Delta-neutral strategies focus on minimizing directional market risk by balancing long and short positions, often using options to hedge exposure and maintain a neutral delta. Mean reversion strategies aim to exploit price fluctuations by betting that asset prices will revert to their historical average over time. Explore these trading approaches to understand their risk profiles and potential for steady returns.
Why it is important
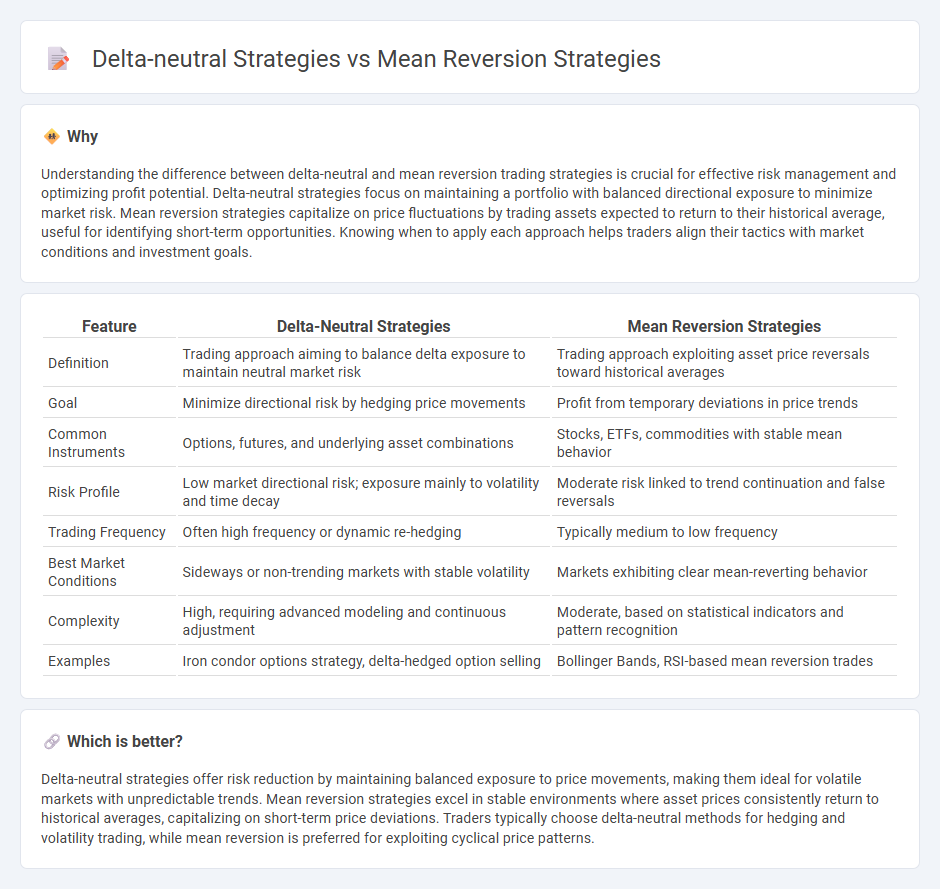
Understanding the difference between delta-neutral and mean reversion trading strategies is crucial for effective risk management and optimizing profit potential. Delta-neutral strategies focus on maintaining a portfolio with balanced directional exposure to minimize market risk. Mean reversion strategies capitalize on price fluctuations by trading assets expected to return to their historical average, useful for identifying short-term opportunities. Knowing when to apply each approach helps traders align their tactics with market conditions and investment goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Delta-Neutral Strategies | Mean Reversion Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading approach aiming to balance delta exposure to maintain neutral market risk | Trading approach exploiting asset price reversals toward historical averages |
| Goal | Minimize directional risk by hedging price movements | Profit from temporary deviations in price trends |
| Common Instruments | Options, futures, and underlying asset combinations | Stocks, ETFs, commodities with stable mean behavior |
| Risk Profile | Low market directional risk; exposure mainly to volatility and time decay | Moderate risk linked to trend continuation and false reversals |
| Trading Frequency | Often high frequency or dynamic re-hedging | Typically medium to low frequency |
| Best Market Conditions | Sideways or non-trending markets with stable volatility | Markets exhibiting clear mean-reverting behavior |
| Complexity | High, requiring advanced modeling and continuous adjustment | Moderate, based on statistical indicators and pattern recognition |
| Examples | Iron condor options strategy, delta-hedged option selling | Bollinger Bands, RSI-based mean reversion trades |
Which is better?
Delta-neutral strategies offer risk reduction by maintaining balanced exposure to price movements, making them ideal for volatile markets with unpredictable trends. Mean reversion strategies excel in stable environments where asset prices consistently return to historical averages, capitalizing on short-term price deviations. Traders typically choose delta-neutral methods for hedging and volatility trading, while mean reversion is preferred for exploiting cyclical price patterns.
Connection
Delta-neutral strategies and mean reversion strategies both aim to capitalize on price fluctuations while minimizing directional risk, often by balancing long and short positions to hedge against market movements. Delta-neutral trading maintains a portfolio's overall delta near zero, allowing traders to profit from small price oscillations, which aligns with mean reversion's focus on prices returning to their average values over time. By combining these approaches, traders can exploit temporary market inefficiencies and price reversions without exposure to significant directional trends.
Key Terms
**Mean Reversion Strategies:**
Mean reversion strategies capitalize on the tendency of asset prices to revert to their historical average or mean, identifying overbought or oversold conditions to exploit potential price corrections. These strategies commonly use statistical measures such as moving averages, Bollinger Bands, or the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to pinpoint entry and exit points in markets ranging from equities to Forex. Explore detailed methodologies and performance analyses to deepen your understanding of mean reversion trading techniques.
Z-score
Mean reversion strategies exploit Z-score to identify assets trading significantly away from their historical mean, signaling potential price corrections. Delta-neutral strategies maintain a balanced portfolio with minimal directional risk by offsetting positive and negative deltas, often adjusting positions based on Z-score thresholds for volatility management. Explore how Z-score integration enhances the performance of these strategies in dynamic markets.
Moving Average
Mean reversion strategies utilize moving averages to identify price levels where an asset is likely to revert to its historical average, capitalizing on temporary deviations. Delta-neutral strategies employ moving averages to dynamically hedge positions, maintaining a balance in options trading that minimizes directional risk. Explore further to understand how moving averages enhance effectiveness in these distinct trading approaches.
Source and External Links
Mean Reversion Strategies: Introduction, Trading, Strategies and More - Mean reversion trading strategies exploit temporary price deviations by buying assets when prices fall below their mean and selling when above, using tools like SMA crossover, Bollinger Bands, RSI, pairs trading, and statistical arbitrage to identify entry and exit points.
Mean Reversion Trading Strategies - Backtest With Mean Reverting ... - Mean reversion strategies revolve around buying assets that have dropped and selling those that have risen above their historical average, relying on simple, testable hypotheses and emphasizing the importance of well-defined buy, sell, and exit rules to avoid curve fitting and ensure robustness.
Mean Reversion Trading Strategy: Your Ultimate Guide - TIOmarkets - To build a mean reversion strategy, select markets with oscillating price behavior, analyze historical data for mean reverting periods, choose appropriate timeframes, and create precise entry and exit rules based on prices relative to mean and support/resistance levels.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com