Dark pool aggregation consolidates private, off-exchange trading venues to enhance liquidity and reduce market impact for large orders. Auction markets operate through transparent, competitive bidding processes where orders are matched based on price and time priority. Explore how these trading mechanisms influence market efficiency and execution strategies.
Why it is important
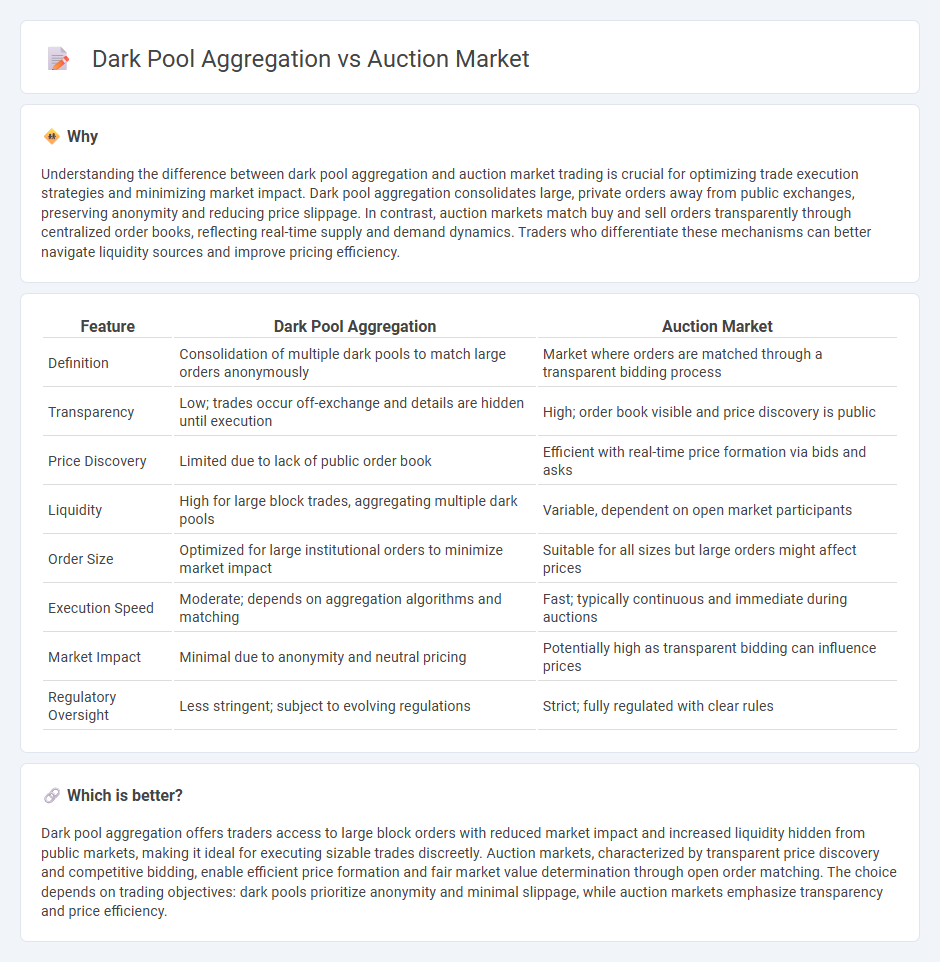
Understanding the difference between dark pool aggregation and auction market trading is crucial for optimizing trade execution strategies and minimizing market impact. Dark pool aggregation consolidates large, private orders away from public exchanges, preserving anonymity and reducing price slippage. In contrast, auction markets match buy and sell orders transparently through centralized order books, reflecting real-time supply and demand dynamics. Traders who differentiate these mechanisms can better navigate liquidity sources and improve pricing efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dark Pool Aggregation | Auction Market |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consolidation of multiple dark pools to match large orders anonymously | Market where orders are matched through a transparent bidding process |
| Transparency | Low; trades occur off-exchange and details are hidden until execution | High; order book visible and price discovery is public |
| Price Discovery | Limited due to lack of public order book | Efficient with real-time price formation via bids and asks |
| Liquidity | High for large block trades, aggregating multiple dark pools | Variable, dependent on open market participants |
| Order Size | Optimized for large institutional orders to minimize market impact | Suitable for all sizes but large orders might affect prices |
| Execution Speed | Moderate; depends on aggregation algorithms and matching | Fast; typically continuous and immediate during auctions |
| Market Impact | Minimal due to anonymity and neutral pricing | Potentially high as transparent bidding can influence prices |
| Regulatory Oversight | Less stringent; subject to evolving regulations | Strict; fully regulated with clear rules |
Which is better?
Dark pool aggregation offers traders access to large block orders with reduced market impact and increased liquidity hidden from public markets, making it ideal for executing sizable trades discreetly. Auction markets, characterized by transparent price discovery and competitive bidding, enable efficient price formation and fair market value determination through open order matching. The choice depends on trading objectives: dark pools prioritize anonymity and minimal slippage, while auction markets emphasize transparency and price efficiency.
Connection
Dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from multiple private trading venues, enhancing price discovery within auction markets by integrating hidden buy and sell orders. Auction markets benefit from this aggregated data through more accurate matching of supply and demand, leading to better execution prices for traders. By combining dark pool insights with auction mechanisms, market efficiency and transparency improve despite the inherently private nature of dark pools.
Key Terms
Price Transparency
Auction markets provide high price transparency by publicly displaying available bids and offers, allowing all participants to see and respond to price signals in real-time. Dark pool aggregation, conversely, reduces price transparency as trades occur anonymously without pre-trade price visibility, limiting market participants' ability to gauge true supply and demand. Explore deeper insights into how price transparency impacts trading strategies and market efficiency.
Order Matching
Auction markets aggregate buy and sell orders at specific intervals, optimizing order matching through transparent price discovery and batch processing. Dark pool aggregation consolidates trades from multiple private venues, preserving anonymity and minimizing market impact while matching large orders discreetly. Explore how order matching innovations in both systems influence liquidity and trading efficiency.
Liquidity Discovery
Auction markets provide transparent price formation by matching buy and sell orders in a public order book, facilitating efficient liquidity discovery through open competition. Dark pool aggregation consolidates large, non-displayed orders across multiple venues, enabling institutional traders to access hidden liquidity with minimized market impact. Explore how blending auction market transparency with dark pool aggregation innovations enhances liquidity discovery dynamics.
Source and External Links
Auction markets: What is it, types, Importance, Example, FAQ | POEMS - An auction market is where buyers and sellers compete by placing bids and offers, and prices are determined transparently through this competitive process without pre-set prices, commonly used for trading financial instruments like stocks, bonds, and commodities.
AUCTION MARKET: Easy explanation. - YouTube - The auction market process matches buyers' bid prices with sellers' ask prices, completing trades when these prices align, and can operate through traditional open outcry systems or electronic trading platforms for efficiency and reduced manipulation.
Auction markets - Ch2sec5 - Auction markets, such as the New York Stock Exchange, are physical or electronic exchanges where most buying and selling is done by matching bids and offers, distinct from dealer markets, and are used for trading large firms' equity shares internationally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com