Flash loan arbitrage leverages instant, uncollateralized loans to exploit price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges, enabling quick, low-risk profits without upfront capital. Liquidity provision involves supplying assets to decentralized pools to facilitate trading, earning fees and incentives but exposing providers to impermanent loss and market volatility. Discover how each strategy impacts DeFi ecosystems and can optimize your trading portfolio.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loan arbitrage and liquidity provision is crucial for trading because flash loan arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across platforms without upfront capital, while liquidity provision involves committing assets to earn fees and support market stability. Flash loan arbitrage can yield rapid profits by executing atomic transactions within blockchain systems, but carries higher risk and complexity. Liquidity provision helps maintain market efficiency and reduces slippage, attracting passive income through transaction fees. Traders must distinguish these strategies to optimize risk management, capital allocation, and profit potential in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Comparison Table
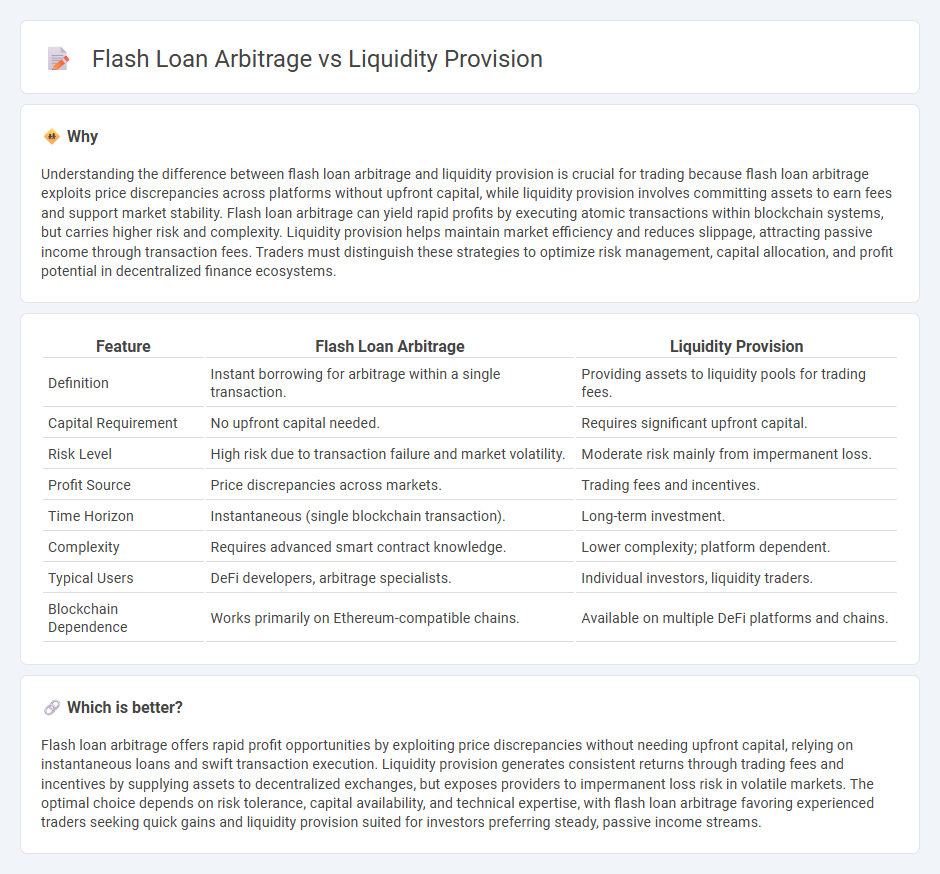
| Feature | Flash Loan Arbitrage | Liquidity Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant borrowing for arbitrage within a single transaction. | Providing assets to liquidity pools for trading fees. |
| Capital Requirement | No upfront capital needed. | Requires significant upfront capital. |
| Risk Level | High risk due to transaction failure and market volatility. | Moderate risk mainly from impermanent loss. |
| Profit Source | Price discrepancies across markets. | Trading fees and incentives. |
| Time Horizon | Instantaneous (single blockchain transaction). | Long-term investment. |
| Complexity | Requires advanced smart contract knowledge. | Lower complexity; platform dependent. |
| Typical Users | DeFi developers, arbitrage specialists. | Individual investors, liquidity traders. |
| Blockchain Dependence | Works primarily on Ethereum-compatible chains. | Available on multiple DeFi platforms and chains. |
Which is better?
Flash loan arbitrage offers rapid profit opportunities by exploiting price discrepancies without needing upfront capital, relying on instantaneous loans and swift transaction execution. Liquidity provision generates consistent returns through trading fees and incentives by supplying assets to decentralized exchanges, but exposes providers to impermanent loss risk in volatile markets. The optimal choice depends on risk tolerance, capital availability, and technical expertise, with flash loan arbitrage favoring experienced traders seeking quick gains and liquidity provision suited for investors preferring steady, passive income streams.
Connection
Flash loan arbitrage leverages temporary, uncollateralized loans to exploit price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges, enhancing market efficiency. Liquidity provision creates the pools where assets are held, enabling the execution of flash loan arbitrage by offering the necessary depth for instant trades. Both mechanisms rely on decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols' smart contracts to facilitate rapid, automated transactions without intermediaries.
Key Terms
Market Making
Liquidity provision in market making involves continuously supplying asset pairs to centralized or decentralized exchanges to facilitate smooth trades and earn fees from transaction spreads. Flash loan arbitrage leverages instant, uncollateralized loans to exploit temporary price discrepancies across multiple markets without holding inventory, relying on rapid contract execution within a single blockchain transaction. Explore deeper insights into how liquidity provisioning strategies compare with flash loan arbitrage techniques in enhancing market efficiency and profitability.
Collateralization
Liquidity provision involves supplying assets to decentralized exchanges or lending platforms, requiring collateralization to secure positions and reduce risk of default. Flash loan arbitrage leverages uncollateralized loans executed within a single transaction, allowing traders to exploit price discrepancies without upfront collateral. Explore detailed mechanisms and strategies behind collateralization in DeFi to optimize your trading and liquidity deployment.
Liquidation
Liquidity provision involves supplying assets to decentralized finance (DeFi) pools to facilitate trades and earn fees, while flash loan arbitrage exploits temporary price discrepancies using uncollateralized loans executed within a single transaction. In liquidation contexts, flash loan arbitrage allows traders to repay undercollateralized loans instantly, seize collateral at a discount, and profit from rapid market corrections, whereas liquidity providers gain indirectly through trading fees but bear risks of impermanent loss during liquidation events. Explore how liquidation strategies in DeFi can be optimized by balancing liquidity provision and flash loan arbitrage techniques.
Source and External Links
Liquidity Provision: Strategy & Examples - Macroeconomics - Vaia - Liquidity provision is a strategy crucial to maintain economic stability by ensuring financial institutions or markets have sufficient access to funds, balancing risk and return, and enabling the economy to function smoothly even during crises.
The Role and Benefits of Liquidity Providers in Financial Markets - Liquidity provision facilitates the buying and selling of assets with minimal price impact, reduces transaction costs, improves price discovery, enhances market efficiency and depth, and involves regulatory and technological risks for providers.
Liquidity Provision Strategies - DayTrading.com - Liquidity provision strategies include market making, high-frequency trading, arbitrage, and central bank actions like open market operations and emergency liquidity assistance to ensure market stability and reduce transaction costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com