High frequency trading relies on powerful algorithms and ultra-low latency to execute thousands of trades per second, capitalizing on minute price differences across markets. Scalping is a short-term strategy where traders seek small profits from numerous quick trades, often holding positions for seconds to minutes. Discover more about these fast-paced trading techniques and their impact on market dynamics.
Why it is important
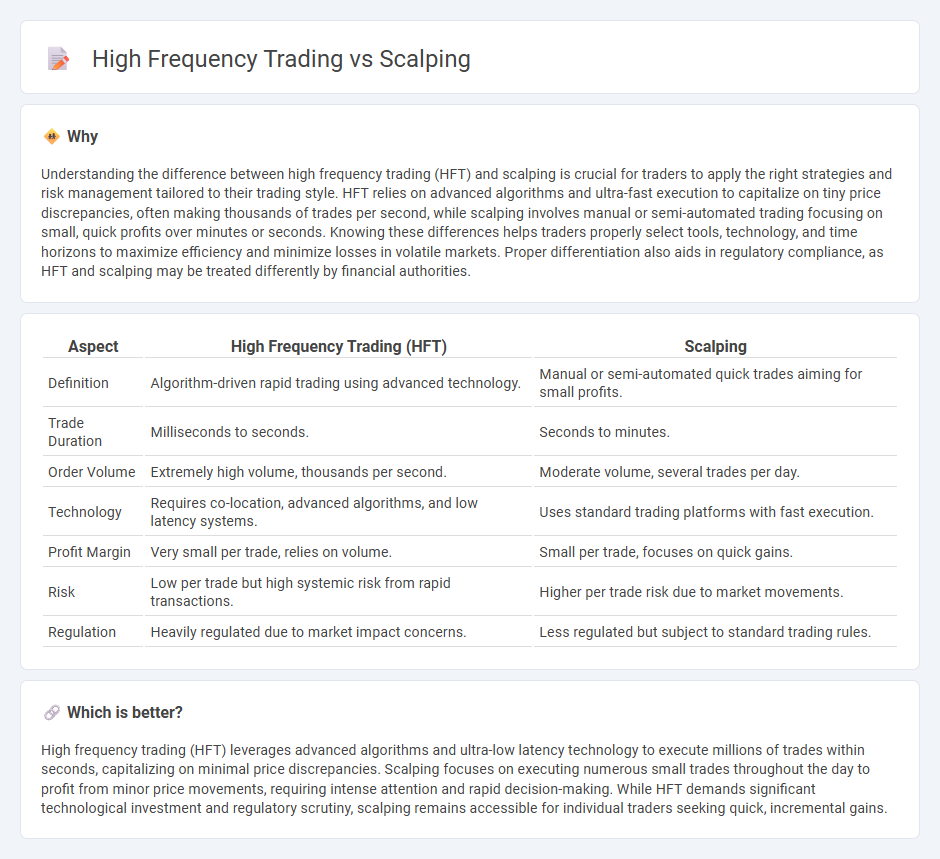
Understanding the difference between high frequency trading (HFT) and scalping is crucial for traders to apply the right strategies and risk management tailored to their trading style. HFT relies on advanced algorithms and ultra-fast execution to capitalize on tiny price discrepancies, often making thousands of trades per second, while scalping involves manual or semi-automated trading focusing on small, quick profits over minutes or seconds. Knowing these differences helps traders properly select tools, technology, and time horizons to maximize efficiency and minimize losses in volatile markets. Proper differentiation also aids in regulatory compliance, as HFT and scalping may be treated differently by financial authorities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | High Frequency Trading (HFT) | Scalping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Algorithm-driven rapid trading using advanced technology. | Manual or semi-automated quick trades aiming for small profits. |
| Trade Duration | Milliseconds to seconds. | Seconds to minutes. |
| Order Volume | Extremely high volume, thousands per second. | Moderate volume, several trades per day. |
| Technology | Requires co-location, advanced algorithms, and low latency systems. | Uses standard trading platforms with fast execution. |
| Profit Margin | Very small per trade, relies on volume. | Small per trade, focuses on quick gains. |
| Risk | Low per trade but high systemic risk from rapid transactions. | Higher per trade risk due to market movements. |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated due to market impact concerns. | Less regulated but subject to standard trading rules. |
Which is better?
High frequency trading (HFT) leverages advanced algorithms and ultra-low latency technology to execute millions of trades within seconds, capitalizing on minimal price discrepancies. Scalping focuses on executing numerous small trades throughout the day to profit from minor price movements, requiring intense attention and rapid decision-making. While HFT demands significant technological investment and regulatory scrutiny, scalping remains accessible for individual traders seeking quick, incremental gains.
Connection
High frequency trading (HFT) and scalping both exploit minute price fluctuations to generate profits, using rapid trade execution and short holding periods. HFT relies on sophisticated algorithms and ultra-low latency systems to execute thousands of trades per second, while scalping focuses on smaller, frequent trades often executed manually or semi-automatically. Both strategies require advanced technology, deep market liquidity, and strict risk management to capitalize on fleeting market inefficiencies.
Key Terms
Trade Duration
Scalping involves executing trades that last from a few seconds to several minutes, aiming to capture small price movements multiple times a day. High-frequency trading (HFT) operates at a much faster pace, with trade durations often measured in milliseconds or microseconds, relying on advanced algorithms and ultra-low latency systems. Explore the intricacies of trade duration and strategy performance by learning more about scalping and high-frequency trading methodologies.
Order Execution Speed
Scalping relies on rapid order execution to capitalize on small price movements, often holding positions for seconds or minutes, whereas high-frequency trading (HFT) employs ultra-fast algorithms and infrastructure to execute thousands of trades per second across multiple markets. Order execution speed in HFT is measured in microseconds or nanoseconds, leveraging co-location and direct market access to outpace competitors, while scalping typically operates at millisecond speeds. Discover how differences in order execution speed impact trading strategies and market dynamics in greater detail.
Position Size
Scalping typically involves smaller position sizes held for very short durations, aiming to capitalize on minimal price movements with rapid trade execution. High-frequency trading (HFT) utilizes sophisticated algorithms to execute a vast number of trades with varying position sizes, often leveraging significant volume to exploit tiny market inefficiencies. Explore detailed differences in risk management and profit potential between scalping and HFT strategies.
Source and External Links
Scalping (Day Trading Technique) - Scalping is a day trading strategy where an investor buys and sells an individual stock multiple times throughout the same day, aiming to make small profits repeatedly on highly volatile stocks.
Scalping (trading) - Scalping in trading refers to either a legitimate arbitrage method exploiting small bid-ask spreads through rapid trades or a fraudulent market manipulation tactic.
What is a scalping strategy in the stock market and how ... - Scalping is a lightning-fast trading strategy that relies on technical indicators like the Stochastic Oscillator, Moving Averages, and RSI to capitalize on brief price changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com