Delta hedging involves managing the price risk of options by offsetting the underlying asset's price movements, focusing on maintaining a delta-neutral position to minimize portfolio sensitivity. Dispersion hedging, on the other hand, aims to exploit the volatility difference between an index option and its constituent stocks by hedging correlation risk instead of price risk. Discover more about how these strategies can optimize trading risk management and improve portfolio performance.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between delta hedging and dispersion hedging is crucial for managing risk and optimizing trading strategies in options markets. Delta hedging focuses on neutralizing directional risk by adjusting positions in the underlying asset, while dispersion hedging aims to profit from the implied volatility differences between individual options and their corresponding index options. Properly distinguishing these strategies enables traders to enhance portfolio performance and mitigate unintended exposure. Understanding these concepts improves decision-making and risk management in complex derivatives trading.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta Hedging | Dispersion Hedging |
|---|---|---|
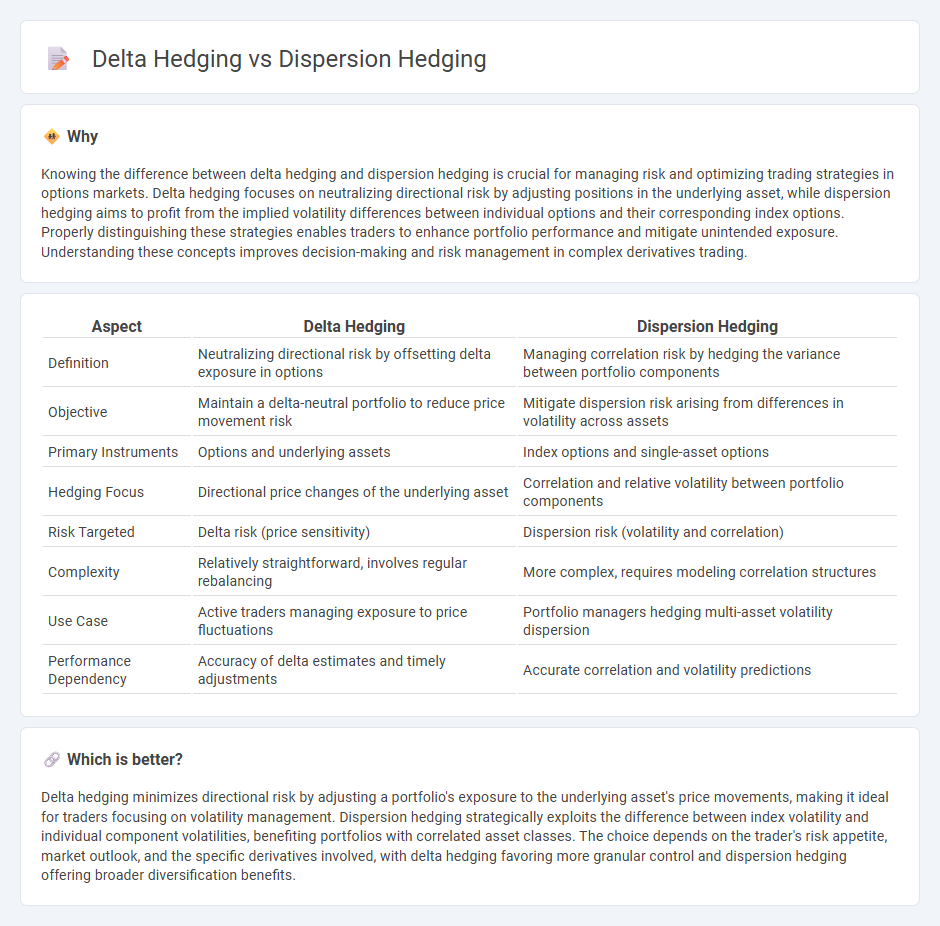
| Definition | Neutralizing directional risk by offsetting delta exposure in options | Managing correlation risk by hedging the variance between portfolio components |
| Objective | Maintain a delta-neutral portfolio to reduce price movement risk | Mitigate dispersion risk arising from differences in volatility across assets |
| Primary Instruments | Options and underlying assets | Index options and single-asset options |
| Hedging Focus | Directional price changes of the underlying asset | Correlation and relative volatility between portfolio components |
| Risk Targeted | Delta risk (price sensitivity) | Dispersion risk (volatility and correlation) |
| Complexity | Relatively straightforward, involves regular rebalancing | More complex, requires modeling correlation structures |
| Use Case | Active traders managing exposure to price fluctuations | Portfolio managers hedging multi-asset volatility dispersion |
| Performance Dependency | Accuracy of delta estimates and timely adjustments | Accurate correlation and volatility predictions |
Which is better?
