Prop firm challenges offer traders the opportunity to trade with significant capital provided by the firm, often requiring strict adherence to risk management rules and performance targets. Personal trading accounts rely solely on the individual's capital, allowing more freedom but limiting the potential scale of trades. Explore the advantages and challenges of each approach to determine the best fit for your trading goals.
Why it is important
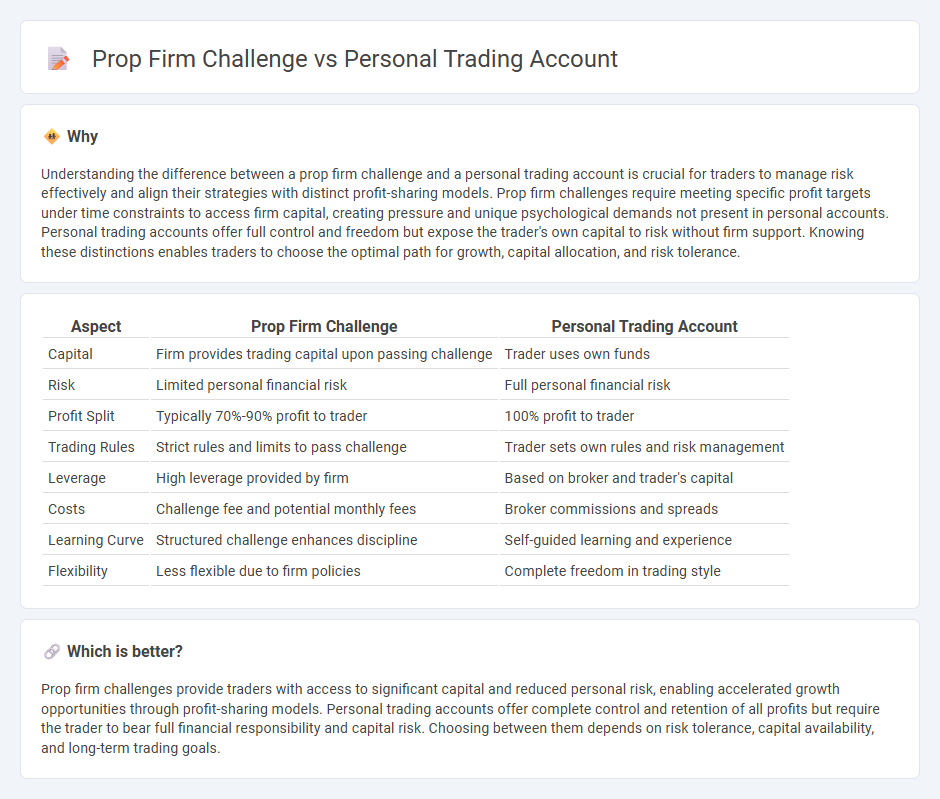
Understanding the difference between a prop firm challenge and a personal trading account is crucial for traders to manage risk effectively and align their strategies with distinct profit-sharing models. Prop firm challenges require meeting specific profit targets under time constraints to access firm capital, creating pressure and unique psychological demands not present in personal accounts. Personal trading accounts offer full control and freedom but expose the trader's own capital to risk without firm support. Knowing these distinctions enables traders to choose the optimal path for growth, capital allocation, and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Prop Firm Challenge | Personal Trading Account |
|---|---|---|
| Capital | Firm provides trading capital upon passing challenge | Trader uses own funds |
| Risk | Limited personal financial risk | Full personal financial risk |
| Profit Split | Typically 70%-90% profit to trader | 100% profit to trader |
| Trading Rules | Strict rules and limits to pass challenge | Trader sets own rules and risk management |
| Leverage | High leverage provided by firm | Based on broker and trader's capital |
| Costs | Challenge fee and potential monthly fees | Broker commissions and spreads |
| Learning Curve | Structured challenge enhances discipline | Self-guided learning and experience |
| Flexibility | Less flexible due to firm policies | Complete freedom in trading style |
Which is better?
Prop firm challenges provide traders with access to significant capital and reduced personal risk, enabling accelerated growth opportunities through profit-sharing models. Personal trading accounts offer complete control and retention of all profits but require the trader to bear full financial responsibility and capital risk. Choosing between them depends on risk tolerance, capital availability, and long-term trading goals.
Connection
Prop firm challenges evaluate traders' skills and risk management on demo accounts to secure funded trading capital, directly impacting personal trading account growth. Success in these challenges often leads to access to larger capital pools, enabling traders to scale their personal trading accounts with reduced personal financial risk. This connection fosters professional discipline and strategic development, enhancing long-term profitability in personal trading ventures.
Key Terms
Leverage
Personal trading accounts typically offer limited leverage, often ranging from 1:10 to 1:50 depending on the broker and regulatory restrictions, which can constrain potential profit margins. Prop firm challenges provide significantly higher leverage, commonly up to 1:100 or more, enabling traders to control larger positions with less capital and amplify their earning potential. Explore the differences in leverage options to determine which trading pathway aligns best with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Drawdown
Personal trading accounts often face stricter drawdown limits set by individual risk tolerance, directly impacting capital preservation and trading strategies. Prop firm challenges typically impose predefined drawdown thresholds as part of evaluation criteria, encouraging disciplined risk management to qualify for funded accounts. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your approach to drawdowns in both trading environments.
Profit Split
Personal trading accounts offer 100% profit retention but require full capital risk and management responsibility. Prop firm challenges often demand passing strict evaluation criteria, rewarding traders with profit splits typically ranging from 70% to 90%. Explore the nuances of profit splits and risk management strategies to decide the best path for maximizing trading gains.
Source and External Links
What is a Brokerage account and how does it work? - Vanguard - A personal trading account, often called a brokerage account, is a nonretirement investing account where you can buy and hold stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, bonds, and more by funding the account through bank transfers and placing trades online.
Types of Brokerage Accounts - Schwab - Individual brokerage accounts are personal trading accounts owned by one person, providing options such as margin trading, check writing, and options trading, useful for managing investments and meeting financial goals.
Online Brokerage Account | Open an Account - E*TRADE - Opening a personal trading account involves providing identification and funding options like electronic transfer, wire transfer, or direct deposit, allowing you to trade stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, and options with $0 commissions for online US-listed trades.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com