalize on minute price fluctuations. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how latency optimization shapes trading strategies and market efficiency.
Source and External Links
Scalping (Day Trading Technique) - Corporate Finance Institute - Scalping is a day trading strategy where an investor buys and sells an individual stock multiple times within a single day, seeking to make small profits on numerous trades, often focusing on highly volatile stocks.
What is a scalping strategy in the stock market and how does it work? - Scalping involves fast-paced buying and selling of securities, supported by technical indicators such as RSI, MACD, and moving averages to identify price trends and market reversals.
Scalping (trading) - Wikipedia - Scalping is a legitimate trading method involving rapid transactions to exploit small price gaps created by bid-ask spreads, typically done in seconds or minutes to make small profits repeatedly.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com