Delta hedging minimizes directional risk by adjusting a portfolio's exposure to the underlying asset's price movements, making it ideal for traders focusing on volatility management. Dispersion hedging strategically exploits the difference between index volatility and individual component volatilities, benefiting portfolios with correlated asset classes. The choice depends on the trader's risk appetite, market outlook, and the specific derivatives involved, with delta hedging favoring more granular control and dispersion hedging offering broader diversification benefits.
Connection
Delta hedging and dispersion hedging are connected through their focus on managing risk in options trading by mitigating exposure to varying underlying factors. Delta hedging aims to neutralize directional risk by offsetting price movements in the underlying asset, while dispersion hedging involves offsetting volatility risk across a basket of correlated assets to exploit differences in implied and realized volatility. Both strategies rely on sophisticated quantitative models to adjust positions dynamically and enhance portfolio stability.
Key Terms
Correlation
Dispersion hedging targets the risk from correlations among multiple assets by balancing a portfolio to protect against volatility differences within an index, while delta hedging manages the directional risk of a single asset by neutralizing price movements through derivatives. The key distinction lies in correlation exposure: dispersion hedging relies heavily on correlation estimates to mitigate index variance, whereas delta hedging does not explicitly consider correlation but focuses on the underlying asset's price sensitivity. Explore more to understand how managing correlation impacts portfolio risk strategies effectively.
Volatility
Dispersion hedging targets the volatility of a basket of stocks by trading index options against the individual options of the constituents, aiming to exploit mispricings in their relative correlations. Delta hedging, on the other hand, involves continuously adjusting the positions in options and underlying assets to maintain a neutral delta exposure, primarily neutralizing price risk rather than volatility risk. Explore the nuances of volatility considerations in dispersion and delta hedging to optimize your risk management strategy.
Option Greeks
Dispersion hedging involves managing portfolio risk by offsetting volatility differences among individual options relative to the overall index, primarily relying on the Vega Greek to neutralize volatility exposure. Delta hedging focuses on eliminating directional risk by balancing the Delta of an option with the underlying asset, adjusting positions to maintain a Delta-neutral stance as prices fluctuate. Explore the distinct impacts of Vega and Delta in hedging strategies to enhance your options risk management skills.
Source and External Links
Hedging Volatility Dispersion Portfolios: A Comparative Analysis - Dispersion hedging involves managing market risk in portfolios constructed from options on an index and its components, with delta hedging proven generally effective in reducing volatility of portfolio profit, though further quantitative comparison with other hedging methods like variance swaps is needed.
Profitability of a Dispersion Trading Strategy - Dispersion trading capitalizes on volatility discrepancies between an index and its constituents by trading their options, resulting in a long/short volatility exposure with confirmed profitability and low correlation to the underlying index, but execution challenges remain.
Dispersion Trading: A Way to Hedge Vega Risk in Index Options - Dispersion trading effectively hedges vega risk by taking offsetting volatility positions in index options and their underlying assets, with delta hedging eliminating directional risk, though practical profitability may be impacted by bid-ask spreads and liquidity factors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com